Abstract
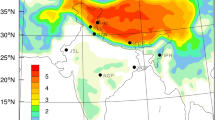
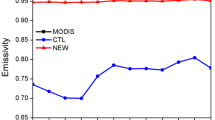
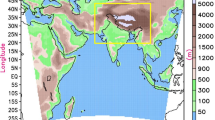
Using a balance model of the snow layer, we estimate the concentration of black carbon (BC) in the snow; then, with the help of radiative transfer model SNICAR, we calculate the snow albedo and radiative forcing (RF) from snow darkening with BC. Data from an ensemble simulation with INMCM5, the 5th version of the climate model of Marchuk Institute of Numerical Mathematics, Russian Academy of Sciences for the period 1998–2002 are used as input, which include snow both on land and on sea ice. The regionally averaged results are compared with other model data and field measurements.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. G. Flanner, C. S. Zender, P. G. Hess, N. M. Mahowald, T. H. Painter, V. Ramanathan, and P. J. Rasch, “Springtime warming and reduced snow cover from carbonaceous particles,” Atmos. Chem. Phys. 9, 2481–2497 (2009).
K. M. Keegan, M. R. Albert, J. R. McConnell, and I. Baker, “Climate change and forest fires synergistically drive widespread melt events of the Greenland ice sheet,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 7964–7967 (2014).
C. Dang, S. G. Warren, Q. Fu, S. J. Doherty, M. Sturm, and J. Su, “Measurements of light-absorbing particles in snow across the Arctic, North America, and China: Effects on surface albedo,” J. Geophys. Res. 122, 10149–10168 (2017).
M. G. Flanner, C. S. Zender, J. T. Randerson, and P. J. Rasch, “Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow,” J. Geophys. Res. 112, D11202 (2007).
C. Jiao, M. G. Flanner, Y. Balkanski, S. E. Bauer, N. Bellouin, T. K. Berntsen, H. Bian, K. S. Carslaw, M. Chin, N. De Luca, T. Diehl, S. J. Ghan, T. Iversen, A. Kirkevåg, D. Koch, X. Liu, G. W. Mann, J. E. Penner, G. Pitari, M. Schulz, Ø. Seland, R. B. Skeie, S. D. Steenrod, P. Stier, T. Takemura, K. Tsigaridis, T. van Noije, Y. Yun, and K. Zhang, “An AeroCom assessment of black carbon in Arctic snow and sea ice,” Atmos. Chem. Phys. 14, 2399–2417 (2014).
C. Textor, M. Schulz, S. Guibert, S. Kinne, Y. Balkanski, S. Bauer, T. Berntsen, T. Berglen, O. Boucher, M. Chin, F. Dentener, T. Diehl, R. Easter, H. Feichter, D. Fillmore, S. Ghan, P. Ginoux, S. Gong, A. Grini, J. Hendricks, L. Horowitz, P. Huang, I. Isaksen, I. Iversen, S. Kloster, D. Koch, A. Kirkevåg, J. E. Kristjansson, M. Krol, A. Lauer, J. F. Lamarque, X. Liu, V. Montanaro, G. Myhre, J. Penner, G. Pitari, S. Reddy, Ø. Seland, P. Stier, T. Takemura, and X. Tie, “Analysis and quantification of the diversities of aerosol life cycles within AeroCom,” Atmos. Chem. Phys. 6, 1777–1813 (2006).
E. M. Volodin, E. V. Mortikov, S. V. Kostrykin, V. Ya. Galin, V. N. Lykossov, A. S. Gritsun, N. A. Diansky, A. V. Gusev, and N. G. Yakovlev, “Simulation of the present-day climate with the climate model INMC-M5,” Clim. Dyn. 49, 3715–3734 (2017).
H. Conway, A. Gades, and C. F. Raymond, “Albedo of dirty snow during conditions of melt,” Water Resour. Res. 32, 1713–1718 (1996).
E. M. Volodin and S. V. Kostrykin, “The aerosol module in the INM RAS climate model,” Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 41 (8), 519–528 (2016).
R. M. Hoesly, S. J. Smith, L. Feng, Z. Klimont, G. Janssens-Maenhout, T. Pitkanen, J. J. Seibert, L. Vu, R. J. Andres, R. M. Bolt, T. C. Bond, L. Dawidowski, N. Kholod, J.-I. Kurokawa, M. Li, L. Liu, Z. Lu, M. C. P. Moura, P. R. O’Rourke, and Q. Zhang, “Historical (1750–2014) anthropogenic emissions of reactive gases and aerosols from the Community Emissions Data System (CEDS),” Geosci. Model Dev. 11, 369–408 (2018).
M. J. E. van Marle, S. Kloster, B. I. Magi, J. R. Marlon, A.-L. Daniau, R. D. Field, A. Arneth, M. Forrest, S. Hantson, N. M. Kehrwald, W. Knorr, G. Lasslop, F. Li, S. Mangeon, C. Yue, J. W. Kaiser, and G. R. van der Werf, “Historic global biomass burning emissions for CMIP6 (BB4CMIP) based on merging satellite observations with proxies and fire models (1750–2015),” Geosci. Model Dev. 10, 3329–3357 (2017).
S. M. Skiles, M. G. Flanner, J. M. Cook, M. Dumont, and T. H. Painter, “Radiative forcing by light-absorbing particles in snow,” Nat. Clim. Change 8, 964–971 (2018).
Funding
This work was carried out at the Marchuk Institute of Numerical Mathematics, Russian Academy of Sciences, with support from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, grant no. 18-05-61083 (assessment of RF from BC in snow), and the Russian Science Foundation, grant no. 20-17-00190 (carrying out numerical experiments with the INMCM5 model).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chernenkov, A.Y., Kostrykin, S.V. Estimation of Radiative Forcing from Snow Darkening with Black Carbon Using Climate Model Data. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 57, 133–141 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433821020031
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433821020031