Abstract
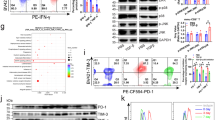
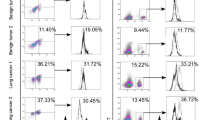
Destabilizing and reprogramming regulatory T (Treg) cells have become a potential strategy to treat tumor. Mounting evidence indicates that the transcription factor Helios is required for the stable differentiation of Treg lineage. Hence, we investigated whether Helios suppression could be a potential treatment option for pancreatic cancer patients. We found that Helios+ cells were predominantly in Foxp3+ Treg cells. By contrast, Foxp3+ Treg cells can be Helios+ or Helios−, but the level of Foxp3 expression was significantly higher in Helios+Foxp3+ Treg cells than in Helios−Foxp3+ Treg cells. Resected pancreatic tumors were highly enriched with both Helios+Foxp3+ Treg cells and Helios−Foxp3+ Treg cells. Also, the proportion of Helios+ cells in total Foxp3+ Treg cells was significantly higher in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of patients than in PBMCs of healthy controls and further increased in patient tumors. Using shRNA, we knocked down Helios expression without significant downregulation of Foxp3. After Helios knockdown, CD4+CD25+CD127− Treg cells presented significantly lower levels of TGF-β secretion, lower levels of IL-10 secretion, and higher levels of IFN-γ secretion. In addition, Helios shRNA-transfected CD4+CD25+CD127− Treg cells presented lower capacity to inhibit CD4+CD25−CD127+ T conventional cell proliferation than control shRNA-transfected CD4+CD25+CD127− Treg cells. Of note, CD4+CD25+CD127− Treg cells from pancreatic cancer patients demonstrated higher TGF-β expression and higher suppression capacity than the cells from healthy controls. Overall, these results suggest that in pancreatic cancer patients, Helios may serve as a candidate to suppress Treg function, which could be used as a target to treat pancreatic cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shevach EM, Thornton AM. tTregs, pTregs, and iTregs: similarities and differences. Immunol Rev. 2014;259:88–102.
Najafi M, Farhood B, Mortezaee K. Contribution of regulatory T cells to cancer: a review. J Cell Physiol. 2019.
Liu W, Putnam AL, Xu-yu Z, Szot GL, Lee MR, Zhu S, et al. CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3 and suppressive function of human CD4 + T reg cells. J Exp Med. 2006.
Schmidt A, Oberle N, Krammer PH. Molecular mechanisms oftreg-mediatedt cell suppression. Front Immunol. 2012.
Kelley CM, Ikeda T, Koipally J, Avitahl N, Wu L, Georgopoulos K, et al. Helios, a novel dimerization partner of Ikaros expressed in the earliest hematopoietic progenitors. Curr Biol. 1998.
Hahm K, Cobb BS, McCarty AS, Brown KE, Klug CA, Lee R, et al. Helios, a T cell-restricted Ikaros family member that quantitatively associates with Ikaros at centromeric heterochromatin. Genes Dev. 1998.
Feng Y, Arvey A, Chinen T, Van Der Veeken J, Gasteiger G, Rudensky AY. Control of the inheritance of regulatory T cell identity by a cis element in the foxp3 locus. Cell. 2014.
Kim HJ, Barnitz RA, Kreslavsky T, Brown FD, Moffett H, Lemieux ME, et al. Stable inhibitory activity of regulatory T cells requires the transcription factor Helios. Science (80- ). 2015.
Getnet D, Grosso JF, Goldberg MV, Harris TJ, Yen HR, Bruno TC, et al. A role for the transcription factor Helios in human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Mol Immunol. 2010.
Thornton AM, Korty PE, Tran DQ, Wohlfert EA, Murray PE, Belkaid Y, et al. Expression of Helios, an Ikaros transcription factor family member, differentiates thymic-derived from peripherally induced Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. J Immunol NIH Public Access. 2010;184:3433–41.
Cai Q, Dierich A, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Chan S, Kastner P. Helios deficiency has minimal impact on T cell development and function. J Immunol Am Assoc Immunol. 2009;183:2303–11.
Zabransky DJ, Nirschl CJ, Durham NM, Park BV, Ceccato CM, Bruno TC, et al. Phenotypic and functional properties of Helios+regulatory T cells. PLoS One. 2012.
Elkord E, Samid MA Al, Chaudhary B. Helios, and not FoxP3. Is the marker of activated Tregs expressing GARP/LAP. Oncotarget. 2015.
Nakagawa H, Sido JM, Reyes EE, Kiers V, Cantor H, Kim H-J. Instability of Helios-deficient Tregs is associated with conversion to a T-effector phenotype and enhanced antitumor immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2016.
Thornton AM, Shevach EM. Tregs. Helios and tumor immunity: the sun has not yet risen. Transl Cancer Res. 2016.
Munn DH, Sharma MD, Johnson TS. Treg destabilization and reprogramming: implications for cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2018.
Simonetta F, Bourgeois C. CD4+FOXP3+ regulatory T-cell subsets in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Front Immunol. 2013.
Deng G. Tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells: origins and features. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2018.
Wang X, Lang M, Zhao T, Feng X, Zheng C, Huang C, et al. Cancer-FOXP3 directly activated CCL5 to recruit FOXP3 + Treg cells in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 2017.
Funding
This study was supported by the Jiangsu Provincial Commission of Health and Family Planning (QNRC2016200); Project of High Level Talents (333 Project) in Jiangsu Province (20161110615); Jiangsu Province Six-One Project (LGY2017012); and Funding of Innovation Team and Elite Talent Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Min-Feng Liu: Conceptualization; Data curation; Formal analysis; Writing, original draft; Writing, review and editing. Cheng Jin: Conceptualization; Data curation; Formal analysis; Writing, original draft; Writing, review and editing. Tao Wu: Conceptualization; Data curation; Formal analysis. En-Hong Chen: Conceptualization; Data curation; Formal analysis. Minxue Lu: Conceptualization; Data curation; Formal analysis; Supervision; Writing, review and editing. Huan-Long Qin: Conceptualization; Data curation; Formal analysis; Supervision; Writing, review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, MF., Jin, C., Wu, T. et al. Helios serves as a suppression marker to reduce regulatory T cell function in pancreatic cancer patients. Immunol Res 69, 275–284 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-021-09200-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-021-09200-9