Abstract
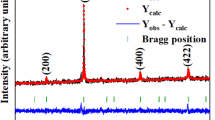
Mn-based magnetic alloys and compounds having large magnetic anisotropy are currently focused as alternate materials for various spintronic applications. In this work, magnetization behavior of Co3Mn alloy nanowires (NWs) was investigated by fabricating with well-known template-based electrodeposition method where the electrodeposition was carried out at sinusoidal high voltage. The NWs were annealed at 300 °C and 400 °C with 10 °C/min heating and cooling rate to eliminate the crystal defects caused by high-voltage deposition. Crystal structure analysis displayed the as-deposited NWs were crystallized into a face-centered cubic (fcc) structure with crystallite size 24.93 nm, while the hexagonal close pack (hcp) phase with crystallite size 38.61 nm was induced after annealing. The as-deposited NWs exhibited the soft ferromagnetic behavior with coercivity (\(H_{{\text{C}}}\)) = 128 Oe and saturation magnetization (\(M_{{\text{S}}}\)) = 311 emu/cm3 along axial direction but magnetic hardening induced after annealing with \(H_{{\text{C}}}\) = 688 Oe and \(M_{{\text{S}}}\) = 228 emu/cm3 caused by strong pinning effects and elastic coupling between hcp and fcc phase. Interestingly, the asymmetric shift in MH-loops of annealed NWs was noted below 150 K when the temperature-dependent MH-loops measured after cooling the sample in the magnetic field. This observation confirmed the existence of exchange bias effect in NWs caused by short-range exchange interaction between ferromagnetic fcc phase and antiferromagnetic hcp phase.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
N. Môri, T. Mitsui, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 25, 82–88 (1968)
A. Menshikov, G. Takzei, Y.A. Dorofeev, V. Kazantsev, A. Kostyshin, I. Sych, Zh. Eksp, Teor. Fiz. 89, 1269–1279 (1985)
W. Abdul-Razzaq, J.S. Kouvel, Phys. Rev. B 35, 1764–1767 (1987)
M. Matsui, T. Ido, K. Sato, K. Adachi, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 28, 791–791 (1970)
D. Wu, G. Liu, C. Jing, Y. Wu, D. Loison, G. Dong, X. Jin, D.-S. Wang, Phys. Rev. B 63, 214403 (2001)
D. Wu, G. Liu, C. Jing, Y. Wu, G. Dong, X. Jin, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 521–523 (2001)
J. Cable, Y. Tsunoda, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 140, 93–94 (1995)
D.J. Rogers, Y. Maeda, K. Takei, J. Appl. Phys. 78, 5842–5844 (1995)
R. Snow, H. Bhatkar, A. N’Diaye, E. Arenholz, Y. Idzerda, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 419, 490–493 (2016)
T.H. Kim, J.S. Moodera, Phys. Rev. B 66, 104436 (2002)
K. Kunimatsu, T. Tsuchiya, T. Roy, K. Elphick, T. Ichinose, M. Tsujikawa, A. Hirohata, M. Shirai, S. Mizukami, Appl. Phys. Express 13, 083007 (2020)
J.S. Kouvel, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 16, 107–114 (1960)
S. Giri, M. Patra, S. Majumdar, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 23, 073201 (2011)
J. Cable, Y. Tsunoda, Phys. Rev. B 50, 9200 (1994)
A. Safeer, N. Ahmad, S. Khan, L.A. Azam, D. Bashir, J. Appl. Phys. 125, 034302 (2019)
M. Awais, N. Ahmad, S. Khan, A. Safeer, K. Javed, I. Murtaza, A. Majid, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 474, 207–214 (2019)
H. Cao, L. Wang, Y. Qiu, Q. Wu, G. Wang, L. Zhang, X. Liu, ChemPhysChem 7, 1500–1504 (2006)
H. Yang, Y. Li, M. Zeng, W. Cao, W.E. Bailey, R. Yu, Sci. Rep. 6, 20427 (2016)
H. Schloerb, V. Haehnel, M.S. Khatri, A. Srivastav, A. Kumar, L. Schultz, S. Faehler, Phys. Status Solidi 247, 2364–2379 (2010)
S. Tang, W. Chen, M. Lu, S. Yang, F. Zhang, Y. Du, Chem. Phys. Lett. 384, 1–4 (2004)
W. Chen, S. Tang, M. Lu, Y. Du, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 15, 4623 (2003)
A. Safeer, L.A. Azam, D. Bashir, S. Khan, B. Parveen, N. Ahmad, Phys. B Condens. Matter 586, 412138 (2020)
Q. Zhan, Z. Chen, D. Xue, F. Li, H. Kunkel, X. Zhou, R. Roshko, G. Williams, Phys. Rev. B 66, 134436 (2002)
H. Zeng, R. Skomski, L. Menon, Y. Liu, S. Bandyopadhyay, D.J. Sellmyer, Phys. Rev. B 65, 134426 (2002)
J.A. De Toro, P.S. Normile, S.S. Lee, D. Salazar, J.L. Cheong, P. Muñiz, J.M. Riveiro, M. Hillenkamp, F. Tournus, A. Tamion, J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 10213–10219 (2013)
G. Muscas, G. Concas, S. Laureti, A. Testa, R. Mathieu, J. De Toro, C. Cannas, A. Musinu, M. Novak, C. Sangregorio, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 28634–28643 (2018)
M. Acet, E. Duman, E.F. Wassermann, L. Manosa, A. Planes, J. Appl. Phys. 92, 3867–3871 (2002)
Acknowledgment
Authors would like to acknowledge the Higher Education Commission, Pakistan, and International Islamic University, Islamabad, Pakistan, for the Financial Support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Liaqat Ali Azam & Affan Safeer: Conceptualization, Resources, Formal analysis, Virtualization, Writing—Original Draft, Review & Editing. Naeem Ahmad: Validation, Supervision. Andrés Rosales-Rivera: Investigation. Suleman Khan & Imran Murtaza: Project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exists in the submission of the manuscript and all authors have approved the manuscript for the publication. The authors would like to declare that the work described is original research that has not been published previously and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azam, L.A., Safeer, A., Ahmed, N. et al. Magnetic hardening and exchange bias effect in dual-phase Co3Mn nanowire arrays. Appl. Phys. A 127, 398 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04529-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04529-2