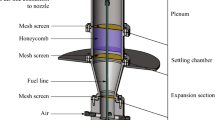
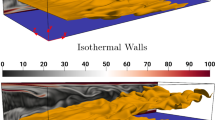
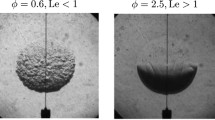
Abstract
Stratified propane air flames stabilized in the near wake region of a premixer/disk arrangement were investigated for a variety of inlet mixture compositions and preheating temperatures. The employed burner is capable of anchoring flames at very lean mixtures, expanding the lean flammability limits and promoting flame stabilization, at global equivalence ratio values of \(\Phi =0.13\) at 743 K. Particle Image Velocimetry and \({\text{OH}}^{*}\) Chemiluminescence Image analysis were performed to investigate flame stabilization characteristics at four inlet preheat levels ranging from 300 to 743 K, for fuel-lean reactant concentrations. Inlet mixture reactivity, 2D aerodynamic stretch rates, Damköhler (\(Da\)) and Karlovitz (\(Ka\)) numbers and flame brush thicknesses were estimated and analyzed to elucidate the effects of turbulence, inlet preheat and mixture composition on the flame topology and anchoring characteristics. Results show that the simultaneous stratification and preheat of the inlet mixture has a notable effect on the turbulent flame stabilization, with \(Ka\) numbers up to 60, for the highly preheated, ultra-lean flames, suggesting that the flames are chemically controlled with turbulence playing a less significant role. Moreover, the 2D aerodynamic stretch rates, evaluated along the mean flame front path, revealed that flame quenching requires both a certain level of mean stretch and a sufficiently large probability of these values to be exerted on the flame. Considering the stretch rate distributions and the respective \(Da\) numbers along the flame sheet it could be conjectured that laminar extinction stretch rates can be used as reference, for turbulent flames, only when the local \(Da\) number exceeds unity.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balachandran, R., Ayoola, B.O., Kaminski, C.F., Dowling, A.P., Mastorakos, E.: Experimental investigation of the nonlinear response of turbulent premixed flames to imposed inlet velocity oscillations. Combust. Flame. 143, 37–55 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2005.04.009
Banyon, C., Rodriguez-Henriquez, J.J., Paterakis, G., Malliotakis, Z., Souflas, K., Keramiotis, C., Vourliotakis, G., Mauss, F., Curran, H.J., Skevis, G., Koutmos, P., Founti, M.: A comparative study of the effect of varied reaction environments on a swirl stabilized flame geometry via optical measurements. Fuel. 216 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.09.105
Barlow, R.S., Dunn, M.J., Magnotti, G.: Preferential transport effects in premixed bluff-body stabilized CH4/H2flames. Combust. Flame. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2014.09.006
Barlow, R.S., Dunn, M.J., Sweeney, M.S., Hochgreb, S.: Effects of preferential transport in turbulent bluff-body-stabilized lean premixed CH 4/air flames. Combust. Flame. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2011.11.013
Benim, A.C., Syed, K.J.: Flashback Mechanisms in Lean Premixed Gas Turbine Combustion (2014)
Blint, R.: The relationship of the laminar flame width to flame speed. Combust. Sci. Technol. (1986). https://doi.org/10.1080/00102208608923903
Borghi, R.: On the Structure and Morphology of Turbulent Premixed Flames. In: Recent Advances in the Aerospace Sciences (1985)
Bradley, D.: How fast can we burn? Symp. Combust. 24, 247–262 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0082-0784(06)80034-2
Bradley, D., Gaskell, P.H., Gu, X.J., Sedaghat, A.: Premixed flamelet modelling: Factors influencing the turbulent heat release rate source term and the turbulent burning velocity. Combust. Flame. 143, 227–245 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2005.05.014
Bradley, D., Hicks, R.A., Lawes, M., Sheppard, C.G.W., Woolley, R.: The measurement of laminar burning velocities and Markstein numbers for iso-octane-air and iso-octane-n-heptane-air mixtures at elevated temperatures and pressures in an explosion bomb. Combust. Flame. 115, 126–144 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-2180(97)00349-0
Budzianowski, W.M., Miller, R.: Towards Improvements in thermal efficiency and reduced harmful emissions of combustion processes by using recirculation of heat and mass: a review. Recent Patents Mech. Eng. (2010). https://doi.org/10.2174/1874477X10902030228
Bush, W.B.: Asymptotic analysis of laminar flame propagation for general Lewis numbers. Combust. Sci. Technol. (1970). https://doi.org/10.1080/00102206908952222
Cadman, P., Thomas, G.O., Butler, P.: The auto-ignition of propane at intermediate temperatures and high pressures. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. (2000). https://doi.org/10.1039/b003665j
Cavaliere, A., De Joannon, M.: Mild combustion (2004)
Chowdhury, R.B., Cetegen, B.M.: Effects of free stream flow turbulence on blowoff characteristics of bluff-body stabilized premixed flames. Combust. Flame. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2017.12.002
Chterev, I., Emerson, B., Lieuwen, T.: Velocity and stretch characteristics at the leading edge of an aerodynamically stabilized flame. Combust. Flame. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2018.02.024
Clarke, A.: Calculation and consideration of the Lewis number for explosion studies. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. Part B. (2002). https://doi.org/10.1205/095758202317576238
Clavin, P.: Dynamic behavior of premixed flame fronts in laminar and turbulent flows (1985)
Driscoll, J.F.: Turbulent premixed combustion: Flamelet structure and its effect on turbulent burning velocities (2008)
Driscoll, J.F., Chen, J.H., Skiba, A.W., Carter, C.D., Hawkes, E.R., Wang, H.: Premixed flames subjected to extreme turbulence: Some questions and recent answers (2020)
Dunn-Rankin, D., Therkelsen, P.: Lean Combustion. Elsevier (2016)
Egolfopoulos, F.N., Hansen, N., Ju, Y., Kohse-Höinghaus, K., Law, C.K., Qi, F.: Advances and challenges in laminar flame experiments and implications for combustion chemistry (2014)
Erickson, R.R., Soteriou, M.C.: The influence of reactant temperature on the dynamics of bluff body stabilized premixed flames. Combust. Flame. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2011.05.006
Filatyev, S.A., Driscoll, J.F., Carter, C.D., Donbar, J.M.: Measured properties of turbulent premixed flames for model assessment, including burning velocities, stretch rates, and surface densities. Combust. Flame. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2004.07.010
Galizzi, C., Escudié, D.: Experimental analysis of an oblique turbulent flame front propagating in a stratified flow. Combust. Flame. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2010.07.008
Gibson, J., Ayoobi, M., Schoegl, I.: Behavior of preheated premixed flames at rich conditions. Proc. Combust. Inst. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proci.2012.06.141
Giovangigli, V., Smooke, M.D.: Calculation of extinction limits for premixed laminar flames in a stagnation point flow. J. Comput. Phys. (1987). https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9991(87)90061-1
Glassman, I., Yetter, R.: Combustion, Fourth Edition (2008)
Griebel, P., Boschek, E., Jansohn, P.: Lean blowout limits and NO[sub x] emissions of turbulent, lean premixed, hydrogen-enriched methane/air flames at high pressure. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power. (2007b). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2436568
Griebel, P., Siewert, P., Jansohn, P.: Flame characteristics of turbulent lean premixed methane/air flames at high pressure: Turbulent flame speed and flame brush thickness. Proc. Combust. Inst. (2007a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proci.2006.07.042
Guyot, D., Guethe, F., Schuermans, B., Lacarelle, A., Paschereit, C.O.: CH*/OH* Chemiluminescence response of an atmospheric premixed flame under varying operating conditions. Proceedings ASME Turbo EXPO (2010). https://doi.org/10.1115/GT2010-23135
Hashemi, H., Christensen, J.M., Harding, L.B., Klippenstein, S.J., Glarborg, P.: High-pressure oxidation of propane. Proc. Combust. Inst. 37, 461–468 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proci.2018.07.009
Ishizuka, S., Law, C.K.: An experimental study on extinction and stability of stretched premixed flames. Symp. Combust. (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0082-0784(82)80204-X
Karagiannaki, C., Dogkas, E., Paterakis, G., Souflas, K., Psarakis, E.Z., Vasiliou, P., Koutmos, P.: A comparison of the characteristics of disk stabilized lean propane flames operated under premixed or stratified inlet mixture conditions. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 59, (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2014.04.002
Kariuki, J., Dawson, J.R., Mastorakos, E.: Measurements in turbulent premixed bluff body flames close to blow-off. Combust. Flame. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2012.01.005
Katsuki, M., Hasegawa, T.: The science and technology of combustion in highly preheated air. In: Symposium (International) on Combustion (1998)
Kennel, C., Göttgens, J., Peters, N.: The basic structure of lean propane flames. Symp. Combust. (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0082-0784(06)80294-8
Kennel, C., Mauss, F., Peters, N.: Reduced Kinetic Mechanisms for Premixed Propane-Air Flames. In: Reduced Kinetic Mechanisms for Applications in Combustion Systems. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (1993)
Kheirkhah, S., Gülder, L.: Topology and brush thickness of turbulent premixed V-shaped flames. Flow, Turbul. Combust (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-014-9563-3
Kheirkhah, S., Gülder, Ö.L.: Turbulent premixed combustion in V-shaped flames: characteristics of flame front. Phys. Fluids. 25, (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4807073
Law, C.K., Ishizuka, S., Cho, P.: On the opening of premixed bunsen flame tips. Combust. Sci. Technol. 28, 89–96 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1080/00102208208952545
Law, C.K., Zhu, D.L., Yu, G.: Propagation and extinction of stretched premixed flames. Symp. Combust. (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0082-0784(88)80374-6
Lee, G.G., Huh, K.Y., Kobayashi, H.: Measurement and analysis of flame surface density for turbulent premixed combustion on a nozzle-type burner. Combust. Flame. (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-2180(00)00102-4
Libby, P.A., Liñán, A., Williams, F.A.: Strained premixed laminar flames with nonunity Lewis numbers. Combust. Sci. Technol. (1983). https://doi.org/10.1080/00102208308923695
Libby, P.A., Williams, F.A.: Structure of laminar flamelets in premixed turbulent flames. Combust. Flame. (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-2180(82)90079-7
Lieuwen, T. C., Yang, V., Lu, F.: Combustion Instabilities in Gas Turbine Engines: Operational Experience, Fundamental Mechanisms, and Modeling (2005)
Lim, J., Gore, J., Viskanta, R.: A study of the effects of air preheat on the structure of methane/air counterflow diffusion flames. Combust. Flame. (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-2180(99)00137-6
Lipatnikov, A.N., Chomiak, J.: Turbulent flame speed and thickness: phenomenology, evaluation, and application in multi-dimensional simulations. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1285(01)00007-7
Matalon, M., Cui, C., Bechtold, J.K.: Hydrodynamic theory of premixed flames: Effects of stoichiometry, variable transport coefficients and arbitrary reaction orders. J. Fluid Mech. (2003). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112003004683
Meneveau, C., Poinsot, T.: Stretching and quenching of flamelets in premixed turbulent combustion. Combust. Flame. (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-2180(91)90126-V
Michaels, D., Shanbhogue, S.J., Ghoniem, A.F.: The impact of reactants composition and temperature on the flow structure in a wake stabilized laminar lean premixed CH4/H2/air flames; mechanism and scaling. Combust. Flame. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2016.10.007
Mishra, D.P., Kumar, P.: Effects of N2gas on preheated laminar LPG jet diffusion flame. Energy Convers. Manag. (2010a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2010.03.007
Mishra, D.P., Kumar, P.: Experimental study of bluff-body stabilized LPG-H2jet diffusion flame with preheated reactant. Fuel (2010b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2009.07.030
Mohammadnejad, S., An, Q., Vena, P., Yun, S., Kheirkhah, S.: Thick reaction zones in non-flamelet turbulent premixed combustion. Combust. Flame. 222, 285–304 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2020.08.047
Namazian M., Shepherd I.G., T.L.: Characterization of the density fluctuations in turbulent V-shaped premixed flames. Combust. Flame. 64, 299–308 (1986)
Paterakis, G., Koutmos, P.: Experimental investigation of isothermal scalar mixing fields downstream of axisymmetric baffles under fully premixed or stratified inlet mixture conditions. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. (2019)
Peters, N.: Laminar flamelet concepts in turbulent combustion. Symp. Combust. (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0082-0784(88)80355-2
Peters, N.: The turbulent burning velocity for large-scale and small-scale turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. (1999). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112098004212
Peters, N.: Turbulent Combustion. Meas. Sci. Technol. (2001). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-0233/12/11/708
Poinsot, T., Veynante, D.: Theoretical and numerical combustion. J. Chem. Inf. Model. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1145/1645953.1646237
Prince, J.C., Treviño, C., Williams, F.A.: Reduced kinetic mechanism for high-temperature propane ignition. In: International Journal of Chemical Kinetics (2008)
Roy Chowdhury, B., Cetegen, B.M.: Experimental study of the effects of free stream turbulence on characteristics and flame structure of bluff-body stabilized conical lean premixed flames. Combust. Flame. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2016.12.019
Roy Chowdhury, B., Wagner, J.A., Cetegen, B.M.: Experimental study of the effect of turbulence on the structure and dynamics of a bluff-body stabilized lean premixed flame. Proc. Combust. Inst. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proci.2016.07.125
Sang, H.W., Bret, W., Bo, J., Yiguang, J.: The role of low temperature fuel chemistry on turbulent flame propagation. Combust. Flame. 161, 475–483 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2013.08.027
Sato, J.: Effects of lewis number on extinction behavior of premixed flames in a stagnation flow. Symp. Combust. (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0082-0784(82)80331-7
Saxena, S., Bedoya, I.D.: Fundamental phenomena affecting low temperature combustion and HCCI engines, high load limits and strategies for extending these limits (2013)
Skiba, A.W., Wabel, T.M., Carter, C.D., Hammack, S.D., Temme, J.E., Driscoll, J.F.: Premixed flames subjected to extreme levels of turbulence part I: Flame structure and a new measured regime diagram. Combust. Flame. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2017.08.016
Smith, G.P., Golden, D.M., Frenklach, M., Moriarty, N.W., Eiteneer, B., Goldenberg, M., Bowman, C.T., Hanson, R.K., Song, S., Gardiner Jr., W.C., Lissianski, V. V, Qin, Z.: GRI-Mech 3.0 (2000)
Souflas, K., Koutmos, P.: On the non-reacting flow and mixing fields of an axisymmetric disk stabilizer, under inlet mixture stratification and preheat. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2018.08.008
Souflas, K., Perrakis, K., Koutmos, P.: On the turbulent flow and pollutant emission characteristics of disk stabilized propane-air flames, under inlet mixture stratification and preheat. Fuel (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116333
Stafford, J., Walsh, E., Egan, V.: A statistical analysis for time-averaged turbulent and fluctuating flow fields using Particle Image Velocimetry. Flow Meas. Instrum. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2012.04.013
Steinberg, A.M., Driscoll, J.F.: Straining and wrinkling processes during turbulence-premixed flame interaction measured using temporally-resolved diagnostics. Combust. Flame. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2009.06.024
Stöhr, M., Boxx, I., Carter, C., Meier, W.: Dynamics of lean blowout of a swirl-stabilized flame in a gas turbine model combustor. Proc. Combust. Inst. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proci.2010.06.103
Sung, C.J., Law, C.K.: Extinction mechanisms of near-limit premixed flames and extended limits of flammability. Symp. Combust. (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0082-0784(96)80296-7
Sweeney, M.S., Hochgreb, S., Dunn, M.J., Barlow, R.S.: The structure of turbulent stratified and premixed methane/air flames I: Non-swirling flows. Combust. Flame. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2012.06.001
Syred, N.: A review of oscillation mechanisms and the role of the precessing vortex core (PVC) in swirl combustion systems (2006)
Tamadonfar, P., Gülder, Ö.L.: Flame brush characteristics and burning velocities of premixed turbulent methane/air Bunsen flames. Combust. Flame. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2014.06.014
Tanaka, S., Ayala, F., Keck, J.C., Heywood, J.B.: Two-stage ignition in HCCI combustion and HCCI control by fuels and additives. Combust. Flame. (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-2180(02)00457-1
Tang, C., He, J., Huang, Z., Jin, C., Wang, J., Wang, X., Miao, H.: Measurements of laminar burning velocities and Markstein lengths of propane-hydrogen-air mixtures at elevated pressures and temperatures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.08.053
Taylor, G.I.: Diffusion by continuous movements. Proc. lLndon Math. Soc. s2–20, 196–212 (1922)
Tropea, C., Yarin, A.L., Foss, J.F.: Springer handbook of experimental fluid mechanics (2007)
Tuttle, S.G., Chaudhuri, S., Kopp-Vaughan, K.M., Jensen, T.R., Cetegen, B.M., Renfro, M.W., Cohen, J.M.: Lean blowoff behavior of asymmetrically-fueled bluff body-stabilized flames. Combust. Flame. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2013.03.009
Vance, F.H., Shoshin, Y., van Oijen, J.A., de Goey, L.P.H.: Effect of Lewis number on premixed laminar lean-limit flames stabilized on a bluff body (2018)
Wang, H., You, X., Joshi, A. V, Davis, S.G., Laskin, A., Egolfopoulos, F., Law, C.K.: USC Mech Version II. High-Temperature Combustion Reaction Model of H2/CO/C1-C4 Compounds-http://ignis.usc.edu/USC_Mech_II.htm (2007)
Weinberg, F.J.: Combustion temperatures: The future? Nature 41, 239–241 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/233239a0
Weinberg, F.: Heat-recirculating burners: Principles and some recent developments. Combust. Sci. Technol. (1996). https://doi.org/10.1080/00102209608935584
Wilk, R.D., Cernansky, N.P., Cohen, R.S.: An Experimental Study of Propene Oxidation at Low and intermediate Temperatures. Combust. Sci. Technol. 52, 39–58 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1080/00102208708952567
Wilk, R.D., Cernansky, N.P., Cohen, R.S.: The oxidation of propane at low and transition temperatures. Combust. Sci. Technol. 49, 41–78 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1080/00102208608923902
Xiouris, C.Z., Koutmos, P.: Fluid dynamics modeling of a stratified disk burner in swirl co-flow. Appl. Therm. Eng. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2011.10.007
Yeung, P.K., Girimaji, S.S., Pope, S.B.: Straining and scalar dissipation on material surfaces in turbulence: implications for flamelets. Combust. Flame. (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-2180(90)90145-H
Yuan, J., Ju, Y., Law, C.K.: Effects of turbulence and flame instability on flame front evolution. Phys. Fluids. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2359744
Zhang, Q., Shanbhogue, S.J., Lieuwen, T., O’Connor, J.: Strain characteristics near the flame attachment point in a swirling flow. Combust. Sci. Technol. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1080/00102202.2010.537288
Zhou, B., Brackmann, C., Wang, Z., Li, Z., Richter, M., Aldén, M., Bai, X.-S.: Thin reaction zone and distributed reaction zone regimes in turbulent premixed methane/air flames: Scalar distributions and correlations. Combust. Flame. 175, 220–236 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2016.06.016
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the Research Council of the University of Patras.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Souflas, K., Koutmos, P. Effects of Stratification and Preheat on Turbulent Flame Characteristics and Stabilization. Flow Turbulence Combust 108, 237–262 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-021-00267-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-021-00267-w