Abstract
Purpose
Seasonal hypoxia in water bodies can increase levels of reduced chemical species in the hypolimnion as they are released from anoxic bottom sediments. Water-lifting aeration (WLA) is a technology known to solve this problem by elevating near-sediment dissolved oxygen (DO) and increasing mixing in the water column in a canyon reservoir with deep water (>20 m). The influence of WLA in reservoirs with large surface area and small water depth has not been adequately evaluated. For this purpose, the efficiency of an innovative WLA system was reviewed in Zhoucun Reservoir (ZCR), a mildly eutrophic reservoir with a mean depth of 15 m.
Methods
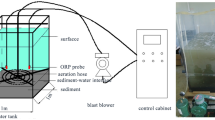
Three years of field experiment was performed in ZCR. Water and sediment samples were collected before and after the operation of the WLA system to explore the causes for the deterioration of water quality in ZCR, and the efficiency of the innovative WLA system installed in 2015. With the use of a microporous aerator and a kinetic energy dissipator, the new-style WLA system is different from WLA studied before.
Results and discussion
As a result of thermal stratification and the long duration of anaerobic environment in the hypolimnion, the sediment oxygen consumption rate in ZCR was calculated to be 16.14 mg m−2 h−1, which was much higher than other reservoirs, and the main pollutants in ZCR were ammonia, phosphorus, manganese and sulphide. After the operation of the new WLA system, the anaerobic environment in the bottom water was completely reversed and the DO concentration in the hypolimnion water has been maintained at more than 6 mg L−1. The release of pollutants from sediments, such as ammonia, phosphorus, manganese and sulphide, was inhibited significantly. Ammonia, phosphorus, manganese and sulphide in water decreased by 89%, 84%, 97% and 87%, respectively.
Conclusions
The results of this study demonstrate that employing WLA systems to oxygenate and mix stagnant water bodies is a viable and potentially favourable management strategy for reservoirs with large surface area and relatively small water depth.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Beutel MW, Horne AJ (1999) A review of the effects of hypolimnetic oxygenation on lake and reservoir water quality. Lake Reserv Manage 15(4):285–297
Beutel MW (2001) Oxygen consumption and ammonia accumulation in the hypolimnion of Walker Lake, Nevada. Hydrobiologia 466:107–117
Bryant LD, Hsu-Kim H, Gantzer PA, Little JC (2011) Solving the problem at the source: controlling Mn release at the sediment-water interface via hypolimnetic oxygenation. Water Res 45:6381–6392
Chai BB, Huang TL, Zhu WH, Yang FY (2011) A new method of inhibiting pollutant release from source water reservoir sediment by adding chemical stabilization agents combined with water-lifting aerator. J Environ Sci 23(12):1977–1982
Chen ML, Hur J (2015) Pre-treatments, characteristics, and biogeochemical dynamics of dissolved organic matter in sediments: a review. Water Res 79:10–25
Cong HB, Huang TL, Zhao JW, Zhou ZM, He WJ, Han HD (2006) Application of the technology of lifting water and aeration for improving water quality. Environ Pollut Control 28(3):215–218
Cong HB, Huang TL, Miao JG, He WJ, Yin PJ (2007) Study on water improvement function, capacity of lifting water and oxygenation of a water-lifting aerator. Chin J Environ Eng 1(1):7–13
Cong HB, Huang TL, Chai BB, Zhao JW (2009) A new mixing-oxygenating technology for water quality improvement of urban water source and its implication in a reservoir. Renew Energy 34(9):2054–2060
Gantzer PA, Bryant LD, Little JC (2009) Effect of hypolimnetic oxygenation on oxygen depletion rates in two water-supply reservoirs. Water Res 43:1700–1710
Gerling AB, Browne RG, Gantzer PA, Mobley MH, Little JC, Carey CC (2014) First report of the successful operation of a side stream supersaturation hypolimnetic oxygenation system in a eutrophic, shallow reservoir. Water Res 67:129–143
He WJ (2006) Novel technology for drinking water safety. Architecture Industry of China Press, Beijing
Horppila J (2019) Sediment nutrients, ecological status and restoration of lakes. Water Res 160:206–208
Huang TL, Ma Y, Cong HB et al (2014) Application of the technology of water lifting and aeration on improving water quality in a deep canyon reservoir - a case study from northern china. Desalin Water Treat 82:1636–1646
Matthews DA, Effler SW (2006) Assessment of long-term trends in the oxygen resources of a recovering urban lake, Onondaga Lake, New York. Lake Reserv Manage 22(1):19–32
Sebnem E (2008) Effects of thermal stratification and mixing on reservoir water quality. Limnology 9:135–142
Sherman B, Whittington J, Oliver R (2000) The impact of artificial destratification on water quality in Chaffey Reservoir. Arch Hydrobiol Spec Iss Adv Limnol 55:15–29
Shi JC, Huang TL, Wen G, Liu F, Qiu X, Wang BS (2016) The variation characteristic of sulfides and VOCs in a source water reservoir and its control using a water-lifting aerator. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13:427. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13040427
Singleton VL, Little JC (2006) Designing hypolimnetic aeration and oxygenation systems – a review. Environ Sci Technol 40:7512–7520
Wetzel RG (2001) Limnology: lakes and river ecosystems, Third edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Visser PM, Ketelaars HAM, Mur LR (1995) Reduced growth of the cyanobacterium microcystis in an artificially mixed lake and reservoir. Water Sci Technol 32(4):53–54
Visser PM, Ibelings BW, Bormans M, Huisman J (2015) Artificial mixing to control cyanobacterial blooms: a review. Aquat Ecol 50(3):423–441
Yang X, Huang TL, Guo L, Xia C, Zhang HH, Zhou SL (2015) Abundance and diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in the sediment of the Zhoucun drinking water reservoir in eastern china. Genet Mol Res 14:5830–5844
Zhou ZM, Huang TL, Cong HB (2007) Algae removal effect by combined process of water-lifting aeration and biological contact oxidation. China Water Wastewater 23(15):13–16
Zhang HH, Yan MM, Huang TL, Huang X, Yang SY, Li N, Wang N (2020) Water-lifting aerator reduces algal growth in stratified drinking water reservoir: Novel insights into algal metabolic profiling and engineering applications. Environ Pollut 266:115–384
Code availability
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2020QE225) and the National Science and Technology Pillar Program (No. 2012BAC04B02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Haihan Zhang
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
JianChao, S., Yongrui, Y., Fei, L. et al. Constraining release of pollutants from anoxic bottom sediment via water-lifting aeration in a source water reservoir, East China. J Soils Sediments 21, 3300–3309 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02963-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02963-6