Abstract
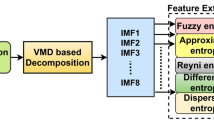
Detecting cognitive performance during mental arithmetic allows researchers to observe and identify the brain’s response to stimuli. Existing non-invasive methods for automated cognitive performance detection need improvements in terms of accuracy. In this work, a novel approach for cognitive performance has been proposed which uses short-duration electroencephalography (EEG) signal (4.094 s). Stationary wavelet transform (SWT) has been used to decompose the signal followed by extraction of entropy-based features and classification using selected attributes. To tackle the imbalanced data issue, adaptive synthetic sampling approach has been used. The proposed technique works in two modes: multi-lead approach (MLA), where EEG signal from multiple leads was used, and a novel lead-specific approach (LSA), where EEG signal from a single lead (F4) was used. A high accuracy of 94.00% in MLA and 93.70% in LSA reflects reliability of the proposed technique. The use of short-duration single-lead EEG signal makes this technique suitable for continuous monitoring system of cognitive performance during mental workload.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stress, H.W.M.: Campaign guide: managing stress and psychosocial risks at work. Osha, European agency for safety health at work (2013)
Alberdi, A., Aztiria, A., Basarab, A.: Towards an automatic early stress recognition system for office environments based on multimodal measurements: a review. J. Biomed. Inform. 59, 49–75 (2016)
Duman, R.S.: Neurobiology of stress, depression, and rapid acting antidepressants: remodeling synaptic connections. Depress. Anxiety 31(4), 291–296 (2014)
Espinosa-Garcia, C., Sayeed, I., Yousuf, S., Atif, F., Sergeeva, E.G., Neigh, G.N., Stein, D.G.: Abstract TP83: stress exacerbates global ischemia-induced inflammatory response: intervention by progesterone. Stroke 48(Suppl-1), ATP183 (2017)
Sharma, N., Gedeon, T.: Objective measures, sensors and computational techniques for stress recognition and classification: a survey. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 108(3), 1287–1301 (2012)
Subhani, A.R., Mumtaz, W., Saad, M.N.B.M., Kamel, N., Malik, A.S.: Machine learning framework for the detection of mental stress at multiple levels. IEEE Access 5, 13545–13556 (2017)
Gowrisankaran, S., Nahar, N.K., Hayes, J.R., Sheedy, J.E.: Asthenopia and blink rate under visual and cognitive loads. Optom. Vis. Sci. 89(1), 97–104 (2012)
Deschênes, A., Forget, H., Daudelin-Peltier, C., Fiset, D., Blais, C.: Facial expression recognition impairment following acute social stress. J. Vis. 15(12), 1383–1383 (2015)
Wielgosz, J., Schuyler, B.S., Lutz, A., Davidson, R.J.: Long-term mindfulness training is associated with reliable differences in resting respiration rate. Sci. Rep. 6, 27533 (2016)
Paiva, J.S., Rodrigues, S., Cunha, J.P.S.: Changes in ST, QT and RR ECG intervals during acute stress in firefighters: a pilot study. In: 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), vol. 2016, pp. 3378–3381 . IEEE (2016)
He, J., Li, K., Liao, X., Zhang, P., Jiang, N.: Real-time detection of acute cognitive stress using a convolutional neural network from electrocardiographic signal. IEEE Access 7, 42710–42717 (2019)
Healey, J.A., Picard, R.W.: Detecting stress during real-world driving tasks using physiological sensors. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 6(2), 156–166 (2005)
Dedovic, K., Renwick, R., Mahani, N.K., Engert, V., Lupien, S.J., Pruessner, J.C.: The montreal imaging stress task: using functional imaging to investigate the effects of perceiving and processing psychosocial stress in the human brain. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 30(5), 319 (2005)
Zyma, I., Tukaev, S., Seleznov, I., Kiyono, K., Popov, A., Chernykh, M., Shpenkov, O.: Electroencephalograms during mental arithmetic task performance. Data 4(1), 14 (2019)
Goldberger, P., et al.: PhysioBank, Physionet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101(13), e215–e220 (2000)
Jatoi, N.-A., Kyvelou, S.-M., Feely, J.: The acute effects of mental arithmetic, cold pressor and maximal voluntary contraction on arterial stiffness in young healthy subjects. Artery Res. 8(2), 44–50 (2014)
Finlay, M.C., Lambiase, P.D., Ben-Simon, R., Taggart, P.: Effect of mental stress on dynamic electrophysiological properties of the endocardium and epicardium in humans. Heart Rhythm 13(1), 175–182 (2016)
Noto, Y., Sato, T., Kudo, M., Kurata, K., Hirota, K.: The relationship between salivary biomarkers and state-trait anxiety inventory score under mental arithmetic stress: a pilot study. Anesth. Analg. 101(6), 1873–1876 (2005)
Sharma, L., Sunkaria, R.: Myocardial infarction detection and localization using optimal features based lead specific approach. IRBM 41(1), 58–70 (2020)
García-Martínez, B., Martínez-Rodrigo, A., Zangróniz, R., Pastor, J., Alcaraz, R.: Symbolic analysis of brain dynamics detects negative stress. Entropy 19(5), 196 (2017)
Jie, X., Cao, R., Li, L.: Emotion recognition based on the sample entropy of EEG. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 24(1), 1185–1192 (2014)
Acharya, U.R., Fujita, H., Sudarshan, V.K., Bhat, S., Koh, J.E.: Application of entropies for automated diagnosis of epilepsy using EEG signals: a review. Knowl.-Based Syst. 88, 85–96 (2015)
Kannathal, N., Choo, M.L., Acharya, U.R., Sadasivan, P.: Entropies for detection of epilepsy in EEG. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 80(3), 187–194 (2005)
He, H., Bai, Y., Garcia, E.A., Li, S.: ADASYN: adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning. In: 2008 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence), pp. 1322–1328. IEEE (2008)
Webb, A.R.: Statistical Pattern Recognition. Wiley, Hoboken (2003)
Yang, X., Gao, M., Shi, J., Ye, H., Chen, S.: Modulating the activity of the dlpfc and ofc has distinct effects on risk and ambiguity decision-making: a tdcs study. Front. Psychol. 8, 1417 (2017)
Lin, C.-T., King, J.-T., Fan, J.-W., Appaji, A., Prasad, M.: The influence of acute stress on brain dynamics during task switching activities. IEEE Access 6, 3249–3255 (2017)
Vanitha, V., Krishnan, P.: Real time stress detection system based on EEG signals. Biomed. Res. Special Issue: S271–S275 (2016)
Hou, X., Liu, Y., Sourina, O., Tan, Y.R.E., Wang, L., Mueller-Wittig, W.: EEG based stress monitoring. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, pp. 3110–3115. IEEE (2015)
Jebelli, H., Hwang, S., Lee, S.: EEG-based workers’ stress recognition at construction sites. Autom. Constr. 93, 315–324 (2018)
Xin, L., Zetao, C., Yunpeng, Z., Jiali, X., Shuicai, W., Yanjun, Z.: Stress state evaluation by an improved support vector machine. Neurophysiology 48(2), 86–92 (2016)
Al-Shargie, F., Tang, T.B., Badruddin, N., Kiguchi, M.:Mental stress quantification using EEG signals. In: International Conference for Innovation in Biomedical Engineering and Life Sciences, pp. 15–19. Springer (2015)
García-Martínez, B., Martínez-Rodrigo, A., Zangróniz Cantabrana, R., PastorGarcía, J., Alcaraz, R.: Application of entropy-based metrics to identify emotional distress from electroencephalographic recordings. Entropy 18(6), 221 (2016)
Villarejo, M.V., Zapirain, B.G., Zorrilla, A.M.: A stress sensor based on galvanic skin response (GSR) controlled by zigbee. Sensors 12(5), 6075–6101 (2012)
Dehzangi, O., Sahu, V., Rajendra, V., Taherisadr, M.: Gsr-based distracted driving identification using discrete & continuous decomposition and wavelet packet transform. Smart Health 14, 100085 (2019)
Kurniawan, H., Maslov, A.V., Pechenizkiy, M.: Stress detection from speech and galvanic skin response signals. In: Proceedings of the 26th IEEE International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, pp. 209–214. IEEE (2013)
Munla, N., Khalil, M., Shahin, A., Mourad, A.: Driver stress level detection using HRV analysis. In: 2015 International Conference on Advances in Biomedical Engineering (ICABME), pp. 61–64. IEEE (2015)
Yaribeygi, H., Panahi, Y., Sahraei, H., Johnston, T.P., Sahebkar, A.: The impact of stress on body function: a review. EXCLI J. 16, 1057 (2017)
Regula, M., Socha, V., Kutilek, P., Socha, L., Hana, K., Hanakova, L., Szabo, S.: Study of heart rate as the main stress indicator in aircraft pilots. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Mechatronics-Mechatronika 2014, pp. 639–643. IEEE (2014)
Andersson, D.: Real-time ECG for objective stress level measurement. Digitala Vetenskapliga Arkivet, master thesis, (Department of Biomedical Engineering) Linkoping University (2017)
Dong, J., Han, Z., Zhao, Y., Wang, W., Prochazka, A., Chambers, J.: Sparse analysis model based multiplicative noise removal with enhanced regularization. Signal Process. 137, 160–176 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work is funded under TEQIP-III, CRS application ID: 1-5730990370.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, L.D., Saraswat, R.K. & Sunkaria, R.K. Cognitive performance detection using entropy-based features and lead-specific approach. SIViP 15, 1821–1828 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01927-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01927-0