Abstract
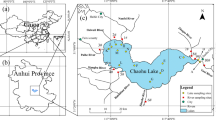
Increasing cases of lake eutrophication globally have raised concerns among stakeholders, and particularly in China. Evaluating the causes of eutrophication in waterways is essential for effective pollution prevention and control. Xiao Xingkai Lake is part of and connected to Xingkai (Khanka) Lake, a boundary lake between China and Russia. In this study, we investigated the spatio-temporal variabilities in water quality (i.e., dissolved oxygen (DO), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), chemical oxygen demand (CODMn) and ammonium-nitrogen (NH +4 -N)) in Xiao Xingkai Lake, from 2012 to 2014, after which a Trophic Level Index was used to evaluate trophic status, in addition to the factors influencing water quality variation in the lake. The DO, TN, TP, CODMn and NH +4 -N concentrations were 0.44–15.57, 0.16–5.11, 0.01–0.45, 0.16–18.31, and 0.19–0.78 mg/L, respectively. Compared to the Environmental Quality Standards for surface water (GB 3838-2002) in China, the lake transitioned to an oligotrophic status in 2013 and 2014 from a mesotrophic status in 2012, TN and TP concentrations were the key factors influencing water quality of Xiao Xingkai Lake. Non-parametric test results showed that sampling time and sites had significant effects on water quality. Water quality was worse in summer and in tourism and aquaculture areas, followed by agricultural drainage areas. Furthermore, lake water trophic status fluctuated between medium eutrophic and light eutrophic status from September 2012 to September 2014, and was negatively correlated with water level. Water quality in tourism and aquaculture sites were medium eutrophic, while in agricultural areas were light eutrophic. According to the results, high water-level fluctuations and anthropogenic activities were the key factor driving variability in physicochemical parameters associated with water quality in Xiao Xingkai Lake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abell J M, Özkundakci D, Hamilton D P et al., 2020. Restoring shallow lakes impaired by eutrophication: approaches, outcomes, and challenges. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology,. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1854564
Bhagowati B, Ahamad K U, 2019. A review on lake eutrophication dynamics and recent developments in lake modeling. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology, 19(1): 155–166. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecohyd.2018.03.002
Bhattrai B D, Kwak S, Choi K et al., 2017. Long-term changes of physicochemical water quality in Lake Youngrang, Korea. Korean Journal of Ecology and Environment, 50(1): 169–185. doi: https://doi.org/10.11614/KSL.2017.50.1.169
Bremner J M, 1998. Nitrogen-total. In: Bartels J M (ed). Methods of Soil Analysis Part 3: Chemical Methods. Madison: ACSESS, 1085–1117.
Butchart S H M, Walpole M, Collen B et al., 2010. Global biodiversity: indicators of recent declines. Science, 328(5982): 1164–1168. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1187512
Bouwman A F, Beusen A H, Griffioen J et al., 2013. Global trends and uncertainties in terrestrial denitrification and N2O emissions. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 368(1621): 20130112. doi: https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2013.0112
Carlson R E, 1977. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 22(2): 361–369. doi: https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1977.22.2.0361
Carpenter S R, Stanley E H, Vander Zanden M J, 2011. State of the world’s freshwater ecosystems: physical, chemical, and biological changes. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 36: 75–99. doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-environ-021810-094524
Chang C, Sun D M, Feng P et al., 2017. Impacts of nonpoint source pollution on water quality in the Yuqiao Reservoir. Environmental Engineering Science, 34(6): 418–432. doi: https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2016.0124
Chique C, Potito A P, Molloy K et al., 2018. Tracking recent human impacts on a nutrient sensitive Irish lake: integrating landscape to water linkages. Hydrobiologia, 807(1): 207–231. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3395-9
Crosa G, Froebrich J, Nikolayenko V et al., 2006. Spatial and seasonal variations in the water quality of the Amu Darya River (Central Asia). Water Research, 40(11): 2237–2245. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.04.004
Heino J, Alahuhta J, Bini L M et al., 2021. Lakes in the era of global change: moving beyond single-lake thinking in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem services. Biological Reviews, 96(1): 89–106. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12647
Imani S, Niksokhan M H, Jamshidi S et al., 2017. Discharge permit market and farm management nexus: an approach for eutrophication control in small basins with low-income farmers. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 189: 346. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6066-4
Jablońska E, Wisniewska M, Marcinkowski P et al., 2020. Catchment-scale analysis reveals high cost-effectiveness of wetland buffer zones as a remedy to non-point nutrient pollution in north-eastern Poland. Water, 12(3): 629. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030629
Jin Xiangcan, Tu Qingying, 1990. Code for Investigation of Lake Eutrophication. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. (in Chinese)
Jones J I, Murphy J F, Anthony S G et al., 2017. Do agri-environment schemes result in improved water quality? Journal of Applied Ecology, 54(2): 537–546. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.12780
Kast J B, Apostel A M, Kalcic M M et al., 2021. Source contribution to phosphorus loads from the Maumee River watershed to Lake Erie. Journal of Environmental Management, 279: 111803. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111803
Li B, Yang G S, Wan R R et al., 2017b. Dynamic water quality evaluation based on fuzzy matter-element model and functional data analysis, a case study in Poyang Lake. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(23): 19138–19148. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9371-0
Li Sijia, Song Kaishan, Chen Zhiwen et al., 2015. Absorption characteristics of particulates and CDOM in spring in the Lake Xingkai. Journal of Lake Sciences, 27(5): 941–952. (in Chinese). doi: https://doi.org/10.18307/2015.0522
Li S Y, Bush R T, Mao R et al., 2017a. Extreme drought causes distinct water acidification and eutrophication in the Lower Lakes (Lakes Alexandrina and Albert), Australia. Journal of Hydrology, 544: 133–146. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.11.015
Li T, Chu C L, Zhang Y N et al., 2017c. Contrasting eutrophication risks and countermeasures in different water bodies: assessments to support targeted watershed management. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(7): 695. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14070695
Lin S S, Shen S L, Zhou A N et al., 2020. Approach based on TOPSIS and Monte Carlo simulation methods to evaluate lake eutrophication levels. Water Research, 187: 116437. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116437
Liu X, Teubner K, Chen Y W, 2016. Water quality characteristics of Poyang Lake, China, in response to changes in the water level. Hydrology Research, 47(S1): 238–248. doi: https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2016.209
Long H, Shen J, 2017. Sandy beach ridges from Xingkai Lake (NE Asia): timing and response to palaeoclimate. Quaternary International, 430: 21–31. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2015.11.009
Mammides C, 2020. A global assessment of the human pressure on the world’s lakes. Global Environmental Change, 63: 102084. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2020.102084
Mueller H, Hamilton D, Doole G et al., 2019. Economic and ecosystem costs and benefits of alternative land use and management scenarios in the Lake Rotorua, New Zealand, catchment. Global Environmental Change, 54: 102–112. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2018.10.013
Ouyang Y, Nkedi-Kizza P, Wu Q T et al., 2006. Assessment of seasonal variations in surface water quality. Water Research, 40(20): 3800–3810. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.08.030
Sarkar S K, Saha M, Takada H et al., 2007. Water quality management in the lower stretch of the river Ganges, east coast of India: an approach through environmental education. Journal of Cleaner Production, 15(16): 1559–1567. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2006.07.030
Sinha E, Michalak A M, Balaji V, 2017. Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science, 357(6349): 405–408. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aan2409
Srinivas R, Singh A P, Dhadse K et al., 2020. An evidence based integrated watershed modelling system to assess the impact of non-point source pollution in the riverine ecosystem. Journal of Cleaner Production, 246: 118963. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118963
SEP (State Environmental Protection Administration), GAQSIQ (General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’ s Republic of China), 2002. GB 3838-2002 Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Beijing: China Environmental Press. (in Chinese)
Sun B, Zhang L X, Yang L Z et al., 2012. Agricultural non-point source pollution in China: causes and mitigation measures. AMBIO, 41(4): 370–379. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-012-0249-6
Sundaray S K, Panda U C, Nayak B B et al., 2006. Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of the Mahanadi river-estuarine system (India)-a case study. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28(4): 317–330. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-005-9001-5
Tao Shengli, Fang Jingyun, Ma Suhui et al., 2020. Changes in China’s lakes: climate and human impacts. National Science Review, 7(1): 132–140. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwz103
Tong Y D, Zhang W, Wang X J et al., 2017. Decline in Chinese lake phosphorus concentration accompanied by shift in sources since 2006. Nature Geoscience, 10(7): 507–511. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2967
Vadeboncoeur Y, McIntyre P B, Vander Zanden M J, 2011. Borders of biodiversity: life at the edge of the world’s large lakes. Bioscience, 61(7): 526–537. doi: https://doi.org/10.1525/bio.2011.61.7.7
Wang J J, Zhao Q H, Pang Y et al., 2017. Research on nutrient pollution load in Lake Taihu, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(21): 17829–17838. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9384-8
Wei Fusheng, 2002. Methods for Monitoring and Analysis of Water and Wastewater. 4th ed. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. (in Chinese)
Wu D, Yan H Y, Shang M S et al., 2017a. Water eutrophication evaluation based on semi-supervised classification: a case study in Three Gorges Reservoir. Ecological Indicators, 81: 362–372. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.06.004
Wu J H, Xue C Y, Tian R et al., 2017b. Lake water quality assessment: a case study of Shahu Lake in the semiarid loess area of northwest China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(5): 232. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6516-x
Xu Y G, Li A J, Qin J H et al., 2017. Seasonal patterns of water quality and phytoplankton dynamics in surface waters in Guangzhou and Foshan, China. Science of the Total Environment, 590–591: 361–369. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.032
Yazdi J, Moridi A, 2017. Interactive reservoir-watershed modeling framework for integrated water quality management. Water Resources Management, 31(7): 2105–2125. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1627-4
Yu Shuling, Li Xiujun, Li Xiaoyu et al., 2013. Evaluation of Water Quality of Xiaoxingkai Lake. Wetland Science, 11(4): 466–469. (in Chinese)
Yu Shuling. 2014. The Research on Phosphorus Release Characteristics of Surficial Sediment and Its Effects on Eutrophication in Lake XiaoXingkai, China. Changchun: Northeast Institute of geography and Agroecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Zhang Jitao, Lu Xinrui, Yang Yanli, Dr. Qin Yan and Dr. Song Hongli for help with sampling.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation item
Under the auspices of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41771120, 41771550), the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2012CB956100)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, S., Li, X., Wen, B. et al. Characterization of Water Quality in Xiao Xingkai Lake: Implications for Trophic Status and Management. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 31, 558–570 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-021-1199-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-021-1199-3