Abstract
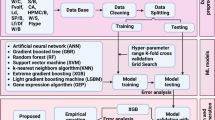
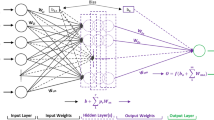
In recent years, with the wide application of image data visual extraction technology in the field of industrial engineering, the development of industrial economy has reached a new situation. To explore the interaction between the pellet microstructure and compressive strength, firstly, the pellet microstructure needed for the experiment was obtained using a Leica DM4500P microscope. The area proportions of hematite, calcium ferrite, magnetite, calcium silicate and pore in pellet microstructure were extracted by visual extraction technology of image data. Moreover, the relationship between the area proportions of mineral components and compressive strength was established by backpropagation neural network (BPNN), generalized regression neural network (GRNN) and beetle antennae search-generalized regression neural network (BAS-GRNN) algorithms, which proves that the pellet microstructure can be used as the prediction standard of compressive strength. The errors of BPNN and BAS-GRNN are 5.13% and 3.37%, respectively, both of which are less than 5.5%. Therefore, through data visualization, we are able to discuss the connection between various components of pellet microstructure and compressive strength and provide new research ideas for improving the compressive strength and metallurgical performance of pellet.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Xing, H. Xu, Y. Tan, X. Liu, Q. Ye, Constr. Build. Mater. 200 (2019) 781–789.
J.D. Tournier, R. Smith, D. Raffelt, R. Tabbara, T. Dhollander, M. Pietsch, D. Christiaens, B. Jeurissen, C.H. Yeh, A. Connelly, NeuroImage 202 (2019) 116137.
K. Schnittker, E. Arrieta, X. Jimenez, D. Espalin, R.B. Wicker, D.A. Roberson, Addit. Manuf. 26 (2019) 129–137.
H. Tang, D. Li, J. Wan, M. Imran, M. Shoaib, IEEE Internet Things J. 7 (2020) 4248–4259.
Q. Zhang, H. Li, J.L. Ma, H.Y. Xu, B.Y. Yu, G. Wang, S. Jiang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 26 (2019) 529–546.
F. Chen, Y.F. Guo, T. Jiang, F.Q. Zheng, S. Wang, L.Z. Yang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 24 (2017) 266–272.
S. Dwarapudi, T.K. Ghosh, V. Tathavadkar, M.B. Denys, D. Bhattacharjee, R. Venugopal, Int. J. Miner. Process. 112–113 (2012) 55–62.
A.M. Yang, Y.X. Zhuansun, Y. Shi, H.X. Liu, Y.J. Chen, R.S. Li, IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 17 (2021) 934–942.
S. Mun, S. Park, D.K. Han, H. Ko, in: Proc. DCASE, Munich, Germany, 2017, pp. 93–97.
N.B. Bahadure, A.K. Ray, H.P. Thethi, Int. J. Biomed. Imag. 2017 (2017) 9749108.
Y.F. Chen, L.G. Shen, R.J. Li, X.C. Xu, H.C. Hong, H.G. Lin, J.R. Chen, J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 565 (2020) 1–10.
D. Bani-Hani, M. Khasawneh, Expert Syst. Appl. 135 (2019) 273–286.
Y. Dai, J. Guo, L. Yang, W. You, Procedia Computer Science 147 (2019) 519–527.
Y. Hu, J. Li, M. Hong, J. Ren, R. Lin, Y. Liu, M. Liu, Y. Man, Energy 170 (2019) 1215–1227.
R. Rooki, Measurement 85 (2016) 184–191.
J. Sun, W. Liu, Y. Hu, J. Wu, M. Li, X. Yang, W. Wang, M. Xu, Chem. Eng. J. 285 (2016) 293–303.
G.P. Luo, B. Zhao, J.Q. Liu, Z.Z. Hao, Sinter. Pelletiz. 40 (2015) No. 5, 25–27.
F. Nellros, M.J. Thurley, Miner. Eng. 24 (2011) 1525–1531.
J. Cheng, Y. Xiong, Procedia Computer Science 107 (2017) 355–360.
X.Y. Jiang, S. Li, arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10724, 2017.
X.Y. Jiang, Z.Y. Lin, T.H. He, X.J. Ma, S.L. Ma, S. Li, IEEE Access 8 (2020) 15459–15471.
Z.S. Luo, M.Y. Yao, J.H. Luo, X.W. Wang, Surface Technology 47 (2018) No. 11, 173–180.
W. Wei, H. Zheng, R. Xu, F. Wu, W. Chen, B. Jia, Z. Xue, Metall. Res. Technol. 116 (2019) 117.
Z. Di, Z. Li, R. Wei, Y. Liu, Q. Meng, T. Chun, H. Long, J. Li, P. Wang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 46 (2019) 159–164.
Acknowledgements
This paper is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51674121) and Fund for Distinguished Youth Scholars in North China University of Science and Technology (JQ201705).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Am., Zhuansun, Yx. Prediction of compressive strength based on visualization of pellet microstructure data. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28, 651–660 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00604-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00604-3