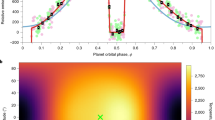
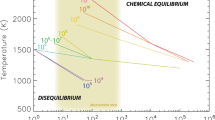
Abstract
Using two-dimensional (2D) thermal structure models and pseudo-2D chemical kinetics models, we explore how atmospheric temperatures and composition change as a function of altitude and longitude within the equatorial regions of close-in transiting Neptune-class exoplanets at different distances from their host stars. Our models predict that the day-night stratospheric temperature contrasts increase with increasing planetary effective temperatures Teff and that the atmospheric composition changes significantly with Teff. We find that horizontal transport-induced quenching is very effective in our simulated exo-Neptune atmospheres, acting to homogenize the vertical profiles of species abundances with longitude at stratospheric pressures where infrared observations are sensitive. Our models have important implications for planetary emission observations as a function of orbital phase with the Ariel mission. Cooler solar-composition exo-Neptunes with Teff = 500–700 K are strongly affected by photochemistry and other disequilibrium chemical processes, but their predicted variations in infrared emission spectra with orbital phase are relatively small, making them less robust phase-curve targets for Ariel observations. Hot solar-composition exo-Neptunes with Teff ≥ 1300 K exhibit strong variations in infrared emission with orbital phase, making them great targets for constraining global temperatures, energy-balance details, atmospheric dynamics, and the presence of certain high-temperature atmospheric constituents. However, such high-temperature exo-Neptunes are arguably less interesting from an atmospheric chemistry standpoint, with spectral signatures being dominated by a small number of species whose abundances are expected to be constant with longitude and consistent with thermochemical equilibrium. Solar-composition exo-Neptunes with Teff = 900–1100 K reside in an interesting intermediate regime, with infrared phase curve variations being affected by both temperature and composition variations, albeit at smaller predicted phase-curve amplitudes than for the hotter planets. This interesting intermediate regime shifts to smaller temperatures as atmospheric metallicity is increased, making cool higher-metallicity Neptune-class planets appropriate targets for Ariel phase-curve observations.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agúndez, M., Parmentier, V., Venot, O., Hersant, F., Selsis, F.: Pseudo 2D chemical model of hot-Jupiter atmospheres: application to HD 209458b and HD 189733b. Astron. Astrophys. 564, A73 (2014a)
Agúndez, M., Venot, O., Iro, N., Selsis, F., Hersant, F., Hébrard, E., Dobrijevic, M.: The impact of atmospheric circulation on the chemistry of the hot Jupiter HD 209458b. Astron. Astrophys. 548, A73 (2012)
Agúndez, M., Venot, O., Selsis, F., Iro, N.: The puzzling chemical composition of GJ 436b’s atmosphere: Influence of tidal heating on the chemistry. Astrophys. J. 781, 68 (2014b)
Allen, M., Yung, Y.L., Waters, J.W.: Vertical transport and photochemistry in the terrestrial mesosphere and lower thermosphere (50-120 km). J. Geophys. Res. 86, 3617–3627 (1981)
Amundsen, D.S., Baraffe, I., Tremblin, P., Manners, J., Hayek, W., Mayne, N.J., Acreman, D.M.: Accuracy tests of radiation schemes used in hot Jupiter global circulation models. Astron. Astrophys. 564, A59 (2014)
Amundsen, D.S., Tremblin, P., Manners, J., Baraffe, I., Mayne, N.J.: Treatment of overlapping gaseous absorption with the correlated-k method in hot Jupiter and brown dwarf atmosphere models. Astron. Astrophys. 598, A97 (2017)
Arcangeli, J., Desert, J.M., Line, M.R., Bean, J.L., Parmentier, V., Stevenson, K.B., Kreidberg, L., Fortney, J.J., Mansfield, M., Showman, A.P.: H− opacity and water dissociation in the dayside atmosphere of the very hot gas giant WASP-18 b. Astrophys. J. Lett. 855, L30 (2018)
Bailey, J.: The Dawes Review 3: The atmospheres of extrasolar planets and brown dwarfs. Pub. Astron. Soc. Australia 31, e043 (2014)
Batalha, N.M., Rowe, J.F., Bryson, S.T., Barclay, T., Burke, C.J., Caldwell, D.A., Christiansen, J.L., Mullally, F., Thompson, S.E., Brown, T.M., Dupree, A.K., Fabrycky, D.C., Ford, E.B., Fortney, J.J., Gilliland, R.L., Isaacson, H., Latham, D.W., Marcy, G.W., Quinn, S.N., Ragozzine, D., Shporer, A., Borucki, W.J., Ciardi, D.R., Gautier, T.N. III, Haas, M.R., Jenkins, J.M., Koch, D.G., Lissauer, J.J., Rapin, W., Basri, G.S., Boss, A.P., Buchhave, L.A., Carter, J.A., Charbonneau, D., Christensen-Dalsgaard, J., Clarke, B.D., Cochran, W.D., Demory, B.O., Desert, J.M., Devore, E., Doyle, L.R., Esquerdo, G.A., Everett, M., Fressin, F., Geary, J.C., Girouard, F.R., Gould, A., Hall, J.R., Holman, M.J., Howard, A.W., Howell, S.B., Ibrahim, K.A., Kinemuchi, K., Kjeldsen, H., Klaus, T.C., Li, J., Lucas, P.W., Meibom, S., Morris, R.L., Prša, A., Quintana, E., Sanderfer, D.T., Sasselov, D., Seader, S.E., Smith, J.C., Steffen, J.H., Still, M., Stumpe, M.C., Tarter, J.C., Tenenbaum, P., Torres, G., Twicken, J.D., Uddin, K., Van Cleve, J., Walkowicz, L., Welsh, W.F.: Planetary candidates observed by Kepler. III. Analysis of the first 16 months of data. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 204, 24 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0067-0049/204/2/24
Blumenthal, S.D., Mandell, A.M., Hébrard, E., Batalha, N.E., Cubillos, P.E., Rugheimer, S., Wakeford, H.R.: A comparison of simulated JWST observations derived from equilibrium and non-equilibrium chemistry models of giant exoplanets. Astrophys. J. 853, 138 (2018)
Bordwell, B., Brown, B.P., Oishi, J.S.: Convective dynamics and disequilibrium chemistry in the atmospheres of giant planets and brown dwarfs. Astrophys. J. 854, 8 (2018)
Caffau, E., Ludwig, H.G., Steffen, M., Freytag, B., Bonifacio, P.: Solar chemical abundances determined with a CO5BOLD 3D model atmosphere. Sol. Phys. 268, 255–269 (2011)
Carone, L., Baeyens, R., Mollière, P., Barth, P., Vazan, A., Decin, L., Sarkis, P., Venot, O., Henning, T.: Equatorial retrograde flow in WASP-43b elicited by deep wind jets. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 496, 3582–3614 (2020)
Cavalié, T., Venot, O., Selsis, F., Hersant, F., Hartogh, P., Leconte, J.: Thermochemistry and vertical mixing in the tropospheres of Uranus and neptune: How convection inhibition can affect the derivation of deep oxygen abundances. Icarus 291, 1–16 (2017)
Charnay, B., Meadows, V., Misra, A., Leconte, J., Arney, G.: 3D Modeling of GJ1214b’s atmosphere: Formation of Inhomogeneous High Clouds and Observational Implications. Astrophys. J. Lett. 813, L1 (2015)
Charnay, B., Mendonça, J., Kreidberg, L., Cowan, N.B., Taylor, J., Bell, T.J., Demangeon, O., Edwards, B., Haswell, C., Morello, G., Mugnai, L.V., Pascale, E., Tinetti, G., Tremblin, P., Zellem, R.: A survey of exoplanet phase curves with ariel. Experimental Astronomy submitted xxx (2020)
Choksi, N., Chiang, E.: Sub-neptune formation: The view from resonant planets. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 495, 4192–4209 (2020)
Cooper, C.S., Showman, A.P.: Dynamics and disequilibrium carbon chemistry in hot Jupiter atmospheres, with application to HD 209458b. Astrophys. J. 649, 1048–1063 (2006)
Cowan, N.B., Agol, E.: A model for thermal phase variations of circular and eccentric exoplanets. Astrophys. J. 726, 82 (2011)
Cowan, N.B., Greene, T., Angerhausen, D., Batalha, N.E., Clampin, M., Colón, K., Crossfield, I.J.M., Fortney, J.J., Gaudi, B.S., Harrington, J., Iro, N., Lillie, C.F., Linsky, J.L., Lopez-Morales, M., Mandell, A.M., Stevenson, K.B.: ExoPAG SAG-10: Characterizing transiting planet atmospheres through 2025. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 127, 311–327 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1086/680855
Cowan, N.B., Machalek, P., Croll, B., Shekhtman, L.M., Burrows, A., Deming, D., Greene, T., Hora, J.L.: Thermal phase variations of WASP-12b: Defying predictions. Astrophys. J. 747, 82 (2012)
Crossfield, I.J.M.: Observations of exoplanet atmospheres. Pub. Astron. Soc. Pacific 127, 941–960 (2015)
Debras, F., Mayne, N., Baraffe, I., Jaupart, E., Mourier, P., Laibe, G., Goffrey, T., Thuburn, J.: Acceleration of superrotation in simulated hot Jupiter atmospheres. Astron. Astrophys. 633, A2 (2020)
Deming, D., Seager, S.: Illusion and reality in the atmospheres of exoplanets. J. Geophys. Res. 122, 53–75 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JE005155
Drummond, B., Hebrard, E., Mayne, N.J., Venot, O., Ridgway, R.J., Changeat, Q., Tsai, S.M., Manners, J., Tremblin, P., Abraham, N.L., Sing, D., Kohary, K.: Implications of three-dimensional chemical transport in hot Jupiter atmospheres: results from a consistently coupled chemistry-radiation-hydrodynamics model. Astron. Astrophys. 636, A68 (2020)
Drummond, B., Mayne, N.J., Baraffe, I., Tremblin, P., Manners, J., Amundsen, D.S., Goyal, J., Acreman, D.: The effect of metallicity on the atmospheres of exoplanets with fully coupled 3D hydrodynamics, equilibrium chemistry, and radiative transfer. Astron. Astrophys. 612, A105 (2018)
Drummond, B., Mayne, N.J., Manners, J., Carter, A.L., Boutle, I.A., Baraffe, I., Hébrard, É., Tremblin, P., Sing, D.K., Amundsen, D.S., Acreman, D.: Observable signatures of wind-driven chemistry with a fully consistent three-dimensional radiative hydrodynamics model of HD 209458b. Astrophys. J. Lett. 855, L31 (2018)
Drummond, B., Tremblin, P., Baraffe, I., Amundsen, D.S., Mayne, N.J., Venot, O., Goyal, J.: The effects of consistent chemical kinetics calculations on the pressure-temperature profiles and emission spectra of hot jupiters. Astron. Astrophys. 594, A69 (2016)
Fegley, B. Jr, Lodders, K.: Atmospheric chemistry of the brown dwarf Gliese 229b: Thermochemical equilibrium predictions. Astrophys. J. 472, L37 (1996)
Fleury, B., Gudipati, M.S., Henderson, B.L., Swain, M.: Photochemistry in hot H2-dominated exoplanet atmospheres. Astrophys. J. 871, 158 (2019)
Fortney, J.J.: The effect of condensates on the characterization of transiting planet atmospheres with transmission spectroscopy. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 364, 649–653 (2005)
Fortney, J.J., Cooper, C.S., Showman, A.P., Marley, M.S., Freedman, R.S.: The influence of atmospheric dynamics on the infrared spectra and light curves of hot Jupiters. Astrophys. J. 652, 746–757 (2006)
Fortney, J.J., Lodders, K., Marley, M.S., Freedman, R.S.: A unified theory for the atmospheres of the hot and very hot jupiters: Two classes of irradiated atmospheres. Astrophys. J. 678, 1419–1435 (2008a)
Fortney, J.J., Mordasini, C., Nettelmann, N., Kempton, E.M.R., Greene, T.P., Zahnle, K.: A framework for characterizing the atmospheres of low-mass low-density transiting planets. Astrophys. J. 775, 80 (2013)
Fressin, F., Torres, G., Charbonneau, D., Bryson, S.T., Christiansen, J., Dressing, C.D., Jenkins, J.M., Walkowicz, L.M., Batalha, N.M.: The false positive rate of Kepler and the occurrence of planets. Astrophys. J. 766, 81 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/766/2/81
Freytag, B., Allard, F., Ludwig, H.G., Homeier, D., Steffen, M.: The role of convection, overshoot, and gravity waves for the transport of dust in M dwarf and brown dwarf atmospheres. Astron. Astrophys. 513, A19 (2010)
Gao, P., Thorngren, D.P., Lee, G.K.H., Fortney, J.J., Morley, C.V., Wakeford, H.R., Powell, D.K., Stevenson, K.B., Zhang, X.: Aerosol composition of hot giant exoplanets dominated by silicates and hydrocarbon hazes. Nature Astronomy 4, 951–956 (2020)
García Muñoz, A.: Physical and chemical aeronomy of HD 209458b. Planet. Space Sci. 55, 1426–1455 (2007)
Gordon, S., McBride, B.J.: Computer program for calculation of complex chemical equilibrium compositions and applications. NASA Reference Publication 1311 (1994)
Goyal, J.M., Mayne, N., Drummond, B., Sing, D.K., Hébrard, E., Lewis, N., Tremblin, P., Phillips, M.W., Mikal-Evans, T., Wakeford, H.R.: A library of self-consistent simulated exoplanet atmospheres. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 498, 4680–4704 (2020)
Goyal, J.M., Mayne, N., Sing, D.K., Drummond, B., Tremblin, P., Amundsen, D.S., Evans, T., Carter, A.L., Spake, J., Baraffe, I., Nikolov, N., Manners, J., Chabrier, G., Hebrard, E.: A library of ATMO forward model transmission spectra for hot Jupiter exoplanets. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 474, 5158–5185 (2018)
Goyal, J.M., Mayne, N., Sing, D.K., Drummond, B., Tremblin, P., Amundsen, D.S., Evans, T., Carter, A.L., Spake, J., Baraffe, I., Nikolov, N., Manners, J., Chabrier, G., Hebrard, E.: Errata: A library of ATMO forward model transmission spectra for hot Jupiter exoplanets. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 486, 783–795 (2019)
Hammond, M., Pierrehumbert, R.T.: Wave-mean flow interactions in the atmospheric circulation of tidally locked planets. Astrophys. J. 869, 65 (2018)
He, C., Hörst, S. M., Lewis, N.K., Moses, J.I., Kempton, E.M.R., Marley, M.S., Morley, C.V., Valenti, J.A., Vuitton, V.: Gas phase chemistry of cool exoplanet atmospheres: Insight from laboratory simulations. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry 3, 39–50 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.8b00133
He, C., Hörst, S.M., Lewis, N.K., Yu, X., Moses, J.I., Kempton, E.M.R., Marley, M.S., McGuiggan, P., Morley, C.V., Valenti, J.A., Vuitton, V.: Photochemical haze formation in the atmospheres of super-Earths and mini-Neptunes. Astron. J. 156, 38 (2018)
He, C., Hörst, S.M., Lewis, N.K., Yu, X., Moses, J.I., Kempton, E.M.R., McGuiggan, P., Morley, C.V., Valenti, J.A., Vuitton, V.: Laboratory simulations of haze formation in the atmospheres of super-Earths and mini-Neptunes: Particle color and size distribution. Astrophys. J. Lett. 856, L3 (2018)
Helled, R., Bodenheimer, P.: The formation of Uranus and neptune: Challenges and implications for intermediate-mass exoplanets. Astrophys. J. 789, 69 (2014)
Helled, R., Lunine, J.: Measuring Jupiter’s water abundance by juno: The link between interior and formation models. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 441, 2273–2279 (2014)
Helling, C.: Exoplanet clouds. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 47, 583–606 (2019)
Helling, C., Kawashima, Y., Graham, V., Samra, D., Chubb, K.L., Min, M., Waters, L.B.F.M., Parmentier, V.: Mineral cloud and hydrocarbon haze particles in the atmosphere of the hot Jupiter JWST target WASP-43b. Astron. Astrophys. 641, A178 (2020)
Helling, C., Lee, G., Dobbs-Dixon, I., Mayne, N., Amundsen, D.S., Khaimova, J., Unger, A.A., Manners, J., Acreman, D., Smith, C.: The mineral clouds on HD 209458b and HD 189733b. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 460, 855–883 (2016)
Hobbs, R., Shorttle, O., Madhusudhan, N., Rimmer, P.: A chemical kinetics code for modelling exoplanetary atmospheres. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 487, 2242–2261 (2019)
Hörst, S.M., He, C., Lewis, N.K., Kempton, E.M.R., Marley, M.S., Morley, C.V., Moses, J.I., Valenti, J.A., Vuitton, V.: Haze production rates in super-Earth and mini-Neptune atmosphere experiments. Nature Astron 2, 303–306 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-018-0397-0
Hu, R., Seager, S.: Photochemistry in terrestrial exoplanet atmospheres. III. Photochemistry and thermochemistry in thick atmospheres on super Earths and mini Neptunes. Astrophys. J. 784, 63 (2014)
Hubeny, I., Burrows, A.: A systematic study of departures from chemical equilibrium in the atmospheres of substellar mass objects. Astrophys. J. 669, 1248–1261 (2007)
Hubeny, I., Burrows, A., Sudarsky, D.: A possible bifurcation in atmospheres of strongly irradiated stars and planets. Astrophys. J. Lett. 594, 1011–1018 (2003)
Iro, N., Deming, L.D.: A time-dependent radiative model for the atmosphere of the eccentric exoplanets. Astrophys. J. 712, 218–225 (2010)
Irwin, P.G.J., Toledo, D., Braude, A.S., Bacon, R., Weilbacher, P.M., Teanby, N.A., Fletcher, L.N., Orton, G.S.: Latitudinal variation in the abundance of methane (CH4) above the clouds in Neptune’s atmosphere from VLT/MUSE Narrow Field Mode Observations. Icarus 331, 69–82 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2019.05.011
Joshi, M.M., Haberle, R.M., Reynolds, R.T.: Simulations of the atmospheres of synchronously rotating terrestrial planets orbiting M dwarfs: Conditions for atmospheric collapse and the implications for habitability. Icarus 129, 450–465 (1997)
Kataria, T., Showman, A.P., Fortney, J.J., Stevenson, K.B., Line, M.R., Kreidberg, L., Bean, J.L., Désert, J. M.: The atmospheric circulation of the hot Jupiter WASP-43b: Comparing three-dimensional models to spectrophotometric data. Astrophys. J. 801, 86 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/801/2/86
Kawashima, Y., Ikoma, M.: Theoretical transmission spectra of exoplanet atmospheres with hydrocarbon haze: Effect of creation, growth, and settling of haze particles. I. Model description and first results. Astrophys. J. 853, 7 (2018)
Kawashima, Y., Ikoma, M.: Theoretical transmission spectra of exoplanet atmospheres with hydrocarbon haze: Effect of creation, growth, and settling of haze particles. II. Dependence on UV irradiation intensity, metallicity, C/O ratio, eddy diffusion coefficient, and temperature. Astrophys. J. 877, 109 (2019)
Kite, E.S., Fegley Bruce, J., Schaefer, L., Ford, E.B.: Atmosphere origins for exoplanet Sub-Neptunes. Astrophys. J. 891, 111 (2020)
Kitzmann, D., Heng, K., Rimmer, P.B., Hoeijmakers, H.J., Tsai, S.M., Malik, M., Lendl, M., Deitrick, R., Demory, B.O.: The peculiar atmospheric chemistry of KELT-9b. Astrophys. J. 863, 183 (2018)
Knutson, H.A., Charbonneau, D., Allen, L.E., Fortney, J.J., Agol, E., Cowan, N.B., Showman, A.P., Cooper, C.S., Megeath, S.T.: A map of the day-night contrast of the extrasolar planet HD 189733b. Nature 447, 183–186 (2007)
Knutson, H.A., Charbonneau, D., Cowan, N.B., Fortney, J.J., Showman, A.P., Agol, E., Henry, G.W., Everett, M.E., Allen, L.E.: Multiwavelength constraints on the day-night circulation patterns of HD 189733b. Astrophys. J. 690, 822–836 (2009)
Knutson, H.A., Lewis, N., Fortney, J.J., Burrows, A., Showman, A.P., Cowan, N.B., Agol, E., Aigrain, S., Charbonneau, D., Deming, D., Désert, J. M., Henry, G.W., Langton, J., Laughlin, G.: 3.6 and 4.5 μ m phase curves and evidence for non-equilibrium chemistry in the atmosphere of extrasolar planet HD 189733b. Astrophys. J. 754, 22 (2012)
Komacek, T.D., Showman, A.P.: Atmospheric circulation of hot jupiters: Dayside-nightside temperature differences. Astrophys. J. 821, 16 (2016)
Komacek, T.D., Showman, A.P., Parmentier, V.: Vertical tracer mixing in hot Jupiter atmospheres. Astrophys. J. 881, 152 (2019)
Komacek, T.D., Showman, A.P., Tan, X.: Atmospheric circulation of hot jupiters: Dayside-nightside temperature differences. II. Comparison with observations. Astrophys. J. 835, 198 (2017)
Kopparapu, R.K., Kasting, J.F., Zahnle, K.J.: A photochemical model for the carbon-rich planet WASP-12b. Astrophys. J. 745, 77 (2012)
Koskinen, T.T., Harris, M.J., Yelle, R.V., Lavvas, P.: The escape of heavy atoms from the ionosphere of HD209458b. I. A photochemical-dynamical model of the thermosphere. Icarus 226, 1678–1694 (2013)
Koskinen, T.T., Yelle, R.V., Harris, M.J., Lavvas, P.: The escape of heavy atoms from the ionosphere of HD209458b. II. Interpretation of the observations. Icarus 226, 1695–1708 (2013)
Kurokawa, H., Nakamoto, T.: Mass-loss evolution of close-in exoplanets: Evaporation of hot Jupiters and the effect on population. Astrophys. J. 783, 54 (2104)
Lambrechts, M., Morbidelli, A., Jacobson, S.A., Johansen, A., Bitsch, B., Izidoro, A., Raymond, S.N.: Formation of planetary systems by pebble accretion and migration. How the radial pebble flux determines a terrestrial-planet or super-Earth growth mode. Astron. Astrophys. 627, A83 (2019)
Lavvas, P., Koskinen, T., Yelle, R.V.: Electron densities and alkali atoms in exoplanet atmospheres. Astrophys. J. 796, 15 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/796/1/15
Leconte, J., Forget, F., Lammer, H.: On the (anticipated) diversity of terrestrial planet atmospheres. Exp. Astron. 40, 449–467 (2015)
Lee, G., Dobbs-Dixon, I., Helling, C., Bognar, K., Woitke, P.: Dynamic mineral clouds on HD 189733b. i. 3D RHD with kinetic, non-equilibrium cloud formation. Astron. Astrophys. 594, A48 (2016)
Lee, G.K.H., Wood, K., Dobbs-Dixon, I., Rice, A., Helling, C.: Dynamic mineral clouds on HD 189733b. II. Monte Carlo radiative transfer for 3D cloudy exoplanet atmospheres: combining scattering and emission spectra. Astron. Astrophys. 601, A22 (2017)
Lewis, N.K., Knutson, H.A., Showman, A.P., Cowan, N.B., Laughlin, G., Burrows, A., Deming, D., Crepp, J.R., Mighell, K.J., Agol, E., Bakos, GÁ, Charbonneau, D., Désert, J.M., Fischer, D.A., Fortney, J.J., Hartman, J.D., Hinkley, S., Howard, A.W., Johnson, J.A., Kao, M., Langton, J., Marcy, G.W.: Orbital phase variations of the eccentric giant planet HAT-P-2b. Astrophys. J. 766, 95 (2013)
Lewis, N.K., Showman, A.P., Fortney, J.J., Marley, M.S., Freedman, R.S., Lodders, K.: Atmospheric circulation of eccentric hot Neptune GJ436b. Astrophys. J. 720, 344–356 (2010)
Lindzen, R.S.: Turbulence and stress owing to gravity wave and tidal breakdown. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 9707–9714 (1981)
Line, M.R., Vasisht, G., Chen, P., Angerhausen, D., Yung, Y.L.: Thermochemical and photochemical kinetics in cooler hydrogen-dominated extrasolar planets: A methane-poor GJ436b? Astrophys. J. 738, 32 (2011)
Lines, S., Manners, J., Mayne, N.J., Goyal, J., Carter, A.L., Boutle, I.A., Lee, G.K.H., Helling, C., Drummond, B., Acreman, D.M., Sing, D.K.: Exonephology: transmission spectra from a 3D simulated cloudy atmosphere of HD 209458b. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 481, 194–205 (2018)
Lines, S., Mayne, N.J., Boutle, I.A., Manners, J., Lee, G.K.H., Helling, C., Drummond, B., Amundsen, D.S., Goyal, J., Acreman, D.M., Tremblin, P., Kerslake, M.: Simulating the cloudy atmospheres of HD 209458 b and HD 189733 b with the 3D Met Office Unified Model. Astron. Astrophys. 615, A97 (2018)
Lines, S., Mayne, N.J., Manners, J., Boutle, I.A., Drummond, B., Mikal-Evans, T., Kohary, K., Sing, D.K.: Overcast on osiris: 3D radiative-hydrodynamical simulations of a cloudy hot Jupiter using the parametrized, phase-equilibrium cloud formation code EDDYSED. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 488, 1332–1355 (2019)
Liou, K.N.: An Introduction to Atmospheric Radiation, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York (2002)
Lodders, K., Fegley, B.: Atmospheric chemistry in giant planets, brown dwarfs, and low-mass dwarf stars. i. carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. Icarus 155, 393–424 (2002)
Lopez, E.D., Fortney, J.J.: The role of core mass in controlling evaporation: The Kepler radius distribution and the Kepler-36 density dichotomy. Astrophys. J. 777, 2 (2013)
Lopez, E.D., Fortney, J.J.: Understanding the mass-radius relation for sub-neptunes: Radius as a proxy for composition. Astrophys. J. 792, 1 (2014)
Lupu, R.E., Marley, M.S., Lewis, N., Line, M., Traub, W.A., Zahnle, K.: Developing atmospheric retrieval methods for direct imaging spectroscopy of gas giants in reflected light. I. Methane abundances and basic cloud properties. Astron. J. 152, 217 (2016)
Madhusudhan, N.: Exoplanetary atmospheres: Key insights, challenges and prospects. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 57, 617–663 (2019)
Madhusudhan, N., Agúndez, M., Moses, J.I., Hu, Y.: Exoplanetary atmospheres — chemistry, formation conditions, and habitability. Space Sci Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-016-0254-3 (2016)
Marley, M.S., Ackerman, A.S., Cuzzi, J.N., Kitzmann, D.: Clouds and Hazes in Exoplanet Atmospheres. In: Mackwell, S.J., Simon-Miller, A.A., Harder, J.W., Bullock, M.A. (eds.) Comparative Climatology of Terrestrial Planets, pp 367–391. Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson (2013)
Mazeh, T., Holczer, T., Faigler, S.: Dearth of short-period Neptunian exoplanets: A desert in period-mass and period-radius planes. Astron. Astrophys. 589, A75 (2106)
Mendonça, J.M., Tsai, S.M., Malik, M., Grimm, S.L., Heng, K.: Three-dimensional circulation driving chemical disequilibrium in WASP-43b. Astrophys. J. 869, 107 (2018)
Mendonċa, J.M.: Angular momentum and heat transport on tidally locked hot Jupiter planets. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 491, 1456–1470 (2020)
Miguel, Y., Kaltenegger, L.: Exploring atmospheres of hot mini-Neptunes and extrasolar giant planets orbiting different stars with application to HD 97658b, WASP-12b, CoRoT-2b, XO-1b, and HD 189733b. Astrophys. J. 780, 166 (2014)
Miguel, Y., Kaltenegger, L., Linsky, J.L., Rugheimer, S.: The effect of Lyman α radiation on mini-Neptune atmospheres around M stars: application to GJ 436b. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 446, 345–353 (2015)
Molaverdikhani, K., Henning, T., Mollière, P.: From cold to hot irradiated gaseous exoplanets: Fingerprints of chemical disequilibrium in atmospheric spectra. Astrophys. J. 883, 194 (2019)
Moran, S.E., Hörst, S.M., Vuitton, V., He, C., Lewis, N.K., Flandinet, L., Moses, J.I., North, N., Orthous-Daunay, F.R., Sebree, J., Wolters, C., Kempton, E.M.R., Marley, M.S., Morley, C.V., Valenti, J.A.: Chemistry of temperate super-Earth and mini-Neptune atmospheric hazes from laboratory experiments. Planet. Sci. J. 1, 17 (2020)
Mordasini, C.: Planetary evolution with atmospheric photoevaporation. I. Analytical derivation and numerical study of the evaporation valley and transition from super-Earths to sub-Neptunes. Astron. Astrophys. 638, A52 (2020)
Mordasini, C., van Boekel, R., Mollière, P., Henning, T., Benneke, B.: The imprint of exoplanet formation history on observable present-day spectra of hot Jupiters. Astrophys. J. 832, 41 (2016)
Morley, C.V., Fortney, J.J., Marley, M.S., Visscher, C., Saumon, D., Leggett, S.K.: Neglected clouds in T and Y dwarf atmospheres. Astrophys. J. 756, 172 (2012)
Moses, J.I.: Chemical kinetics on extrasolar planets. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 372, 20130,073 (2014)
Moses, J.I., Bézard, B., Lellouch, E., Gladstone, G.R., Feuchtgruber, H., Allen, M.: Photochemistry of Saturn’s atmosphere. I. Hydrocarbon chemistry and comparisons with ISO observations. Icarus 143, 244–298 (2000)
Moses, J.I., Fouchet, T., Bézard, B., Gladstone, G.R., Lellouch, E., Feuchtgruber, H.: Photochemistry and diffusion in Jupiter’s stratosphere: Constraints from ISO observations and comparisons with other giant planets. J. Geophys. Res. 110, E08,001 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JE002411
Moses, J.I., Line, M.R., Visscher, C., Richardson, M.R., Nettelmann, N., Fortney, J.J., Barman, T.S., Stevenson, K.B., Madhusudhan, N.: Compositional diversity in the atmospheres of hot Neptunes, with application to GJ 436b. Astrophys. J. 777, 34 (2013)
Moses, J.I., Madhusudhan, N., Visscher, C., Freedman, R.S.: Chemical consequences of the C/O ratio on hot jupiters: Examples from WASP-12b, CoRoT-2b, XO-1b, and HD 189733b. Astrophys. J. 763, 25 (2013)
Moses, J.I., Marley, M.S., Zahnle, K., Line, M.R., Fortney, J.J., Barman, T.S., Visscher, C., Lewis, N.K., Wolff, M.J.: On the composition of young, directly imaged giant planets. Astrophys. J. 829, 66 (2016)
Moses, J.I., Visscher, C., Fortney, J.J., Showman, A.P., Lewis, N.K., Griffith, C.A., Klippenstein, S.J., Shabram, M., Friedson, A.J., Marley, M.S., Freedman, R.S.: Disequilibrium carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen chemistry in the atmospheres of HD 189733b and HD 209458b. Astrophys. J. 737, 15 (2011)
Mugnai, L.V., Pascale, E., Edwards, B., Papageorgiou, A., Sarkar, S.: Arielrad: The Ariel radiometric model. Exp. Astron. 50, 303–328 (2020)
Murray-Clay, R.A., Chiang, E.I., Murray, N.: Atmospheric escape from hot Jupiters. Astrophys. J. 693, 23–42 (2009)
Owen, J.E., Wu, Y.: Kepler planets: A tale of evaporation. Astrophys. J. 775, 105 (2013)
Parmentier, V., Crossfield, I.J.M.: Exoplanet Phase Curves: Observations and Theory. In: Deeg, H., Belmonte, J. (eds.) Handbook of Exoplanets, pp 1419–1440. Springer (2018)
Parmentier, V., Fortney, J.J., Showman, A.P., Morley, C., Marley, M.S.: Transitions in the cloud composition of hot Jupiters. Astrophys. J. 828, 22 (2016)
Parmentier, V., Showman, A.P., Lian, Y.: 3D mixing in hot Jupiters atmospheres. I. Application to the day/night cold trap in HD 209458b. Astron. Astrophys. 558, A91 (2013)
Perez-Becker, D., Showman, A.P.: Atmospheric heat redistribution on hot Jupiters. Astrophys. J. 776, 134 (2013)
Petigura, E.A., Marcy, G.W., Howard, A.W.: A plateau in the planet population below twice the size of earth. Astrophys. J. 770, 69 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/770/1/69
Prinn, R.G., Barshay, S.S.: Carbon monoxide on Jupiter and implications for atmospheric convection. Science 198, 1031–1034 (1977)
Rimmer, P.B., Helling, C.: A chemical kinetics network for lightning and life in planetary atmospheres. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 224, 9 (2016)
Roman, M.T., Kempton, E.M.R., Rauscher, E., Harada, C.K., Bean, J.L., Stevenson, K.B.: Clouds in three-dimensional models of hot Jupiters over a wide range of temperatures I: Thermal structures and broadband phase curve predictions. arXiv:2010.06936 (2020)
collab=Sanchis-Ojeda, R., Rappaport, S., Winn, J.N., Kotson, M.C., Levine, A., El Mellah, I.: A study of the shortest-period planets found with Kepler. Astrophys. J. 787, 47 (2104)
Saumon, D., Geballe, T.R., Leggett, S.K., Marley, M.S., Freedman, R.S., Lodders, K., Fegley Jr., B., Sengupta, S.K.: Molecular abundances in the atmosphere of the T Dwarf GL 229B. Astrophys. J. 541, 374–389 (2000)
Schwartz, J.C., Kashner, Z., Jovmir, D., Cowan, N.B.: Phase offsets and the energy budgets of hot Jupiters. Astrophys. J. 850, 154 (2017)
Showman, A.P., Cho, J.Y.K., Menou, K.: Atmospheric Circulation of Exoplanets. In: Seager, S. (ed.) Exoplanets, pp 471–516. Univ. Arizona Press, Tucson (2010)
Showman, A.P., Fortney, J.J., Lian, Y., Marley, M.S., Freedman, R.S., Knutson, H.A., Charbonneau, D.: Atmospheric circulation of hot jupiters: Coupled radiative-dynamical general circulation model simulations of HD 189733b and HD 209458b. Astrophys. J. 699, 564–584 (2009)
Showman, A.P., Guillot, T.: Atmospheric circulation and tides of “51 Pegasus b-like” planets. Astron. Astrophys. 385, 166–180 (2002)
Showman, A.P., Kaspi, Y., Flierl, G.R.: Scaling laws for convection and jet speeds in the giant planets. Icarus 211, 1258–1273 (2011)
Shulyak, D., Lara, L.M., Rengel, M., Nemec, N.E.: Stellar impact on disequilibrium chemistry and on observed spectra of hot Jupiter atmospheres. Astron. Astrophys. 639, A48 (2020)
Sromovsky, L.A., Karkoschka, E., Fry, P.M., Hammel, H.B., de Pater, I., Rages, K.: Methane depletion in both polar regions of Uranus inferred from HST/STIS and keck/NIRC2 observations. Icarus 238, 137–155 (2014)
Steinrueck, M.E., Parmentier, V., Showman, A.P., Lothringer, J.D., Lupu, R.E.: The effect of 3D transport-induced disequilibrium carbon chemistry on the atmospheric structure, phase curves, and emission spectra of hot Jupiter HD 189733b. Astrophys. J. 880, 14 (2019)
Stevenson, K.B., Désert, J.M., Line, M.R., Bean, J.L., Fortney, J.J., Showman, A.P., Kataria, T., Kreidberg, L., McCullough, P.R., Henry, G.W., Charbonneau, D., Burrows, A., Seager, S., Madhusudhan, N., Williamson, M.H., Homeier, D.: Thermal structure of an exoplanet atmosphere from phase-resolved emission spectroscopy. Science 346, 838–841 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1256758
Tinetti, G., Drossart, P., Eccleston, P., Hartogh, P., Heske, A., Leconte, J., Micela, G., Ollivier, M., Pilbratt, G., Puig, L., et al.: A chemical survey of exoplanets with ARIEL. Exp. Astron. 46, 135–209 (2018)
Tremblin, P., Amundsen, D.S., Chabrier, G., Baraffe, I., Drummond, B., Hinkley, S., Mourier, P., Venot, O.: Cloudless atmospheres for L/T dwarfs and extrasolar giant planets. Astrophys. J. Lett. 817, L19 (2016)
Tremblin, P., Amundsen, D.S., Mourier, P., Baraffe, I., Chabrier, G., Drummond, B., Homeier, D., Venot, O.: Fingering convection and cloudless models for cool brown dwarf atmospheres. Astrophys. J. Lett. 804, L17 (2015)
Tremblin, P., Chabrier, G., Baraffe, I., Liu, M.C., Magnier, E.A., Lagage, P.O., Alves de Oliveira, C., Burgasser, A.J., Amundsen, D.S., Drummond, B.: Cloudless atmospheres for young low-gravity substellar objects. Astrophys. J. 850, 46 (2017)
Tremblin, P., Chabrier, G., Mayne, N.J., Amundsen, D.S., Baraffe, I., Debras, F., Drummond, B., Manners, J., Fromang, S.: Advection of potential temperature in the atmosphere of irradiated exoplanets: a robust mechanism to explain radius inflation. Astrophys. J. 841, 30 (2017)
Tsai, S.M., Kitzmann, D., Lyons, J.R., Mendonça, J., Grimm, S.L., Heng, K.: Toward consistent modeling of atmospheric chemistry and dynamics in exoplanets: Validation and generalization of chemical relaxation method. Astrophys. J. 862, 31 (2018)
Tsai, S.M., Lyons, J.R., Grosheintz, L., Rimmer, P.B., Kitzmann, D., Heng, K.: VULCAN: An Open-source, Validated chemical kinetics Python code for exoplanetary atmospheres. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 228, 20 (2017)
Venot, O., Agúndez, M., Selsis, F., Tessenyi, M., Iro, N.: The atmospheric chemistry of the warm Neptune GJ 3470b: Influence of metallicity and temperature on the CH4/CO ratio. Astron. Astrophys. 562, A51 (2014)
Venot, O., Bounaceur, R., Dobrijevic, M., Hébrard, E., Cavalié, T., Tremblin, P., Drummond, B., Charnay, B.: Reduced chemical scheme for modelling warm to hot hydrogen-dominated atmospheres. Astron. Astrophys. 624, A58 (2019)
Venot, O., Drummond, B., Miguel, Y., Waldmann, I.P., Pascale, E., Zingales, T.: A better characterization of the chemical composition of exoplanets atmospheres with ARIEL. Exp. Astron. 46, 101–134 (2018)
Venot, O., Fray, N., Bénilan, Y., Gazeau, M.C., Hébrard, E., Larcher, G., Schwell, M., Dobrijevic, M., Selsis, F.: High-temperature measurements of VUV-absorption cross sections of CO2 and their application to exoplanets. Astron. Astrophys. 551, A131 (2013)
Venot, O., Hébrard, E., Agúndez, M., Dobrijevic, M., Selsis, F., Hersant, F., Iro, N., Bounaceur, R.: A chemical model for the atmosphere of hot Jupiters. Astron. Astrophys. 546, A43 (2012)
Venot, O., Parmentier, V., Blecic, J., Cubillos, P.E., Waldmann, I.P., Changeat, Q., Moses, J.I., Tremblin, P., Crouzet, N., Gao, P., Powell, D., Lagage, P.O., Dobbs-Dixon, I., Steinrueck, M.E., Kreidberg, L., Batalha, N., Bean, J.L., Stevenson, K.B., Casewell, S., Carone, L.: Global chemistry and thermal structure models for the Hot Jupiter WASP-43b and predictions for JWST. Astrophys. J. 890, 176 (2020)
Venturini, J., Helled, R.: The formation of mini-Neptunes. Astrophys. J. 848, 95 (2017)
Visscher, C., Lodders, K., Fegley Jr., B.: Atmospheric chemistry in giant planets, brown dwarfs, and low-mass dwarf stars. III. iron, magnesium, and silicon. Astrophys. J. 716, 1060–1075 (2010a)
Visscher, C., Moses, J.I.: Quenching of carbon monoxide and methane in the atmospheres of cool brown dwarfs and hot Jupiters. Astrophys. J. 738, 72 (2011)
Visscher, C., Moses, J.I., Saslow, S.A.: The deep water abundance on jupiter: New constraints from thermochemical kinetics and diffusion modeling. Icarus 209, 602–615 (2010b)
Wang, D., Miguel, Y., Lunine, J.: Modeling synthetic spectra for transiting extrasolar giant planets: Detectability of H2S and PH3 with the James Webb Space Telescope. Astrophys. J. 850, 199 (2017)
Wang, H., Wordsworth, R.: Extremely long convergence times in a 3D GCM simulation of the sub-Neptune Gliese 1214b. Astrophys. J. 891, 7 (2020)
Yung, Y.L., Allen, M., Pinto, J.P.: Photochemistry of the atmosphere of titan: Comparison between model and observations. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 55, 465–506 (1984)
Yung, Y.L., DeMore, W.B.: Photochemistry of planetary atmospheres. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1999)
Zahnle, K., Marley, M.S., Morley, C.V., Moses, J.I.: Photolytic hazes in the atmosphere of 51 Eri b. Astrophys. J. 824, 137 (2016)
Zahnle, K.J., Marley, M.S.: Methane, carbon monoxide, and ammonia in brown dwarfs and self-luminous giant planets. Astrophys. J. 797, 41 (2014)
Zhang, X., Showman, A.P.: Effects of bulk composition on the atmospheric dynamics on close-in exoplanets. Astrophys. J. 836, 73 (2017)
Zhang, X., Showman, A.P.: Global-mean vertical tracer mixing in planetary atmospheres. I. Theory and fast-rotating planets. Astrophys. J. 866, 1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/aada85
Zhang, X., Showman, A.P.: Global-mean vertical tracer mixing in planetary atmospheres. II. Tidally Locked Planets. Astrophys. J. 866, 2 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/aada7c
Acknowledgements
We thank the two anonymous reviewers for insightful comments that improved the manuscript. We gratefully acknowledge support from the NASA Exoplanets Research Program grant NNX16AC64G (J.M.), the European Research Council Grant Agreement ATMO 757858 (P.T.), the CNRS/INSU Programme National de Planétologie (PNP) and CNES (O.V.), and most recently NASA grant 80NSSC19K0536.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration under grant number NNX16AC64G issued through the Exoplanets Research Program.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moses, J.I., Tremblin, P., Venot, O. et al. Chemical variation with altitude and longitude on exo-Neptunes: Predictions for Ariel phase-curve observations. Exp Astron 53, 279–322 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-021-09749-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-021-09749-1