Abstract
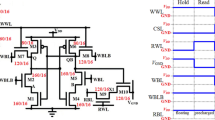
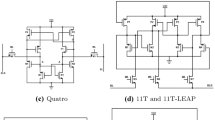
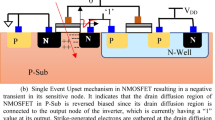
This work evaluates the Soft Error sensitivity of the complete SRAM architecture using the 16 nm Bulk CMOS technology model. The paper investigated the fault propagation in cells and bitlines during the Hold, Read, Write operations, and the half-selection situation. The 6T, 8T, 9T, 8TSER, and DICE SRAM cells are compared not only about the radiation effects but also observing the timing, power, and static noise margin outcomes. DICE cell presents the highest robustness to the radiation effects. The 8T-SER presented the best stability results. The half-selection situation shows the potential to increase the cell sensitivity by \(\approx\) 50 \(\%\) compared to the Hold perspective.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alorda B, Torrens G, Bota S, Segura J (2011) 8T vs. 6T SRAM cell radiation robustness: A comparative analysis. Proc Microelectron Reliab. 51(2):350–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2010.09.002
Artola L, Hubert G, Alioto M (2014) Comparative soft error evaluation of layout cells in finFET technology. Proc Microelectron Reliab 54(9–10):2300–2305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2014.07.109
Asai S (2019) VLSI Design and Test for Systems Dependability. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-56594-9
ASU. Predictive technology model. Accessible in: http://ptm.asu.edu, last access: 5 Nov 2019
Calin T, Nicolaidis M, Velazco R (1996) Upset hardened memory design for submicron CMOS technology. Proc IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 43(6):2874–2878. https://doi.org/10.1109/23.556880
Dodd PE, Massengill LW (2003) Basic mechanisms and modeling of single-event upset in digital microelectronics. Proc IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 50(3):583–602. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNS.2003.813129
Hubert G, Artola L, Regis D (2015) Impact of scaling on the soft error sensitivity of bulk, FDSOI and finFET technologies due to atmospheric radiation. Proc Integration 50:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vlsi.2015.01.003
Kim TT, Lee ZC, Do AT (2018) A 32 kb 9T near-threshold SRAM with enhanced read ability at ultra-low voltage operation. Proc Solid State Electron 139:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sse.2017.10.002
Manabe S, Watanabe Y, Liao W, Hashimoto M, Abe S-I (2019) Estimation of muon-induced SEU rates for 65-nm bulk and UTBB-SOI SRAMs. Proc IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 66(7):1398-1403 https://doi.org/10.1109/TNS.2019.2916191
Marques CM, Meinhardt C, Butzen PF (2020) Soft error reliability of SRAM cells during the three operation states. Proc IEEE Latin-American Test Symposium, p 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/LATS49555.2020.9093684
Messenger GC (1982) Collection of charge on junction nodes from ion tracks. Proc IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 29(6):2024–2031. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNS.1982.4336490
NGSPICE. Open source spice simulator. Accessible in: http://ngspice.sourceforge.net/index.html., last access: 5 Nov 2019
Nicolaidis M (2005) Design for soft error mitigation. Proc IEEE Trans Device Mater Reliab 5(3):405–418. https://doi.org/10.1109/TDMR.2005.855790
Noh J et al (2015) Study of neutron soft error rate (SER) sensitivity: Investigation of upset mechanisms by comparative simulation of finFET and planar MOSFET SRAMs. Proc IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 62(4):1642–1649. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNS.2015.2450997
Pavlov A, Sachdev M (2008) CMOS SRAM circuit design and parametric test in nano-scaled technologies: process-aware SRAM design and test, volume 40. Springer Science & Business Media: ISBN 978-1-4020-8363-1
Rajendran A, Shiyanovskii Y, Wolff F, Papachristou C (2011) Noise margin, critical charge and power-delay tradeoffs for SRAM design. Proc IEEE Int On-Line Testing Symposium, p 145–150. https://doi.org/10.1109/IOLTS.2011.5993828
Rajput AS, Pattanaik M, Tiwari RK (2018) Estimation of static noise margin by butterfly method using curve-fitting technique. Journal of Active and Passive Electronic Devices 13(1):1–9
Sajit AS, Turi MA (2017) SEU tolerance of finFET 6T SRAM, 8T SRAM and DICE memory cells. In Proc IEEE Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), p 1–5. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/CCWC.2017.7868477
Samandari-Rad J, Hughey R (2016) Power/energy minimization techniques for variability-aware high-performance 16-nm 6t-SRAM. Proc IEEE Access 4:594–613. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2521385
Seevinck E, List FJ, Lohstroh J (1987) Static-noise margin analysis of MOS SRAM cells. Proc IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 22(5):748–754. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSSC.1987.1052809
Shah JS, Nairn D, Sachdev M (2015) A 32 kb macro with 8T soft error robust, SRAM cell in 65-nm CMOS. Proc IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 62(3):1367-1374. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNS.2015.2429589
Uznanski S, Gasiot G, Roche P, Tavernier C, Autran J-L (2010) Single event upset and multiple cell upset modeling in commercial bulk 65-nm CMOS SRAMs and flip-flops. Proc IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 57(4):1876–1883. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNS.2010.2051039
Vargas F, Nicolaidis M (1994) SEU-tolerant SRAM design based on current monitoring. In Proc IEEE Int Symposium on Fault-Tolerant Computing, p 106–115. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/FTCS.1994.315652
Acknowledgments
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001 and by the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technology Development (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Responsible Editor: L. M. Bolzani-Pöhls
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marques, C.M., Meinhardt, C. & Butzen, P.F. Soft Errors Sensitivity of SRAM Cells in Hold, Write, Read and Half-Selected Conditions. J Electron Test 37, 263–270 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-021-05944-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-021-05944-2