Abstract
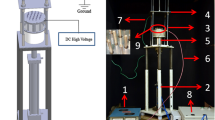
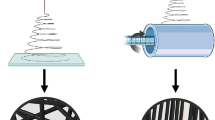
This study focused on understanding the confined crystallization of poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) in electrospun nanofibers. The effect of thermal treatment on PEO crystallization was also studied. An electrospinning process with a rotating drum collector enabled stretching and aligning of polymer chains, which resulted in the formation of a planar zigzag conformation. The confined environment in nanofibers facilitated an ordered crystal arrangement, resulting in an increase in the degree of crystallinity with a decrease in the fiber diameter. By contrast, large fibers extended solvent evaporation, which resulted in large crystallite sizes. The confined geometry and mechanical force provided by a rotating collector induced the preferred crystal orientation parallel to the fiber axis. Upon thermal annealing, the stretched PEO chains relaxed, resulting in a change from the metastable zigzag conformation to a stable helical conformation. Thermal treatment monotonically increased the melting temperature, degree of crystallinity, and crystallite size of PEO nanofibers regardless of the fiber diameter but did not influence the orientation of the organized crystals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frank CW, Rao V, Despotopoulou MM, Pease RFW, Hinsberg WD, Miller RD, et al. Structure in thin and ultrathin spin-cast polymer films. Science. 1996;273:912–5.
Hu ZJ, Huang HY, Zhang FJ, Du BY, He TB. Thickness-dependent molecular chain and lamellar crystal orientation in ultrathin poly(di-n-hexylsilane) films. Langmuir. 2004;20:3271–7.
Jin Y, Rogunova M, Hiltner A, Baer E, Nowacki R, Galeski A, et al. Structure of polypropylene crystallized in confined nanolayers. J Polym Sci Polym Phys Ed. 2004;42:3380–96.
Wang HP, Kenum JK, Hiltner A, Baer E, Freeman B, Rozanski A, et al. Confined crystallization of polyethylene oxide in nanolayer assemblies. Science. 2009;323:757–60.
Orench IP, Stribeck N, Ania F, Baer E, Hiltner A, Calleja FJB. SAXS study on the crystallization of PET under physical confinement in PET/PC multilayered films. Polymer. 2009;50:2680–7.
Woo E, Huh J, Jeong YG, Shin K. From homogeneous to heterogeneous nucleation of chain molecules under nanoscopic cylindrical confinement. Phys Rev Lett. 2007;98:136103.
Shin K, Woo E, Jeong YG, Kim C, Huh J, Kim KW. Crystalline structures, melting, and crystallization of linear polyethylene in cylindrical nanopores. Macromolecules. 2007;40:6617–23.
Rangarajan P, Register RA, Fetters LJ, Bras W, Naylor S, Ryan AJ. Crystallization of a weakly segregated polyolefin diblock copolymer. Macromolecules. 1995;28:4932–8.
Ryan AJ, Fairclough JPA, Hamley IW, Mai SM, Booth C. Chain folding in crystallizable block copolymers. Macromolecules. 1997;30:1723–7.
Chen HL, Wu JC, Lin TL, Lin JS. Crystallization kinetics in microphase-separated poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(1,4-butadiene). Macromolecules. 2001;34:6936–44.
Huang P, Zhu L, Guo Y, Ge Q, Jing AJ, Chen WY, et al. Confinement size effect on crystal orientation changes of poly(ethylene oxide) blocks in poly(ethylene oxide)-b-polystyrene diblock copolymers. Macromolecules. 2004;37:3689–98.
Chen YW, Yeh BJ, Hashimoto T, Liao SY, Lo CT. Hydrogen bonding induced co-ordering and interfacial curvature controlled crystallization behavior of binary copolymer blends. Macromolecules. 2018;51:7699–712.
Zhu L, Cheng SZD, Calhoum BH, Ge Q, Quirk RP, Thomas EL, et al. Crystallization temperature-dependent crystal orientations within nanoscale confined lamellar of a self-assembled crystalline-amorphous diblock copolymer. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:5957–67.
Carr JM, Langhe DS, Ponting MT, Hiltner A, Baer E. Confined crystallization in polymer nanolayered films: a review. J Mater Res. 2012;27:1326–50.
Kakade MV, Givens S, Gardner K, Lee KH, Chase DB, Rabolt JF. Electric field induced orientation of polymer chains in macroscopically aligned electrospun polymer nanofibers. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:2777–82.
Yee WA, Kotaki M, Liu Y, Lu X. Morphology, polymorphism behavior and molecular orientation of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibers. Polymer. 2007;48:512–21.
Kongkhlang T, Tashiro K, Kotaki M, Chirachanchai S. Electrospinning as a new technique to control the crystal morphology and molecular orientation of polyoxymethylene nanofibers. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:15460–6.
Lim CT, Tan EPS, Ng SY. Effects of crystalline morphology on the tensile properties of electrospun polymer nanofibers. Appl Phys Lett. 2008;92:141908.
Chan KHK, Wong SY, Li X, Zhang YZ, Lim PC, Lim CT. et al.Effect of molecular orientation on mechanical property of single electrospun fiber of poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-(R)-3-hydroxyvalerate].J Phys Chem B.2009;113:13179–85.
Cheng YW, Lu HA, Wang YC, Thierry A, Lotz B, Wang C. Syndiotactic polystyrene nanofibers obtained from high-temperature solution electrospinning process. Macromolecules. 2010;43:2371–6.
Kolbuk D, Sajkiewicz P, Kowalewski TA. Optical birefringence and molecular orientation of electrospun polycaprolactone fibers by polarizing-interference microscopy. Eur Polym J. 2012;48:275–83.
Ma Q, Pyda M, Mao B, Cebe P. Relationship between the rigid amorphous phase and mesophase in electrospun fibers. Polymer. 2013;54:2544–54.
Gong L, Chase DB, Noda I, Liu J, Martin DC, Ni C. et al.Discovery of β-form crystal structure in electrospun poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-(R)-3-hydroxyhexanoate] (PHBHx) nanofibers: from fiber mats to single fibers.Macromolecules. 2015;48:6197–205.
Wang C, Fang CY, Wang CY. Electrospun poly(butylene terephthalate) fibers: entanglement density effect on fiber diameter and fiber nucleating ability towards isotactic polypropylene. Polymer. 2015;72:21–9.
Gazzano M, Gualandi C, Zucchelli A, Sui T, Korsunsky AM, Reinhard C, et al. Structure-morphology correlation in electrospun fibers of semicrystalline polymers by simultaneous synchrotron SAXS-WAXD. Polymer. 2015;63:154–63.
Baqeri M, Abolhasani MM, Mozdianfard MR, Guo Q, Oroumei A, Naebe M. Influence of processing conditions on polymorphic behavior, crystallinity, and morphology of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers. J Appl Polym Sci. 2015;132:42304.
Liu J, Lin DY, Wei B, Martin DC. Single electrospun PLLA and PCL polymer nanofibers: increased molecular orientation with decreased fiber diameter. Polymer. 2017;118:143–9.
Chung J, Chung JW, Priestley RD, Kwak SY. Confinement-induced change in chain topology of ultrathin polymer fibers. Macromolecules. 2018;51:4229–37.
Song Z, Chiang SW, Chu X, Du H, Li J, Gan L, et al. Effects of solvent on structures and properties of electrospun poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibers. J Appl Polym Sci. 2018;135:45787.
Maurya AK, Weidenbacher L, Spano F, Forunato G, Rossi RM, Frenz M, et al. Structure insights into semicrystalline states of electrospun nanofibers: a multiscale analytical approach. Nanoscale. 2019;11:7176–87.
Li D, Xia Y. Electrospinning of nanofibers: reinventing the wheel? Adv Mater. 2004;16:1151–70.
Ding Y, Rabolt JF, Chen Y, Olson KL, Baker GL. Studies of chain conformation in triblock oligomers and microblock copolymers of ethylene and ethylene oxide. Macromolecules. 2002;35:3914–20.
Takahashi Y, Sumita I, Tadokoro H. Structural studies of polyethers. IX. Planar zigzag modification of poly(ethylene oxide). J Polym Sci Polym Phys Ed. 1973;11:2113–22.
Lisowski MS, Liu Q, Cho J, Runt J, Yeh F, Hsiao BS. Crystallization behavior of poly(ethylene oxide) and its blends using time-resolved wide- and small-angle X-ray scattering. Macromolecules. 2000;33:4842–9.
Mohamed A, Larbi FBC, Dubault A, Halary JL. Structural study of semi-crystalline blends of poly(vinylidene fluoride) and poly(methyl methacrylate) by means of linear correlation and interface distribution functions. e-Polymers. 2005;5:56.
Li X, Hsu SL. An analysis of the crystallization behavior of poly(ethylene oxide)/poly(methyl methacrylate) blends by spectroscopic and calorimetric techniques. J Polym Sci Polym Phys Ed. 1984;22:1331–42.
Chrissopoulou K, Andrikopoulos KS, Fotiadou S, Bollas S, Karageorgaki C, Christofilos D, et al. Crystallinity and chain conformation in PEO/layered silicate nanocomposites. Macromolecules. 2011;44:9710–22.
Su Z, Li J, Li Q, Ni T, Wei G. Chain conformation, crystallization behavior, electrical and mechanical properties of electrospun polymer-carbon nanotube hybrid nanofibers with different orientations. Carbon. 2012;50:5605–17.
Yoshioka T, Dersch R, Tsuji M, Schaper AK. Orientation analysis of individual electrospun PE nanofibers by transmission electron microscopy. Polymer. 2010;51:2383–9.
Joziasse CAP, Veenstra H, Grijpma DW, Pennings AJ. On the chain stiffness of poly(1actide)s. Macromol Chem Phys. 1996;197:2219–29.
Zhang H, Luo X, Lin X, Lu X, Zhou Y, Tang Y. Polycaprolactone/chitosan blends: simulation and experimental design. Mater Des. 2016;90:396–402.
Mattice WL, Helfer CA, Sokolov AP. On the relationship between the characteristic ratio of a finite chain, Cn, and the asymptotic limit, C∞. Macromolecules. 2003;36:9924–8.
Kugler J, Fixher EW, Peuscher M, Eisenbach CD. Small angle neutron scattering studies of poly(ethylene oxide) in the melt. Makromol Chem. 1983;184:2325–34.
Bortel E, Hodorowicz S, Lamot R. Relation between crystallinity degree and stability in solid state of high molecular wight poly(ethylene oxide)s. Makromol Chem. 1979;180:2491–8.
Saujanya C, Radhakrishnan S. Crystallization behavior of polyethylene oxide/para-nitroaniline microdispersed composites. J Appl Polym Sci. 1997;65:1127–37.
Luo H, Huang Y, Wang D, Shi J. Coaxial-electrospinning as a new method to study confined crystallization of polymer. J Polym Sci Polym Phys Ed. 2013;51:376–83.
Wang C, Hsieh TC, Cheng YW. Solution-electrospun isotactic polypropylene fibers: processing and microstructure development during stepwise annealing. Macromolecules. 2010;43:9022–9.
Strobl GR, Schneider M. Direct evaluation of the electron density correlation function of partially crystalline polymers. J Polym Sci Polym Phys Ed. 1980;18:1343–59.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan under Grant Nos. 105-2628-E-006-009-MY3 and 108-2221-E-006-053-MY3. The authors gratefully acknowledge the use of SAXS belonging to the Instrument Center of National Cheng Kung University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, N.Q., Chen, TF. & Lo, CT. Confined crystallization and chain conformational change in electrospun poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibers. Polym J 53, 895–905 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-021-00492-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-021-00492-0
This article is cited by
-
The Transition of Molecular Alignment of Poly(ethylene oxide) Film via Thermal Annealing
Macromolecular Research (2022)