Abstract
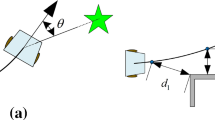
In order to assist college football training, an edge computing-based path planning algorithm for the football robot, and an improved PSO (particle swarm optimization) algorithm are proposed. First, the cartesian coordinate system is transformed into the polar coordinate system, and the coordinates of the robots’ path coding are calculated and displayed in the polar coordinate system. Then, the robots’ coordinates in the current, the next, and the obstacle point are measured and compared to determine whether path planning is needed. Consequently, the PSO, optimized by the “concentration selection” strategy in the artificial immune algorithm, is chosen for path planning. The experiments show that with the improved PSO, five robots of 0.4 m in radius and moving less than 2 m/s can be avoided easily. The static obstacle avoidance experiment shows that obstacles can be avoided more easily, using the path planned through improved PSO. The dynamic obstacle avoidance experiments indicate that the robot can avoid all moving obstacles, blocking in front, intercepting from all sides, and tracking from behind timely. The experiments prove that the proposed path planning is effective, which has reference value for promoting the application of path planning algorithms in college football training.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen P, Shen P, Zhang P et al (2019a) Path planning of underwater terrain-aided navigation based on improved artificial potential field method. Mar Technol Soc J 53(2):65–74
Chen T, Shi J, Yang J et al (2019b) Enhancing network cluster synchronization capability based on artificial immune algorithm. Hum-centric Comput Inf Sci 9(1):1–28
Chen S, Li Q, Zhou M et al (2021) Recent advances in collaborative scheduling of computing tasks in an edge computing paradigm. Sensors 21(3):779
Dadvar AA, Vahidi J, Hajizadeh Z et al (2021) Experimental study on classical and metaheuristics algorithms for optimal nano-chitosan concentration selection in surface coating and food packaging. Food Chem 335:127681
Ding H, Gu X (2020) Hybrid of human learning optimization algorithm and particle swarm optimization algorithm with scheduling strategies for the flexible job-shop scheduling problem - ScienceDirect. Neurocomputing 414:313–332
Garg S, Singh A, Batra S et al (2018) UAV-empowered edge computing environment for cyber-threat detection in smart vehicles. IEEE Netw 32(3):42–51
Han X, Xu Q, Yue L et al (2020) An improved crow search algorithm based on spiral search mechanism for solving numerical and engineering optimization problems. IEEE Access 8:92363–92382
Hayyolalam V, Kazem AAP (2020) Black widow optimization algorithm: a novel meta-heuristic approach for solving engineering optimization problems. Eng Appl Artif Intell 87:103249
Hu L, Miao Y, Wu G et al (2019) iRobot-Factory: An intelligent robot factory based on cognitive manufacturing and edge computing. Futur Gener Comput Syst 90:569–577
Imperlini E, Mancini A, Orrù S et al (2020) Long-term recreational football training and health in aging. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(6):2087
Jiang Y, Wang S, Lei L (2020) A multi-UAV formation maintaining method based on formation reference point. J Phys Conf Ser 1621(1):012014
Johnston JT, Mandelbaum BR, Schub D et al (2018) Video analysis of anterior cruciate ligament tears in professional american football athletes. Am J Sports Med 46(1):862
Li X, Yu D (2019) Study on an optimal path planning for a robot based on an improved ANT colony algorithm. Autom Control Comput Sci 53(3):236–243
Liao J (2018) Research on PAGV path planning based on artificial immune ant colony fusion algorithm. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 35(3):1–6
Lin B, Zhu F, Zhang J et al (2019) A time-driven data placement strategy for a scientific workflow combining edge computing and cloud computing. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 15(73):4254–4265
Mcsharry PE (2020) Effect of altitude on football performance. BMJ 15(4):289–298
Neshat M, Pourahmad AA, Rohani Z (2020) Improving the cooperation of fuzzy simplified memory A* search and particle swarm optimisation for path planning. Int J Swarm Intell 5(1):1
Nguyen BM, Thi Thanh Binh H, Do Son B (2019) Evolutionary algorithms to optimize task scheduling problem for the IoT based bag-of-tasks application in cloud–fog computing environment. Appl Sci 9(9):1730
Onwunalu JE, Durlofsky LJ (2010) Application of a particle swarm optimization algorithm for determining optimum well location and type. Comput Geosci 14(1):183–198
Song B, Wang Z, Zou L (2017) On global smooth path planning for mobile robots using a novel multimodal delayed PSO algorithm. Cogn Comput 9(1):5–17
Subramani DN, Wei QJ, Lermusiaux PFJ (2018) Stochastic time-optimal path-planning in uncertain, strong, and dynamic flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 333:218–237
Taherizadeh S, Jones AC, Taylor I et al (2018) Monitoring self-adaptive applications within edge computing frameworks: a state-of-the-art review. J Syst Softw 136:19–38
Tang J, Wen R, Quek TQS et al (2017) Fully exploiting cloud computing to achieve a green and flexible C-RAN. IEEE Commun Mag 55(111):40–46
Tharwat A, Elhoseny M, Hassanien AE et al (2019) Intelligent Bézier curve-based path planning model using Chaotic Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm. Clust Comput 22(4):1–22
Wang X, Shi Y, Ding D et al (2016) Double global optimum genetic algorithm–particle swarm optimization-based welding robot path planning. Eng Optim 48(2):299–316
Wang B, Li S, Guo J et al (2018) Car-like mobile robot path planning in rough terrain using multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm. Neurocomputing 282:42–51
Xiong X (2019) Artificial intelligence control algorithm for the steering motion of wheeled soccer robot. Int J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell 33(10):238–252
Yu L, Wang K, Zhang Q et al (2020) Trajectory planning of a redundant planar manipulator based on joint classification and particle swarm optimization algorithm. Multibody Syst Dyn 50(1):25–43
Zhen XU (2020) Rotary unmanned aerial vehicles path planning in rough terrain based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization. J Syst Eng Electron 31(1):130–141
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, C. Applying edge computing to analyse path planning algorithm in college football training. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 12, 844–852 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-021-01134-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-021-01134-7