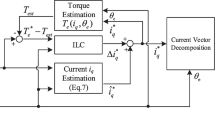
Abstract
This paper proposes an advanced fault ride-through strategy using feedback linearization (FL) and sliding mode control (SMC) for squirrel-cage induction generator (SCIG)-based wind energy conversion systems (WECSs). Based on FL theory, a nonlinear dynamic model of a SCIG wind turbine system is linearized with only two decoupled state variables: d-axis stator current and DC-link voltage. Thus, d-axis stator current and DC-link voltage controllers can be simply designed with the linear control theory. Moreover, with the proposed FL control law, the DC-link voltage control can be performed by directly regulating the q-axis stator voltage without a q-axis current controller. During grid voltage sags, the output power of the SCIG is reduced to maintain the DC-link voltage. By applying SMC theory to the design of d-axis stator current and DC-link voltage controllers, robust performance of control systems can be achieved even under parameter variations. The feasibility of the proposed method has been demonstrated via simulation and experimental results.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nguyen, A.T., Lee, D.-C.: Sensorless vector control of SCIG-based small wind turbine systems using cascaded second-order generalized integrators. J. Power Electron. 20(3), 764–773 (2020)
Yaramasu, V., Wu, B., Sen, P., Kouro, S., Narimani, M.: High-power wind energy conversion systems: State of-the-art and emerging technologies. Proc. IEEE 103(5), 740–788 (2015)
[Online] https://pdf.archiexpo.com/pdf/siemens-gamesa/swt-36-107/88089–134485.html
Conroy, J.F., Watson, R.: Low-voltage ride-through of a full converter wind turbine with permanent magnet generator. IET Renew. Power Gener. 1(3), 182–189 (2007)
Abbey, C., Joos, G.: Supercapacitor energy storage for wind energy applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 43(3), 769–776 (2007)
Ibrahim, A.O., Nguyen, T.H., Lee, D.-C., Kim, S.-C.: A fault ride- through technique of DFIG wind turbine systems using dynamic voltage restorers. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 26(3), 871–882 (2011)
Hansen, A.D., Michalke, G.: Multi-pole permanent magnet synchronous generator wind turbines’ grid support capability in uninterrupted operation during grid faults. IET Renew. Power Gener. 3(3), 333–348 (2009)
Yuan, X., Wang, F., Boroyevich, D., Li, Y., Burgos, R.: DC-link voltage control of a full power converter for wind generator operating in weak-grid systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 24(9), 2178–2192 (2009)
Kim, K.-H., Jeung, Y.-C., Lee, D.-C., Kim, H.-G.: LVRT scheme of PMSG wind power systems based on feedback linearization. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 27(5), 2376–2384 (2012)
Zhou, S., Liu, J., Zhou, L., Zhu, Y.: Improved DC-link voltage control of PMSG WECS based on feedback linearization under grid faults, in Twenty-Eighth Annual IEEE applied power electronics conf. and exposition (APEC), 2013, pp. 2895–2899
Accetta, A., Alonge, F., Cirrincione, M., Pucci, M., Sferlazza, A.: Feedback linearizing control of induction motor considering magnetic saturation effects. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 52(6), 4843–4854 (2016)
Accetta, A., Alonge, F., Cirrincione, M., D’Ippolito, F., Pucci, M., Rabbeni, R., Sferlazza, A.: Robust control for high performance induction motor drives based on partial state-feedback linearization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 55(1), 490–503 (2019)
Matas, J., Castilla, M., Guerrero, J.M., Garcia de Vicuna, L., Miret, J.: Feedback linearization of direct-drive synchronous wind-turbines via a sliding mode approach. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 23(3), 1093–1103 (2008)
Martins, L.T., Stefanello, M., Pinheiro, H., Vieira, R.P.: Current control of grid-tied LCL-VSI with a sliding mode controller in a multiloop approach. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 34(12), 12356–12367 (2019)
Yan, Z., Jin, C., Utkin, V.I.: Sensorless sliding-mode control of induction motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 47, 1286–1297 (2000)
Jezernik, K., Korelic, J., Horvat, R.: PMSM sliding mode FPGA-based control for torque ripple reduction. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 28(7), 3549–3556 (2013)
Yazdanpanah, R., Soltani, J., Markadeh, G.R.A.: Nonlinear torque and stator flux controller for induction motor drive based on adaptive input-output feedback linearization and sliding mode control. Energy Convers. Manag. 49(4), 541–550 (2008)
Lascu, C., Jafarzadeh, S., Fadali, S.M., Blaabjerg, F.: Direct torque control with feedback linearization for induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 32(3), 2072–2080 (2017)
Talla, J., Leu, V.Q., Šmídl, V., Peroutka, Z.: Adaptive speed control of induction motor drive with inaccurate model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(11), 8532–8542 (2018)
Nguyen, A.T., Lee, D.-C.: LVRT control based on partial state-feedback linearization for SCIG wind turbine systems. IEEE Energy Convers. Congr. Expos. (ECCE) 2020, 93–98 (2020)
Sul, S.-K.: Control of electric machine drive systems. Wiley, Hoboken (2011)
Koutroulis, E., Kalaitzakis, K.: Design of a maximum power tracking system for wind-energy-conversion applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 53(2), 486–494 (2006)
Song, H.-S., Nam, K.: Dual current control scheme for PWM converter under unbalanced input voltage conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 46(5), 953–959 (1999)
Tsili, M., Papathanassiou, S.: A review of grid code technical requirements for wind farms. IET Renew. Power Gen. 3(3), 308–332 (2009)
Zhao, R., Xin, Z., Loh, P.C., Blaabjerg, F.: A novel flux estimator based on multiple second-order generalized integrators and frequency-locked loop for induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 32(8), 6286–6296 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Korea Electric Power Corporation under Grant R18XA06-35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, A.T., Lee, DC. Advanced LVRT strategy for SCIG-based wind energy conversion systems using feedback linearization and sliding mode control. J. Power Electron. 21, 1180–1189 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-021-00256-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-021-00256-2