Abstract
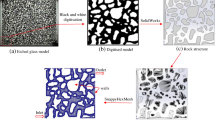
Polymer solution has extremely extensive applications in many natural and industrial processes, especially in oilfield development field, such as polymer flooding, fracturing and water shut-off. Thus, the study of flow behaviors of polymer in formation pores is significantly important. In this paper, the flow behaviors of the polymer droplets in the 3-D pore throat structure were systematically studied. Additionally, the influencing factors (polymer concentration, molecular weight and pore throat ratio, for instance) were investigated. As the increasing of polymer concentration and molecular weight, the polymer droplets were more difficult to break, which means the critical flow rate decreased and the average sizes of the first daughter droplets (FDD) were longer synchronously. Moreover, with the increase in pore throat ratio, the critical flow rate increased and the length of the FDD decreased. In addition, the prediction models of the length of the FDD with polymer concentration and pore throat ratio were established, respectively. The prediction model revealed that the length of the FDD satisfied an exponential relationship with the polymer concentration and a linear relationship with the pore throat ratio. Finally, the average size of droplets after macroscopic core flooding experiment was 8 μm and 17 μm when the polymer concentration was 0.01% and 0.1%, respectively. The results were consistent with the breakup behaviors of polymer droplets in the microscopic pore throat structure.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, Y.X., Jiang, G.C., Qi, Y.R., Ge, Q.Y.: Plugging agent of shale base on nano flexible polymer. In: Applied Mechanics and Materials 2016, pp. 15–19. Trans Tech Publ
Chauliac, C., Aragonés, J.-M., Bestion, D., Cacuci, D.G., Crouzet, N., Weiss, F.-P., Zimmermann, M.A.: NURESIM–A European simulation platform for nuclear reactor safety: Multi-scale and multi-physics calculations, sensitivity and uncertainty analysis. Nucl. Eng. Des. 241(9), 3416–3426 (2011)
Chen, Y.-T., Chang, W.-C., Fang, W.-F., Ting, S.-C., Yao, D.-J., Yang, J.-T.: Fission and fusion of droplets in a 3-D crossing microstructure. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 13(2), 239–247 (2012)
Christopher, G., Anna, S.: Passive breakup of viscoelastic droplets and filament self-thinning at a microfluidic T-junction. J. Rheol. 53(3), 663–683 (2009)
Clarke, A., Howe, A.M., Mitchell, J., Staniland, J., Hawkes, L., Leeper, K.: Mechanism of anomalously increased oil displacement with aqueous viscoelastic polymer solutions. Soft Matter 11(18), 3536–3541 (2015)
Conn, C.A., Ma, K., Hirasaki, G.J., Biswal, S.L.: Visualizing oil displacement with foam in a microfluidic device with permeability contrast. Lab Chip 14(20), 3968–3977 (2014)
Cooke Jr, C.E.: Method and materials for hydraulic fracturing of wells. In. Google Patents (2005)
Cubaud, T., Jose, B.M., Darvishi, S., Sun, R.: Droplet breakup and viscosity-stratified flows in microchannels. Int. j. Multiph. Flow 39, 29–36 (2012)
Delshad, M., Kim, D.H., Magbagbeola, O.A., Huh, C., Pope, G.A., Tarahhom, F.: Mechanistic interpretation and utilization of viscoelastic behavior of polymer solutions for improved polymer-flood efficiency. In: SPE Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery 2008. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Ehrenfried, D.H.: Impact of viscoelastic polymer flooding on residual oil saturation in sandstones. (2013)
Emadi, A., Sohrabi, M.: Visual investigation of low salinity waterflooding. In: International Symposium of the Society of Core Analysts, Aberdeen, Scotland, UK 2012, pp. 27–30
Ferry, J.D.: Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers. Wiley, Hoboken (1980)
Fidalgo, L.M., Abell, C., Huck, W.T.: Surface-induced droplet fusion in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 7(8), 984–986 (2007)
Fu, L., Zhang, G., Ge, J., Liao, K., Pei, H., Jiang, P., Li, X.: Study on organic alkali-surfactant-polymer flooding for enhanced ordinary heavy oil recovery. Colloids Surf. A 508, 230–239 (2016)
Garstecki, P., Fuerstman, M.J., Stone, H.A., Whitesides, G.M.: Formation of droplets and bubbles in a microfluidic T-junction—scaling and mechanism of break-up. Lab Chip 6(3), 437–446 (2006)
Harris, P.C.: Fracturing-fluid additives. J. Pet. Technol. 40(10), 1277–271279 (1988)
Herbas, J., Wegner, J., Hincapie, R., Födisch, H., Ganzer, L., Del Castillo, J., Mugizi, H.M.: Comprehensive micromodel study to evaluate polymer EOR in unconsolidated sand reservoirs. In: SPE Middle East Oil & Gas Show and Conference 2015. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Hua, Z., Lin, M., Guo, J., Xu, F., Li, Z., Li, M.: Study on plugging performance of cross-linked polymer microspheres with reservoir pores. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 105, 70–75 (2013)
Jayne, R.S., Wu, H., Pollyea, R.M.: Geologic CO2 sequestration and permeability uncertainty in a highly heterogeneous reservoir. Int. j. Greenh. Gas Control 83, 128–139 (2019)
Kenney, S., Poper, K., Chapagain, G., Christopher, G.F.: Large Deborah number flows around confined microfluidic cylinders. Rheol. Acta 52(5), 485–497 (2013)
Kim, D.H., Lee, S., Ahn, C.H., Huh, C., Pope, G.A.: Development of a viscoelastic property database for EOR polymers. In: SPE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium 2010. Society of Petroleum Engineers
Kovscek, A., Tang, G.-Q., Radke, C.: Verification of roof snap off as a foam-generation mechanism in porous media at steady state. Colloids Surf. A 302(1–3), 251–260 (2007)
Le Moullec, Y., Potier, O., Gentric, C., Leclerc, J.P.: Flow field and residence time distribution simulation of a cross-flow gas–liquid wastewater treatment reactor using CFD. Chem. Eng. Sci. 63(9), 2436–2449 (2008)
Lenormand, R., Zarcone, C., Sarr, A.: Mechanisms of the displacement of one fluid by another in a network of capillary ducts. J. Fluid Mech 135(34), 337–353 (1983)
Loveless, D., Holtsclaw, J., Weaver, J., Ogle, J., Saini, R.: Multifunctional boronic acid crosslinker for fracturing fluids. In: IPTC 2014: International petroleum technology conference 2014, pp. cp-395-00206. European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers
Ma, K., Liontas, R., Conn, C.A., Hirasaki, G.J., Biswal, S.L.: Visualization of improved sweep with foam in heterogeneous porous media using microfluidics. Soft Matter 8(41), 10669–10675 (2012)
Macosko, C.W.: Rheology Principles. Measurements and Applications (1994)
Medici, G., West, L., Banwart, S.: Groundwater flow velocities in a fractured carbonate aquifer-type: implications for contaminant transport. J. Contam. Hydrol. 222, 1–16 (2019)
Nekouei, M., Vanapalli, S.A.: Volume-of-fluid simulations in microfluidic T-junction devices: Influence of viscosity ratio on droplet size. Phys. Fluids 29(3), 032007 (2017)
Nisisako, T., Torii, T., Higuchi, T.: Droplet formation in a microchannel network. Lab Chip 2(1), 24–26 (2002)
Quennouz, N., Ryba, M., Argillier, J.-F., Herzhaft, B., Peysson, Y., Pannacci, N.: Microfluidic study of foams flow for enhanced oil recovery (EOR). Oil Gas Sci. Technol. Revue d’IFP Energies Nouvelles 69(3), 457–466 (2014)
Roof, J.: Snap-off of oil droplets in water-wet pores. Soc. Pet. Eng. j. 10(01), 85–90 (1970)
Rossen, W.R.: Snap-off in constricted tubes and porous media. Colloids Surf. A 166(1–3), 101–107 (2000)
Sareen, A., Zhou, M.J., Zaghmoot, I., Cruz, C., Sun, H., Qu, Q., Li, L.: Successful slickwater fracturing in ultrahigh TDS produced water by novel environmentally preferred friction reducer. In: International Petroleum Technology Conference 2014. International Petroleum Technology Conference
Sheng, J.J., Leonhardt, B., Azri, N.: Status of polymer-flooding technology. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 54(02), 116–126 (2015)
Shi, X., Kenney, S., Chapagain, G., Christopher, G.F.: Mechanisms of onset for moderate Mach number instabilities of viscoelastic flows around confined cylinders. Rheol. Acta 54(9), 805–815 (2015)
Skauge, A., Zamani, N., Gausdal Jacobsen, J., Shaker Shiran, B., Al-Shakry, B., Skauge, T.: Polymer flow in porous media: Relevance to enhanced oil recovery. Colloids Interfaces 2(3), 27 (2018)
Squires, T.M., Quake, S.R.: Microfluidics: fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77(3), 977 (2005)
Sydansk, R.D.: Hydraulic fracturing process using a polymer gel. In. Google Patents, (1988)
Tan, Y.-C., Cristini, V., Lee, A.P.: Monodispersed microfluidic droplet generation by shear focusing microfluidic device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 114(1), 350–356 (2006)
Teh, S.-Y., Lin, R., Hung, L.-H., Lee, A.P.: Droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 8(2), 198–220 (2008)
Thomas, S., Farouq Ali, S.: Flow of emulsions in porous media, and potential for enhanced oil recovery. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 3, 121–136 (1989)
Wang, X., Wang, K., Riaud, A., Wang, X., Luo, G.: Experimental study of liquid/liquid second-dispersion process in constrictive microchannels. Chem. Eng. j. 254, 443–451 (2014)
Wei, B., Romero-Zerón, L., Rodrigue, D.: Mechanical properties and flow behavior of polymers for enhanced oil recovery. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 53(4), 625–644 (2014a)
Wei, B., Romero-Zerón, L., Rodrigue, D.: Oil displacement mechanisms of viscoelastic polymers in enhanced oil recovery (EOR): a review. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 4(2), 113–121 (2014b)
Xu, K., Liang, T., Zhu, P., Qi, P., Lu, J., Huh, C., Balhoff, M.: A 2.5-D glass micromodel for investigation of multi-phase flow in porous media. Lab Chip 17(4), 640–646 (2017)
Zhao, G., Dai, C., Li, W., Yan, Z., Zhao, M.: Research on a temporary plugging agent based on polymer gel for reservoir acidification. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 6(3), 465–472 (2016a)
Zhao, Y., Shen, A.Q., Haward, S.J.: Flow of wormlike micellar solutions around confined microfluidic cylinders. Soft Matter 12(42), 8666–8681 (2016b)
Zhao, M., Cao, M., Hu, Y., Yang, Q., Wu, Y., Chu, Z., Hu, X., Dai, C.: Investigating breakup behaviors of the non-Newtonian fluid: a case study of oil droplet using 3-D pore throat structured microchannels. Colloids Surf. A 587, 124330 (2020)
Zhou, H., Zhu, C., Fu, T., Ma, Y., Li, H.Z.: Dynamics and interfacial evolution for bubble breakup in shear-thinning non-Newtonian fluid in microfluidic T-junction. Chem. Eng. Sci. 208, 115158 (2019)
Zoveidavianpoor, M., Gharibi, A.: Application of polymers for coating of proppant in hydraulic fracturing of subterraneous formations: a comprehensive review. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 24, 197–209 (2015)
Funding
Funding was provided by National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2019YFA0708700), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51704313) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 18CX02028A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, C., Chu, Z., Jiang, Q. et al. Breakup Behaviors of Viscoelastic Polymer Droplets in 3-D Pore Throat Structure Microchannel. Transp Porous Med 144, 133–148 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-021-01608-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-021-01608-z