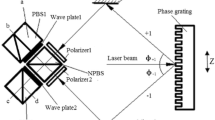
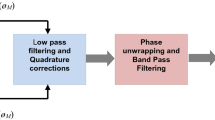
Abstract
In recent years, the performance of an interferometric fiber optic gyroscope (IFOG) has been increased a lot and widely used for dynamic angle measurement. In this paper, we present an investigation on measurement uncertainty of the IFOG and propose a comparison angular vibration calibration approach based on an IFOG. The operation principle of the closed-loop IFOG is introduced, and its error model in angle measurement is derived. Furthermore, the measurement uncertainty components in angular vibration calibration are analyzed by comparing with primary angular vibration calibration. By using a standard angular vibration system in the Nanjing Institute of Measurement and Testing Technology, China, the angular vibration calibration capability of the IFOG is evaluated within frequency range of 1–200 Hz. In addition, the traceability of this proposed calibration approach is also discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.-J. von Martens, Invited article: expanded and improved traceability of vibration measurements by laser interferometry, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 84 (2013) 181.
S. Levy and R.R. Bouche, Calibration of vibration pickups by the reciprocity method, J. Res. Natl. Bureau Stand., 57 (1956) 227–243.
N. Garg and B. Chauhan, Measurement Uncertainty in Vibration Calibration in Frequency Range of 5 Hz to 10 kHz, MAPAN, 35 (2020) 397–405.
A. Täubner and H.-J. von Martens, Measurement of angular accelerations, angular velocities and rotation angles by grating interferometry, Measurement, 24 (1998) 21–32.
W.-S. Cheung and S.-M. Park, Progress in development of primary angular vibration calibration systems, in TC3, TC16 & TC22 IMEKO international conference, (2007).
W. Kokuyama, T. Watanabe, H. Nozato and A. Ota, Angular velocity calibration system with a self-calibratable rotary encoder, Measurement, 82 (2016) 246–253.
L. Zhang and J. Peng, Calibrating angular transducer using sinusoidal and shock excitation, in AIP conference proceedings, American Institute of Physics, (2012) 176–180.
ISO 16063-15, Methods for the calibration of vibration and shock transducers-part 15: primary calibration by laser interferometry, (2006).
V. Vali and R. Shorthill, Fiber ring interferometer, Appl. Opt., 15 (1976) 1099–1100.
P. Lu, Z. Wang, R. Luo, D. Zhao, C. Peng and Z. Li, Polarization nonreciprocity suppression of dual-polarization fiber-optic gyroscope under temperature variation, Opt. Lett., 40 (2015) 1826–1829.
S. W. Lloyd, M. J. Digonnet, and S. Fan, Near shot-noise limited performance of an open loop laser-driven interferometric fiber optic gyroscope, in 21st International Conference on Optical Fiber Sensors, International Society for Optics and Photonics, (2011) 7753A7753.
J.M. Mackintosh and B. Culshaw, Analysis and observation of coupling ratio dependence of Rayleigh backscattering noise in a fiber optic gyroscope, J. Lightw. Technol., 7 (1989) 1323–1328.
K. Böhm, K. Petermann and E. Weidel, Sensitivity of a fiber-optic gyroscope to environmental magnetic fields, Opt. Lett., 7 (1982) 180–182.
J. Mou, T. Huang, G. Ying, S. Che and X. Shu, Scale factor calibration and dynamic angle measurement method based on self-collimator and fiber optic gyroscope, Opt. Fiber Technol., 52 (2019) 101945.
W. He, B. Tang and S. Jia, Design, simulation and development of a broadband electromagnetic angular vibrator, Int. J. Appl. Electromag. Mech., 57 (2018) 295–307.
K.-N. Joo, J.D. Ellis, E.S. Buice, J.W. Spronck and R.H.M. Schmidt, High resolution heterodyne interferometer without detectable periodic nonlinearity, Opt. Express, 18 (2010) 1159–1165.
H. Yan, H.-Z. Duan, L.-T. Li, Y.-R. Liang, J. Luo and H.-C. Yeh, A dual-heterodyne laser interferometer for simultaneous measurement of linear and angular displacements, Rev. Sci. Instrum., 86 (2015) 123102.
Acknowledgements
We thank the National Institute of Metrology, China, and the Nanjing Institute of Measurement and Testing Technology, China, for their help in experiments.
Funding
This research was funded by National Key Research and Development Program of China Grant No. 2017YFF0204901 and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China Grant No. Y19F050039.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Mou, J., Miao, L. et al. A Comparison Angular Vibration Calibration Approach Based on the IFOG. MAPAN 36, 607–613 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-021-00464-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12647-021-00464-y