Abstract
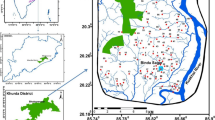
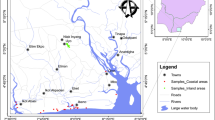
Shivalik region is one of the agri-intensive regions in Punjab, India, wherein groundwater quality is a major human health concern. In this study, a total of 57 groundwater samples were collected from the Rupnagar district of this region (one sample per 36 km2) to evaluate its quality, the role of hydrogeochemical processes in its contamination, and further their potential human health hazards. The results indicate that the major water chemistry is governed by carbonate weathering followed by silicate weathering. The Fe, Mg, Mn, Se, and HCO3- concentrations exceeded the BIS drinking water standards in 86, 51, 11, 9, and 79% of the samples, respectively. Piper and Durov plots indicated the dominance of Ca-HCO3- water types, followed by Ca-Mg-Cl- and Ca-Cl-. Furthermore, multivariate analyses indicated the geogenic origin for Fe, Mg, Mn, Se, SO42-, and anthropogenic sources (agrochemicals, cement factories, and fly ash) for NO3-, Cu, and Cr. The estimated carcinogenic risk of As and Cr falls under the very low (10-6) to low (10-5) risks category. Furthermore, the cumulative risk of non-carcinogenic contaminants (F-, U, NO3-) (HI-0.93) is at an alarming level and also close to the boundary line of USEPA limits (HI-1). There is an urgent need to undertake suitable policy measures for sustainability of groundwater quality.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data set used in the current manuscript is original. The corresponding author has all raw data of the manuscript and related experiments; it can be provided as a reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahada CP, Suthar S (2018) Groundwater nitrate contamination and associated human health risk assessment in southern districts of Punjab, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(25):25336–25347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2581-2
Ahada CP, Suthar S (2019) Assessment of human health risk associated with high groundwater fluoride intake in southern districts of Punjab, India. Expo Health 11(4):267–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-017-0268-4
Anim-Gyampo M, Anornu GK, Appiah-Adjei EK, Agodzo SK (2019) Quality and health risk assessment of shallow groundwater aquifers within the Atankwidi basin of Ghana. Groundw Sustain Dev 9:100217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100217
APHA (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, pp 4–72
Bajaj M, Eiche E, Neumann T, Winter J, Gallert C (2011) Hazardous concentrations of selenium in soil and groundwater in North-West India. J Hazard Mater 189(3):640–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.086
Bajwa BS, Kumar S, Singh S, Sahoo SK, Tripathi RM (2017) Uranium and other heavy toxic elements distribution in the drinking water samples of SW-Punjab, India. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 10(1):13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.01.002
Bhutiani R, Kulkarni DB, Khanna DR, Gautam A (2017) Geochemical distribution and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of an industrial area and its surroundings, Haridwar, India. Energy Ecol Environ 2(2):155–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-016-0019-6
BIS (2012) Indian Standards Specifications for Drinking Water.IS: 10500. New Delhi: Bureau of Indian Standards
CGWB (Central Ground Water Board) (2017) Report on Aquifer Mapping and Management Plan Rupnagar District, Punjab. <http://cgwb.gov.in/AQM/NAQUIM_REPORT/Punjab/Ropar.pdf> Accessed 30 August 2020
Chaudhry AK, Sachdeva P (2020) Groundwater quality and non-carcinogenic health risk assessment of nitrate in the semi-arid region of Punjab, India. J Water Health 18(6):1073–1083. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2020.121
Chowdhury S, Mazumder MJ, Al-Attas O, Husain T (2016) Heavy metals in drinking water: occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci Total Environ 569:476–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.166
Chung SY, Rajendran R, Senapathi V, Sekar S, Ranganathan PC, Oh YY, Elzain HE (2020) Processes and characteristics of hydrogeochemical variations between unconfined and confined aquifer systems: a case study of the Nakdong River Basin in Busan City, Korea. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:10087–10102. 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07451-6
Coyte RM, Singh A, Furst KE, Mitc WA, Vengosh A (2019) Co-occurrence of geogenic and anthropogenic contaminants in groundwater from Rajasthan, India. Sci Total Environ 688:1216–1227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.334
Dev R, Bali M (2019) Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in district Kangra of Himachal Pradesh, India. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 18(4):462–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2018.03.002
Dhawan V (2017) Water and Agriculture in India. <https://www.oav.de/fileadmin/user_upload/5_Publikationen/5_Studien/170118_Study_Water_Agriculture_India.pdf> Accessed on 15 August 2020
Dhillon KS, Dhillon SK (2014) Development and mapping of seleniferous soils in northwestern India. Chemosphere 99:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.09.072
Dhillon KS, Dhillon SK (2016) Selenium in groundwater and its contribution towards daily dietary Se intake under different hydrogeological zones of Punjab, India. J Hydrol 533:615–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.12.016
District survey report Rupnagar (2016) https://cdn.s3waas.gov.in/s3e2c0be24560d78c5e599c2a9c9d0bbd2/uploads/2020/10/2020102231.pdf <Accessed on 15 February 2021>
Doneen LD 1964 Notes on water quality in Agriculture Published as a Water Science and Engineering Paper 4001. Department of Water Science and Engineering, University of California.
Egbi CD, Anornu GK, Ganyaglo SY, Appiah-Adjei EK, Li SL, Dampare SB (2020) Nitrate contamination of groundwater in the Lower Volta River Basin of Ghana: sources and related human health risks. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191:110227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110227
Eiche E, Bardelli F, Nothstein AK, Charlet L, Göttlicher J, Steininger R, Sadana US (2015) Selenium distribution and speciation in plant parts of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) from a seleniferous area of Punjab, India. Sci Total Environ 505:952–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.10.080
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 170:795–840. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
He S, Li P (2020) A MATLAB based graphical user interface (GUI) for quickly producing widely used hydrogeochemical diagrams. Geochemistry 80(4):125550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2019.125550
He X, Li P, Wu J, Wei M, Ren X, Wang D (2020) Poor groundwater quality and high potential health risks in the Datong Basin, northern China: research from published data. Environ Geochem Health 43:791–812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00520-7
Hossain M, Patra PK (2020) Contamination zoning and health risk assessment of trace elements in groundwater through geostatistical modeling. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 189:110038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110038
Hou D, O'Connor D, Igalavithana AD, Alessi DS, Luo J, Tsang DC, Ok YS (2020) Metal contamination and bioremediation of agricultural soils for food safety and sustainability. Nat Rev Earth Environ 1:366–381. 16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-020-0061-y
Houria B, Mahdi K, Zohra TF (2020) Hydrochemical characterization of groundwater quality: Merdja plain (Tebessa town, Algeria). Civil Eng J 6(2):318–325. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-2020-03091473
Hundal HS, Khurana MP (2013) An appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes in southern part of Bathinda district of Punjab, northwest India. Environ Earth Sci 70(4):1841–1851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2272-8
IS (2003) Methods of sampling and test (physical and chemical) for water and wastewater. IS: 3025 (Part 24)-1985-Reaffirmed 2003. New Delhi: Bureau of Indian Standards.
Ji Y, Wu J, Wang Y, Elumalai V, Subramani T (2020) Seasonal variation of drinking water quality and human health risk assessment in Hancheng City of Guanzhong Plain, China. Expo Health 12(3):469–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-020-00357-6
Kansoh R, Abd-El-Mooty M, Abd-El-Baky R (2020) Computing the water budget components for lakes by using meteorological data. Civil Eng J 6(7):1255–1265. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-2020-03091545
Kaur T, Bhardwaj R, Arora S (2017) Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes using hydrochemical studies in Malwa region, southwestern part of Punjab, India. Appl Water Sci 7(6):3301–3316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0476-2
Kaur G, Kumar R, Mittal S, Sahoo PK, Vaid U (2021) Ground/drinking water contaminants and cancer incidence: a case study of rural areas of South West Punjab, India. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 27(1):205–226. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1705145
Krishan G, Lapworth DJ, Rao MS, Kumar CP, Smilovic M, Semwal P (2014) Natural (baseline) groundwater quality in the Bist-Doab catchment, Punjab, India: a pilot study comparing shallow and deep aquifers. Int J Earth Sci Eng 7:16–26
Kumar R, Chauhan A, Rawat L (2017) Physico-chemical analysis of surface and ground water in selected sites of Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India. J Anal Toxicol 6:420. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0525.1000420
Kumar R, Vaid U, Mittal S (2018) Water crisis: issues and challenges in Punjab. In: Vijay PS, Shalini Y (eds) Water resources management. Springer, Singapore, pp 93–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5711-3_7
Kumar R, Mittal S, Sahoo PK, Sahoo SK (2020a) Source apportionment, chemometric pattern recognition and health risk assessment of groundwater from southwestern Punjab, India. Environ Geochem Health 43:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00518-1
Kumar R, Mittal S, Peechat S, Sahoo PK, Sahoo SK (2020b) Quantification of groundwater–agricultural soil quality and associated health risks in the agri-intensive Sutlej River Basin of Punjab, India. Environ Geochem Health 42:4245–4268. 1-24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00636-w
Lapworth DJ, Krishan G, MacDonald AM, Rao MS (2017) Groundwater quality in the alluvial aquifer system of northwest India: new evidence of the extent of anthropogenic and geogenic contamination. Sci Total Environ 599:1433–1444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.223
Lee JY, Song SH (2007) Evaluation of groundwater quality in coastal areas: implications for sustainable agriculture. Environ Geol 52(7):1231–1242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0560-2
Li P, Qian H, Wu J, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2014) Occurrence and hydrogeochemistry of fluoride in shallow alluvial aquifer of Weihe River, China. Environ Earth Sci 71(7):3133–3145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2691-6
Li P, Wu J, Tian R, He S, He X, Xue C, Zhang K (2018) Geochemistry, hydraulic connectivity and quality appraisal of multilayered groundwater in the Hongdunzi Coal Mine, northwest China. Mine Water Environ 37(2):222–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0507-8
Li P, Tian R, Liu R (2019a) Solute geochemistry and multivariate analysis of water quality in the Guohua Phosphorite Mine, Guizhou Province, China. Expo Health 11(2):81–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0277-y
Li P, He X, Li Y, Xiang G (2019b) Occurrence and health implication of fluoride in groundwater of loess aquifer in the Chinese Loess Plateau: a case study of Tongchuan, northwest China. Expo Health 11(2):95–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0278-x
Li P, Karunanidhi D, Subramani T, Srinivasamoorthy K (2021) Sources and consequences of groundwater contamination. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 80(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-020-00805-z
Martins L, Pereira A, Oliveira A, Fernandes A, Sanches Fernandes LF, Pacheco FAL (2019a) An assessment of groundwater contamination risk with radon based on clustering and structural models. Water 11(5):1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11051107
Martins L, Pereira A, Oliveira A, Sanches Fernandes LF, Pacheco FA (2019b) A new framework for the management and radiological protection of groundwater resources: the implementation of a portuguese action plan for radon in drinking water and impacts on human health. Water 11(4):760. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040760
Martins LMO, Pereir AJSC, Oliveira AS, Fernandes LS, Pacheco FAL (2020) A new radon prediction approach for an assessment of radiological potential in drinking water. Sci Total Environ 712:136427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136427
Mittal S, Kaur G, Vishwakarma GS (2014) Effects of environmental pesticides on the health of rural communities in the Malwa Region of Punjab, India: a review. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 20(2):366–387. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2013.788972
Mittal S, Kumar R, Sahoo PK, Sahoo SK (2020) Geochemical assessment of groundwater contaminants and associated health risks in the Shivalik region of Punjab, India. Toxin Rev 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1705145
National Ground Water Association (2020) Facts about global groundwater usage. https://www.ngwa.org/what-is-groundwater/About-groundwater/facts-about-global-groundwater-usage Acceesed on 20 February 2021
Pacheco FAL, MartinsL MO, Quininha M, Oliveira AS, Fernandes LS (2018a) An approach to validate groundwater contamination risk in rural mountainous catchments: the role of lateral groundwater flows. Methods X 5:1447–1455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2018.11.002
Pacheco FAL, Martins LMO, Quininha M, Oliveira AS, Fernandes LS (2018b) Modification to the DRASTIC framework to assess groundwater contaminant risk in rural mountainous catchments. J Hydrol 566:175–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.09.013
Palansooriya KN, Yang Y, Tsang YF, Sarkar B, Hou D, Cao X, Ok YS (2020) Occurrence of contaminants in drinking water sources and the potential of biochar for water quality improvement: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 50(6):549–611. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1629803
Rahman A, Mondal NC, Fauzia F (2021) Arsenic enrichment and its natural background in groundwater at the proximity of active floodplains of Ganga River, northern India. Chemosphere 265:129096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129096
Rajesh R, Brindha K, Murugan R, Elango L (2012) Influence of hydrogeochemical processes on temporal changes in groundwater quality in a part of Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Earth Sci 65:1203–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1368-2
Ramakrishnaiah CR, Sadashivaiah C, Ranganna G (2009) Assessment of water quality index for the groundwater in Tumkur Taluk, Karnataka State, India. E-J Chem 6(2):523–530. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/757424
Raman V (1985) Impact of corrosion in the conveyance and distribution of water. J IWWA 15(11):115–121
Rao PN, Rao SA, Rao NS (2017) Geochemical evolution of groundwater in the western delta region of river Godavari, Andhra Pradesh, India. Appl Water Sci 7(2):813–822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0294-y
Rasool A, Farooqi A, Xiao T, Ali W, Noor S, Abiola O, Nasim W (2018) A review of global outlook on fluoride contamination in groundwater with prominence on the Pakistan current situation. Environ Geochem Health 40(4):1265–1281
Rathore DPS (2013) Interpretation and evaluation of the variations in the uranium, major cations and anions content of hydrogeochemical samples with reference to the time interval between sampling and analysis. Explor Res Atom Minerals 23:207–215
Richards LA (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Soil Sci 78(2):154
Sahoo PK, Dall’Agnol R, Salomão GN, Junior JF, Silva MS, Souza Filho PWM, Powell MA, Angélica, Pontes PR, Costa MF, Siqueira JO (2019) High resolution hydrogeochemical survey and estimation of baseline concentrations of trace elements in surface water of the Itacaiúnas River Basin, southeastern Amazonia: Implication for environmental studies. J Geochem Explor 205:106321
Shaji E, Santosh M, Sarath KV, Prakash P, Deepchand V, Divya BV (2020) Arsenic contamination of groundwater: a global synopsis with focus on the Indian Peninsula. Geosci Front 12:101079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2020.08.015
Sharma N, Singh J (2016) Radiological and chemical risk assessment due to high uranium contents observed in the ground waters of Mansa District (Malwa region) of Punjab state, India: an area of high cancer incidence. Expo Health 8(4):513–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0215-9
Sharma S, Kaur I, Nagpal AK (2017) Assessment of arsenic content in soil, rice grains and groundwater and associated health risks in human population from Ropar wetland, India, and its vicinity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(23):18836–18848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9401-y
Sharma S, Nagpal AK, Kaur I (2018) Heavy metal contamination in soil, food crops and associated health risks for residents of Ropar wetland, Punjab, India and its environs. Food Chem 255:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.02.037
Sharma S, Nagpal AK, Kaur I (2019) Appraisal of heavy metal contents in groundwater and associated health hazards posed to human population of Ropar wetland, Punjab, India and its environs. Chemosphere 227:179–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.009
Sharma DA, Keesari T, Rishi MS, Thakur N, Pant D, Sangwan P, Kishore N (2020a) Distribution and correlation of radon and uranium and associated hydrogeochemical processes in alluvial aquifers of northwest India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:38901–38915. 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10015-8
Sharma S, Kumar R, Sahoo PK, Mittal S (2020b) Geochemical relationship and translocation mechanism of arsenic in rice plants: a case study from health prone south west Punjab, India. Groundw Sustain Dev 10:100333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100333
Shrivastava BK (2015) Elevated uranium and toxic elements concentration in groundwater in Punjab state of India: extent of the problem and risk due to consumption of unsafe drinking water. Water Qual Expo Health 7(3):407–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-014-0144-4
Singh S, Singh C, Mukherjee S (2010) Impact of land-use and land-cover change on groundwater quality in the Lower Shiwalik hills: a remote sensing and GIS based approach. Open Geosci 2(2):124–131. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10085-010-0003-x
Singh CK, Shashtri S, Mukherjee S, Kumari R, Avatar R, Singh A, Singh RP (2011a) Application of GWQI to assess effect of land use change on groundwater quality in lower Shiwaliks of Punjab: remote sensing and GIS based approach. Water Resour Manag 25(7):1881–1898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9779-0
Singh CK, Shashtri S, Mukherjee S (2011b) Integrating multivariate statistical analysis with GIS for geochemical assessment of groundwater quality in Shiwaliks of Punjab, India. Environ Earth Sci 62(7):1387–1405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0625-0
Singh CK, Rina K, Singh RP, Mukherjee S (2014) Geochemical characterization and heavy metal contamination of groundwater in Satluj River Basin. Environ Earth Sci 71(1):201–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2424-x
Solangi GS, Siyal AA, Siyal P (2019) Analysis of Indus Delta groundwater and surface water suitability for domestic and irrigation purposes. Civ Eng J 5(7):1599–1608. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-2019-03091356
Thakur T, Rishi MS, Naik PK, Sharma P (2016) Elucidating hydrochemical properties of groundwater for drinking and agriculture in parts of Punjab, India. Environ Earth Sci 75(6):467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5306-1
Tiwari R, Aulakh RS, Bedi JS, Gill JPS, Kumar A (2020) Occurrence and spatial distribution of metals and arsenic in groundwater sources of Punjab (India), and their health risk assessment. Toxicol Environ Chem 102:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2020.1808895
UN water report (2015) The United Nations World Water Development Report 2015. <http://www.unesco.org/new/fileadmin/MULTIMEDIA/HQ/SC/images/WWDR2015Facts_Figures_ENG_web.pdf> Accessed on 15 August 2020
UNDP (2020) United Nations Development Programme, The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. <https://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/sustainable-development-goals/goal-6-clean-water-and-sanitation/targets.html> Accessed on 15 February 2021
USEPA (1989) Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A, Interim Final), EPA/540/1-89/002. U.S. EPA, Washington, DC. <https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-09/documents/rags_a.pdf> Accessed on 15 August 2020
USEPA (2005) Guidance on selecting age groups for monitoring and assessing childhood exposures to environmental contaminants. Risk Assessment Forum Washington, DC., pp. 50, 397 K, November 2005, 630-P-03-003F
USEPA IRIS (2020) Environmental Protection Agency’s IRIS Assessments. <http://www.epa.gov/iris/> Accessed 15 August 2020
Vetrimurugan E, Brindha K, Elango L, Ndwandwe OM (2017) Human exposure risk to heavy metals through groundwater used for drinking in an intensively irrigated river delta. Applied Water Science 7(6):3267–3280
Villalba E, Tanjal C, Borzi G, Páez G, Carol E (2020) Geogenic arsenic contamination of wet-meadows associated with a geothermal system in an arid region and its relevance for drinking water. Sci Total Environ 720:137571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137571
Wang D, Wu J, Wang Y, Ji Y (2020) Finding high-quality groundwater resources to reduce the hydatidosis incidence in the Shiqu County of Sichuan Province, China: analysis, assessment, and management. Expo Health 12(2):307–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00314-y
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking water quality, vol 1, 4th edn. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation waters. United States Department of Agriculture, Washington
Wongsasuluk P, Chotpantarat S, Siriwong W, Robson M (2014) Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani province, Thailand. Environ Geochem Health 36(1):169–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9537-8
Wu J, Zhou H, He S, Zhang Y (2019) Comprehensive understanding of groundwater quality for domestic and agricultural purposes in terms of health risks in a coal mine area of the Ordos basin, north of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 78(15):446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8471-1
Wu J, Zhang Y, Zhou H (2020a) Groundwater chemistry and groundwater quality index incorporating health risk weighting in Dingbian County, Ordos basin of northwest China. Geochemistry 80(4):125607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2020.125607
Wu J, Li P, Wang D, Ren X, Wei M (2020b) Statistical and multivariate statistical techniques to trace the sources and affecting factors of groundwater pollution in a rapidly growing city on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 26(6):1603–1621. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1594156
Yadav RP, Panwar P, Arya SL, Mishra PK (2015) Revisit of Shivalik region in different states of northwestern India. J Geol Soc India 86(3):351–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-015-0322-4
Zhou Y, Li P, Xue L, Dong Z, Li D (2020) Solute geochemistry and groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes: a case study in Xinle City, North China. Geochemistry 80(4):125609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2020.125609
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Board of Research in Nuclear Science (BRNS), Department of Atomic Energy, (DAE-BRNS), Mumbai, for providing financial assistance. The authors are thankful to Central University of Punjab, Bathinda, and DST–FIST support for chemical analysis. The authors express sincere gratitude to local people for memorable cooperation during the time of sampling work.
Funding
The research work was funded by the Board of Research in Nuclear Science (BRNS), Department of Atomic Energy, (DAE-BRNS), Mumbai. [Sanction number: 36(4)/14/49/2014-BRNS/36044].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sunil Mittal and Ravishankar Kumar have designed and performed the experimental/research work, as well as written the manuscript. Prafulla Kumar Sahoo and Sunil Kumar Sahoo were involved in the interpretation of data and statistical analysis and also helped to review and edit the manuscript. Raghavendra Prasad Tiwari was involved in data analysis, and manuscript editing works.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable to this research work.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Broder J. Merkel
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2472 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mittal, S., Sahoo, P.K., Sahoo, S.K. et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and human health risk assessment of groundwater in the Shivalik region of Sutlej basin, Punjab, India. Arab J Geosci 14, 847 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07043-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07043-0