Abstract
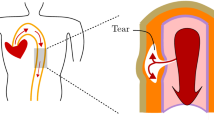
Small superimposed radial oscillations for a class of damaged limited elastic, incompressible, isotropic and homogeneous thick-walled circular cylindrical tube are examined. Both the damage function and the considered limited elastic class depend only on the first invariant \( I_{1} \) of the left Cauchy–Green deformation tensor. The present work puts some light in the context of the surgical procedure of angioplasty, used especially to treat cardiovascular diseases. Our simplified isotropic assumption allows for a much faster and analytical computation of comparably accurate results. The examples of three limited elastic material models are presented, namely the Arruda–Boyce, Gent, and Demiray. The radial oscillations are further investigated for a damaged limited elastic thin membrane, and the examples above are explored. Universal relations are found for the three material membranes. The obtained results are matched with the clinical data of the existing literature. It appears that the pressure ratio for the virgin and damaged arterial tissue is higher before angioplasty and vice versa. A similar trend for the frequency ratio also follows.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
A careful observation of Figure 5 of [17] will assert that the arterial tissue is having the limiting extensibility stretch of \( \lambda _{m}=\lambda _{1M}=1.7827 \). Thus, the limiting value of the invariant is \( I_{m}=I_{1M}=\lambda ^{2}+\dfrac{2}{\lambda }=4.3 \).
References
Ross, R.: Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 340(2), 115–126 (1999)
Balzani, D., Brinkhues, S., Holzapfel, G.A.: Constitutive framework for the modeling of damage in collagenous soft tissues with application to arterial walls. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 213, 139–151 (2012)
Diani, J., Fayolle, B., Gilormini, P.: A review on the mullins effect. Eur. Polym. J. 45(3), 601–612 (2009)
Horgan, C.O., Saccomandi, G.: Constitutive modelling of rubber-like and biological materials with limiting chain extensibility. Math. Mech. Solids 7(4), 353–371 (2002)
Holzapfel, G.A.: Similarities between soft biological tissues and rubberlike materials. In: Constitutive Models for Rubber-Proceedings, Vol. 4, Balkema, p. 607 (2005)
Horgan, C.O., Saccomandi, G.: A description of arterial wall mechanics using limiting chain extensibility constitutive models. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 1(4), 251–266 (2003)
Beatty, M.F.: On constitutive models for limited elastic, molecular based materials. Math. Mech. Solids 13(5), 375–387 (2008)
Knowles, J.K.: Large amplitude oscillations of a tube of incompressible elastic material. Q. Appl. Mech. XVII I, 71–77 (1960)
Knowles, J.K.: On a class of oscillations in the finite-deformation theory of elasticity. J. Appl. Mech. 29(2), 283–286 (1962)
Truesdell, C.: Solutio generalis et accurata problematum quamplurimorum de motu corporum elasticorum incomprimibilium in deformationibus valde magnis. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 11(1), 106–113 (1962)
Truesdell, C.: Addendum. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 12(1), 427–428 (1963)
Beatty, M.F.: On the radial oscillations of incompressible, isotropic, elastic and limited elastic thick-walled tubes. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 42(2), 283–297 (2007)
Beatty, M.F.: Infinitesimal stability of the equilibrium states of an incompressible, isotropic elastic tube under pressure. J. Elast. 104(1–2), 71–90 (2011)
Guo, Z.-H., Solecki, R.: Free and forced finite amplitude oscillations of an elastic thick-walled hollow sphere made of incompressible material. Arch. Mech. Stos 15(3), 427–433 (1963)
Wang, C.-C.: On the radial oscillations of a spherical thin shell in the finite elasticity theory. Q. Appl. Math. 23(3), 270–274 (1965)
Shahinpoor, M., Balakrishnan, R.: Large amplitude oscillations of thick hyperelastic cylindrical shells. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 13(5–6), 295–301 (1978)
Holzapfel, G.A., Gasser, T.C.: Computational stress-deformation analysis of arterial walls including high-pressure response. Int. J. Cardiol. 116(1), 78–85 (2007)
Arruda, E.M., Boyce, M.C.: A three-dimensional constitutive model for the large stretch behavior of rubber elastic materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 41(2), 389–412 (1993)
Chuong, C., Fung, Y.: Three-dimensional stress distribution in arteries. J. Biomech. Eng. 105(3), 268–274 (1983)
Horgan, C.O.: The remarkable Gent constitutive model for hyperelastic materials. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 68, 9–16 (2015)
Lawton, R.W., King, A.L.: Free longitudinal vibrations of rubber and tissue strips. J. Appl. Phys. 22(11), 1340–1343 (1951)
Tauheed, F., Sarangi, S.: An invariant based damage model of stress-softening. Mech. Res. Commun. 56, 11–17 (2014)
Arya, K., Sarangi, S.: Effect of damage on the free radial oscillations of an incompressible isotropic tube. Math. Mech. Solids 1081286517712076 (2017)
Arya, K., Sarangi, S.: The effect of damage on small-amplitude radial oscillations of an incompressible isotropic tube under pressure. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 68, 25–37 (2018)
Holzapfel, G.A., Ogden, R.W.: Constitutive modelling of arteries. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, Vol. 466, The Royal Society, pp. 1551–1597 (2010)
Takamizawa, K., Hayashi, K.: Strain energy density function and uniform strain hypothesis for arterial mechanics. J. Biomech. 20(1), 7–17 (1987)
Kuhn, W., Grün, F.: Beziehungen zwischen elastischen konstanten und dehnungsdoppelbrechung hochelastischer stoffe. Kolloid-Zeitschrift 101(3), 248–271 (1942)
James, H.M., Guth, E.: Theory of the elastic properties of rubber. J. Chem. Phys. 11(10), 455–481 (1943)
Gent, A.N.: A new constitutive relation for rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 69(1), 59–61 (1996)
Demiray, H.: A note on the elasticity of soft biological tissues. J. Biomech. 5(3), 309–311 (1972)
Boyce, M.C.: Direct comparison of the gent and the Arruda–Boyce constitutive models of rubber elasticity. Rubber Chem. Technol. 69(5), 781–785 (1996)
Beatty, M.F., Bhattacharyya, R., Sarangi, S.: Small amplitude, free longitudinal vibrations of a load on a finitely deformed stress-softening spring with limiting extensibility. Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Physik (ZAMP) 60(5), 971–1006 (2009)
Waller, B.F., Orr, C.M., Slack, J.D., Pinkerton, C.A., Van Tassel, J., Peters, T.: Anatomy, histology, and pathology of coronary arteries: a review relevant to new interventional and imaging techniques-part i. Clin. Cardiol. 15(6), 451–457 (1992)
Siebes, M., Verhoeff, B.-J., Meuwissen, M., de Winter, R.J., Spaan, J.A., Piek, J.J.: Single-wire pressure and flow velocity measurement to quantify coronary stenosis hemodynamics and effects of percutaneous interventions. Circulation 109(6), 756–762 (2004)
Han, Y.-F., Liu, W.-H., Chen, X.-L., Xiong, Y.-Y., Yin, Q., Xu, G.-L., Zhu, W.-S., Zhang, R.-L., Ma, M.-M., Li, M., et al.: Severity assessment of intracranial large artery stenosis by pressure gradient measurements: a feasibility study. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 88(2), 255–261 (2016)
Anderson, H.V., Roubin, G.S., Leimgruber, P.P., Cox, W.R., Douglas, J.S., King, S.B., Gruentzig, A.R.: Measurement of transstenotic pressure gradient during percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Circulation 73(6), 1223–1230 (1986)
Beekman, R.H., Rocchini, A.P., Dick, M., Snider, A.R., Crowley, D.C., Serwer, G.A., Spicer, R.L., Rosenthal, A.: Percutaneous balloon angioplasty for native coarctation of the aorta. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 10(5), 1078–1084 (1987)
De Bruyne, B., Paulus, W.J., Vantrimpont, P.J., Sys, S.U., Heyndrickx, G.R., Pijls, N.H.: Transstenotic coronary pressure gradient measurement in humans: in vitro and in vivo evaluation of a new pressure monitoring angioplasty guide wire. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 22(1), 119–126 (1993)
Fawzy, M.E., Sivanandam, V., Galal, O., Dunn, B., Patel, A., Rifai, A., von Sinner, W., Al Halees, Z., Khan, B.: One-to ten-year follow-up results of balloon angioplasty of native coarctation of the aorta in adolescents and adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 30(6), 1542–1546 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1. Detailed derivation of Eq. (26)
Appendix 1. Detailed derivation of Eq. (26)
For the forced radial oscillations presented here, the respective Knowles’ equation (17) incorporating the damage function is detailed below:
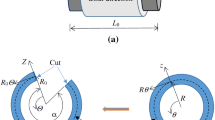
The deformation gradient for the considered tube problem is given by
and so the left Cauchy–Green deformation tensor \(\mathbf{B} =\mathbf{F} {} \mathbf{F} ^{T}\) is obtained as
The respective principal invariants of \(\mathbf{B} \) are
Consequently, from the constitutive relation (15) we obtain the principal components of the Cauchy stress \( \mathbf{T} \) as
Thus, use of the equilibrium equation
and the boundary conditions \( T_{rr}=-p_{1}(t) \) and \( T_{rr}=-p_{2}(t) \) at \( r=r_{1} \) and \( r=r_{2} \), respectively, provides the Knowles’ equation (17) for the damaged case.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arya, K., Bhattacharyya, R. & Sarangi, S. Small superimposed radial oscillations for a class of damaged limited elastic tubes. Acta Mech 232, 2765–2780 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-021-02980-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-021-02980-z