Abstract
In this study we investigate possible applications of observed S2 orbit around Galactic Center for constraining the Yukawa gravity at scales in the range between several tens and several thousands astronomical units (AU) to obtain graviton mass constraints. In our model we suppose that bulk distribution of matter (includes stellar cluster, interstellar gas distribution and dark matter) exists near Supermassive Black Hole (SMBH) in our Galactic Center. We obtain the values of orbital precession angle for different values of mass density of matter, and we require that the value of orbital precession is the same like in general relativity (GR). From that request we determine gravity parameter \(\lambda \) and the upper value for graviton mass. We found that in the cases where the density of extended mass is higher, the maximum allowed value for parameter \(\lambda \) is smaller and the upper limit for graviton mass is higher. It is due to the fact that the extended mass causes the retrograde orbital precession. We believe that this study is a very efficient tool to evaluate a gravitational potential at the Galactic Center, parameter \(\lambda \) of the Yukawa gravity model, and to constrain the graviton mass.
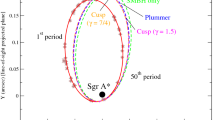
Graphic Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Authors’ comment: All relevant data are in the paper.]
Notes
The remarkable studies got the high recognition in scientific community and Reinhard Genzel (VLT) and Andrea Ghez (Keck) were awarded the Nobel prize in physics in 2020.
References
F. Zwicky, Helv. Phys. Acta 6, 110 (1933)
M.S. Turner, in The Third Stromlo Symposium: The Galactic Halo, eds. B.K. Gibson, T.S. Axelrod, & M.E. Putman, ASP Conference Series Vol. 165, 431 (1999)
A.F. Zakharov, S. Capozziello, F. De Paolis, G. Ingrosso, A.A. Nucita, Space Sci. Rev. 48, 301 (2009)
S. Weinberg, Cosmology (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2008)
M. Milgrom, Astrophys. J. 270, 365 (1983)
J.D. Bekenstein, Phys. Rev. D 70, 083509 (2004)
S. Capozziello, Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 11, 483 (2002)
S.M. Carroll, V. Duvvuri, M. Trodden, M.S. Turner, Phys. Rev. D 70, 043528 (2004)
S. Capozziello, V.F. Cardone, A. Troisi, Phys. Rev. D 73, 104019 (2006)
A.F. Zakharov, A.A. Nucita, F. De Paolis, G. Ingrosso, Phys. Rev. D 74, 107101 (2006)
S. Capozziello, M. de Laurentis, Phys. Rep. 509, 167 (2011)
S. Capozziello, V. Faraoni, Beyond Einstein Gravity: A Survey of Gravitational Theories for Cosmology and Astrophysics (Springer, Berlin, 2011)
D. Borka, P. Jovanović, V. Borka Jovanović, A.F. Zakharov, Phys. Rev. D 85, 124004 (2012)
D. Borka, S. Capozziello, P. Jovanović, V. Borka Jovanović, Astropart. Phys. 79, 41 (2016)
R. Genzel, T. Ott, F. Eisenhauer et al., Astrophys. J. 594, 812 (2003)
A.M. Ghez, S. Salim, N.N. Weinberg et al., Astrophys. J. 689, 1044 (2008)
S. Gillessen, F. Eisenhauer, T.K. Fritz et al., Astrophys. J. 707, L114 (2009)
S. Gillessen, F. Eisenhauer, S. Trippe et al., Astrophys. J. 692, 1075 (2009)
R. Genzel, F. Eisenhauer, S. Gillessen, Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 3121 (2010)
A. Hees, T. Do, A.M. Ghez et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 211101 (2017)
C. Devin, T. Do, A. Hees et al., Astrophys. J. 854, 12 (2018)
A. Hees, T. Do et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 081101 (2020)
A.F. Zakharov, P. Jovanović, D. Borka, V. Borka Jovanović, J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 5, 045 (2016)
A.F. Zakharov, P. Jovanović, D. Borka, V. Borka Jovanović, J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 04, 050 (2018)
A.F. Zakharov, P. Jovanović, D. Borka, V. Borka Jovanović, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 798, 012081 (2017)
A.F. Zakharov, P. Jovanović, D. Borka, V. Borka Jovanović, Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnate Pleso 50, 203 (2020)
D. Borka, P. Jovanović, V. Borka Jovanović, A.F. Zakharov, J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 11, 050 (2013)
B.P. Abbott et al., (LIGO Scientific Collaboration and Virgo Collaboration) Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 061102 (2016)
B.P. Abbott et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 221101 (2017)
B.P. Abbott et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 161101 (2017)
B.P. Abbott et al., Astrophys. J. Lett. 848, L13 (2017)
B.P. Abbott et al., (The LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration) Phys. Rev. D 100, 104036 (2019)
The LIGO Scientific Collaboration and the Virgo Collaboration, arXiv:2010.14529v1 [gr-qc]
G.F. Rubilar, A. Eckart, Astron. Astrophys. 74, 95 (2001)
A.A. Nucita, F. De Paolis, G. Ingrosso et al., Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacific 119, 349 (2007)
A.F. Zakharov, A.A. Nucita, F. De Paolis, G. Ingrosso, Phys. Rev. D 76, 062001 (2007)
M. Preto, P. Saha, Astrophys. J. 703, 1743 (2009)
A.F. Zakharov, D. Borka, V. Borka Jovanović, P. Jovanović, Adv. Sp. Res., 54, 1108 (2014)
V.I. Dokuchaev, Yu. N. Eroshenko, JETP Lett. 101, 777 (2015)
V.I. Dokuchaev, Yu. N. Eroshenko, Phys. Uspekhi 58, 772 (2015)
A. Amorim, M. Bauböck, M. Benisty et al., Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 489, 4606 (2019)
S. Capozziello, E. de Filippis, V. Salzano, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 394, 947 (2009)
V.F. Cardone, S. Capozziello, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 414, 1301 (2011)
N.N. Weinberg, M. Milosavljević, A.M. Ghez, Astrophys. J. 622, 878 (2005)
G.S. Adkins, J. McDonnell, Phys. Rev. D 75, 082001 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia. P.J. wishes to acknowledge the support by this Ministry through the project contract No. 451-03-9/2021-14/200002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All coauthors participated in calculation and discussion of obtained results. The authors contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jovanović, P., Borka, D., Borka Jovanović, V. et al. Influence of bulk mass distribution on orbital precession of S2 star in Yukawa gravity. Eur. Phys. J. D 75, 145 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00154-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-021-00154-z