Abstract
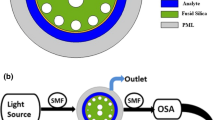
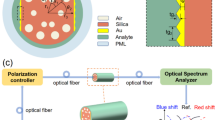
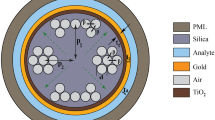
We propose a quasi-D-shaped photonic-crystal-fiber surface-plasmon-resonance (PCF-SPR) biosensor based on ultrashort side polishing. The gold film layer of the ultrashort side-polishing PCF-SPR biosensor is close to the fiber core. It can enhance the surface-plasmon-resonance effect and can test the strong interaction between the samples and the difficulties of the process of lateral fiber transfer. We numerically simulate the coupling characteristics of the sensor by the full vector finite element method (FEM). Based on the insulator–metal–insulator (IMI) structure, black phosphorous films are coated on the upper and lower surfaces of the gold film. Numerical calculation results show that the refractive-index measurement ranges of SPR sensors without black phosphorous film and with black phosphorous film are (1.36 – 1.37) and (1.320 – 1.375), respectively. The dynamic sensitivity of the sensor in the second range is 2800 – 8200 nm/RIU. Therefore, one sees that this structure can enhance the sensitivity of the sensor and increase the measurement range of the sensor. The quasi-Dshaped fiber proposed in this paper has advantages of simple fabrication, large measurement range, and high sensitivity. It can also be applied to the fields of biomolecular detection, clinical medicine, and antigen–antibody interaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Xia and N. J. Halas, MRS Bull., 30, 338 (2005).
X. M. Wang, C. L. Zhao, Y. R. Wang, et al., J. Lightwave Technol., 34, 2324 (2016).
J. Homola, S. S. Yee, and G. Gauglitz, Sensors Actuators B: Chem., 54, 3 (1999).
W. R. Wong, O. Krupin, S. D. Sekaran, et al., Anal. Chem., 86, 1735 (2014).
Y. Chongxiu, J. Yuan, and X. Shen, Acta Optica Sinica, 31, 0900139 (2011).
A. Hassani and M. Skorobogatiy, Opt. Express, 14, 11616 (2006).
A. Hassani and M. Skorobogatiy, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, 24, 1423 (2007).
W.-H. Shi, C.-J. You, and J. Wu, Acta Physica Sinica, 64, 224221 (2015).
X. Fu, Y. Lu, X. Huang, and J. Q. Yao, Opt. Appl., 41, 941 (2011).
N. Luan, R. Wang, W. Lv, and J. Yao, Opt. Express, 23, 8576 (2015).
G. An, S. Li, W. Qin, et al., Plasmonics, 9, 1355 (2014).
Y. B. Zheng, J. Q. Yao, L. Zhang, et al., Optoelectron. Lett., 8, 13 (2012).
P. Malinský, P. Slepicka, V. Hnatowicz, and V. ˇSvorc´ık, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 7, 1 (2012).
N. A. Mortensen, M. D. Nielsen, J. R. Folkenberg, et al., Opt. Lett., 28, 393 (2003).
A. K. Sharma and B. D. Gupta, Opt. Commun., 274, 320 (2007).
H. O. Churchill and P. Jarillo-Herrero, Nature Nanotechnol., 9, 330 (2014).
J. Qiao, X. Kong, Z. X. Hu, et al., Nature Commun., 5, 1 (2014).
A. S. Rodin, A. Carvalho, and A. H. Castro Neto, Phys. Rev. Lett., 112, 176801 (2014).
N. Mao, J. Tang, L. Xie, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 138, 300 (2016).
S. Shukla, N. K. Sharma, and V. Sajal, Sensors Actuators B: Chem., 206, 463 (2015).
L. Wu, J. Guo, Q. Wang, et al., Sensors Actuators B: Chem., 249, 542 (2017).
C. Liu, L. Yang, X. Lu, et al., Opt. Express, 25, 14227 (2017).
K. Tong and P. Dang, China Laser, 45, 268 (2018).
D. Ying, S.-G. Li, and S. Liu, Chin. Phys. B, 21, 094219 (2012).
J. N. Dash and Rajan Jha, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 26, 1092 (2014).
Y. Chen, Q. Xie, X. Li, et al., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 50, 025101 (2016).
L. Y. Niu, Q. Wang, J. Y. Jing, and W. M. Zhao, Opt. Commun., 450, 287 (2019).
C. Zhou, H. K. Zhang, P. Song, et al., IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 32, 589 (2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, K., Wang, J., Cai, Z. et al. Study on Increasing Measurement Range and Enhancing Sensitivity of PCF Surface-Plasmon-Resonance Biosensor using Black Phosphorus. J Russ Laser Res 42, 283–291 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-021-09961-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-021-09961-6