Abstract
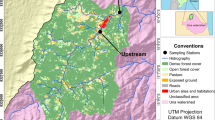
Sewage discharges constitute severe stress in freshwater ecosystems. The Ramalhoso River belongs to the Tagus River watershed and was chosen for a pilot study on the impact of wastewaters discharges in a freshwater ecosystem and its ability for self-depuration. Twelve water samples were collected along the river and were georeferenced. The first point is located upstream of the first discharge point, the second one corresponding to the discharge flow, and all the other samples located downstream of secondary inflows at approximately equal distances. Three sampling campaigns were conducted during the rainy winter (January), the intermediate conditions (March), and the dry season (June). The following chemical parameters were analyzed: biochemical oxygen demand for 5 days (BOD5), dissolved oxygen concentration (DO), total phosphorus (Ptotal), total nitrogen (Ntotal), pH, temperature, total suspended solids (TSS), microbiological parameters (MP), and flow determination. Dissolved oxygen, BOD5, and TSS were used as indicators of environmental pollution. A coupled hydrodynamic and water dispersion model simulated different pollution scenarios using the QUAL2kw software to construct a water quality model. The simulation results are consistent with field observations and demonstrate that the model has been correctly calibrated, allowing feasibility studies of different treatment schemes and the development of specific monitoring activities.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albuquerque, M. T. D., Antunes, I. M. H. R., Oliveira, N. P., & Pelletier, G. (2019). Impact of sewage effluent discharges prediction using QUAL2Kw in a sensitive protected area: Portugal. SN Applied Sciences, 1, 1167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1095-y.
Antunes, I. M. H. R., Albuquerque, M. T. D., Oliveira, S. F., & Sánz, G. L. (2018). Predictive scenarios for surface water quality simulation—A watershed case study. CATENA, 170, 283–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.06.021.
Aubertheau, E., Stalder, T., Mondamert, L., Ploy, M. C., Dagot, C., & Labanowski, J. (2017). Impact of wastewater treatment plant discharge on the contamination of river biofilms by pharmaceuticals and antibiotic resistance. Science of the Total Environment, 579, 1387–1398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.136.
Delhomme, O., Rib, E., & Millet, M. (2008). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons analyzed in rainwater collected on two sites in East France (Strasbourg and Erstein). Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon, France, 28, 4–5.
DiGiano, F., & Grayman, W. M. (2014). Can we better protect vulnerable water supplies? Journal of American Water Works Association, 106, 28. https://doi.org/10.5942/jawwa.2014.106.0067.
European Union. (1991). Council Directive 1991/271/EEC on Urban waste water treatment. Official Journal of the European Union, 1991, 135/40–135/52.
Fan, C., Ko, C. H., & Wang, W. S. (2009). An innovative modeling approach using Qual2K and HEC-RAS integration to assess the impact of tidal effect on river water quality simulation. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(5), 1824–1832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.11.011.
Farhadian, M., Bozorg-Haddad, O., Pazoki, M., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2019). Minimal adverse impact of discharging polluted effluents to rivers with selective locations. Sustainable Cities and Society, 46, 101394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2018.12.022.
Gonzalo, C., & Camargo, J. A. (2013). The impact of an industrial effluent on the water quality, submersed macrophytes and benthic macroinvertebrates in a dammed river of central Spain. Chemosphere, 93(6), 1117–1124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.06.032.
Grabiç, J., Bezdan, A., Benka, P., & Salvai, A. (2011). Spreading and transformation of nutrients in the Reacg of the Becej-Bogojeco Canal, Serbia. Carparth. Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, 6(1), 277–284.
Henderson-Sellers, B. (1991). Water quality modeling: decision support techniques for lakes and reservoirs. CRC Press, London, vol 4 (p. 344). Boston: CRC Press.
Hilario Garcia, A. L., Matzenbacher, C. A., Santos, M. S., Prado, L., Picada, J. N., Premoli, S. M., Correa, D. S., Niekraszewicz, L., Dias, J. F., Grivicich, I., & da Silva, J. (2017). Genotoxicity induced by water and sediment samples from a river under the influence of brewery effluent. Chemosphere, 169, 239–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.081.
Jeznach, L. C., Jones, C., Matthews, T., Tobiason, J. E., & Ahlfeld, D. P. (2016). A framework for modeling contaminant impacts on reservoir water quality. Journal of Hydrology, 537, 322–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/jhydrol.2016.03.041.
Khwairakpam, E., Khosa, R., Gosain, A., et al. (2019). Monitoring and modelling water quality of Loktak Lake catchment. SN Applied Sciences, 1, 491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0517-1.
Li, D., Sharp, J. O., & Drewes, J. E. (2016). Influence of wastewater discharge on the metabolic potential of the microbiological community in river sediments. Microbial Ecology, 71, 78–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-015-0680-x.
Lin, C. E., Kao, C. M., Jou, C. J., Lai, Y. C., Wu, C. Y., & Liang, S. H. (2010). Preliminary identification of watershed management strategies for the Houjing River in Taiwan. Water Science and Technology, 62(7), 1667–1675. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2010.460.
Pelletier, G. J., Chapra, S. C., & Tao, H. (2006). QUAL2 Kw—A framework for modelling water quality in streams and rivers using a genetic algorithm for calibration. Environmental Modelling and Software, 21(3), 419–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2005.07.002.
Sharma, D., & Kansal, A. (2013). Assessment of river quality models: A review. Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 12, 285–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-012-9285.
Sousa, J. C. G., Ribeiro, A. R., Barbosa, M. O., Pereira, F. R., & Silva, A. M. T. (2018). A review on environmental monitoring of water organic pollutants identified by EU guidelines. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 344, 146–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.09.058.
Tiedeken, E. J., Tahar, A., McHugh, B., & Rowan, N. J. (2017). Monitoring, sources, receptors, and control measures for three European Union watch list substances of emerging concern in receiving waters–A 20-year systematic review. Science of the Total Environment, 574, 1140–1163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.084.
Tillaart, S. P. M., Booij, M. J., & Krol, M. S. (2013). Impact of uncertainties in discharge determination on the parameter estimation and performance of a hydrological model. Journal of Hydrology, 44(3), 454–466. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2012.147.
Vystavna, Y., Frkova, Z., Celle-Jeanton, H., Diadin, D., Huneau, F., Steinmann, M., Crini, N., & Loup, C. (2018). Priority substances and emerging pollutants in urban rivers in Ukraine: occurrence, fluxes and loading to transboundary European Union watersheds. Science of the Total Environment, 637–638, 1358–1362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.095.
Whitehead, P. G., Futter, M. N., Comber, S., Butterfield, D., Pope, L., Willows, R., & Burgess, C. (2015). Modelling impacts of seasonal wastewater treatment plant effluent permits and biosolid substitution for phosphorus management in catchments and river systems. Journal of Hydrology, 46(3), 313–324. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2014.100.
Xiao, S., Hu, S., Zhang, Y., Zhao, X., & Pan, W. (2018). Influence of sewage treatment plant effluent discharge into multipurpose river on its water quality: A quantitative health risk assessment of Cryptosporidium and Giardia. Environmental Pollution, 233, 797–805.
Xiaobo, F., Jianying, Z., Yingxu, C., & Xiangyang, X. (2008). QUAL2K model used in the water quality assessment of Qiantang River, China. Water Environment Research, 80(11), 2125–2133.
Zafar, S., Kahan, A., Ullah, H., Khan, M. S., Khan, I., Hammed, A., Rehman, S. U., & Yasmeen, G. (2017). Risk assessment of Giardia from a full scale MBR sewage treatment plant caused by membrane integrity failure. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 30, 252–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.09.033.
Funding
This research was funded by Águas do Centro Enterprise and by the Institute of Earth Sciences (ICT), under contracts UID/GEO/04683/2013 with FCT (Portuguese Science and Technology Foundation).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Gregory Pelletier; Data curation: Pedro Almeida Teresa Albuquerque and Ana Ferreira; Formal analysis: Pedro Almeida, Teresa Albuquerque and Gregory Pelletier; Funding acquisition: Teresa Albuquerque and Margarida Antunes; Investigation: Pedro Almeida, Teresa Albuquerque, Ana Ferreira, and Margarida Antunes; Methodology: Teresa Albuquerque, Margarida Antunes, and Gregory Pelletier; Software: Gregory Pelletier; Supervision, Teresa Albuquerque, and Ana Ferreira; Validation: Pedro Almeida; Visualization: Pedro Almeida; Writing—original draft: Teresa Albuquerque; Writing—review and editing: Pedro Almeida Margarida Antunes and Ana Ferreira
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almeida, P., Albuquerque, T., Antunes, M. et al. Effects of Wastewater Treatment Plant’s Discharges on a Freshwater Ecosystem—a Case Study on the Ramalhoso River (Portugal). Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 206 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05131-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05131-1