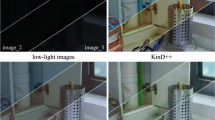
Abstract
Visible light polarization image desmogging aims to recover the clear image solely from an input visible light polarization image with smog. It is a challenging research topic due to desmogging is an ill-posed problem. Most of existing methods effort to build desmogging physical model based on classical atmospheric scattering principle. However, compared with natural image dehazing task, the smog in visible light polarization image is very complex and diverse, which makes it hard to find accurate desmogging physical model. To address this issue, we propose a Cycle Convolutional Neural Network (CCNN), which exploits polarization characteristics explicitly to learn a visible light polarization image desmogging model in an end-to-end way. To be specific, the model computes polarization information of the visible light polarization image via Stokes equation. Object detection sub-network is utilized to detect smog regions according to the polarization information. Then an encoder–decoder sub-network with feature converter structure is proposed to generate smog-free regions. The coarse clear image is obtained by fusing the generated smog-free regions with original smog visible light polarization image. More importantly, to obtain the final clear image, the coarse clear image is considered as the input data to our model again, which makes our model in a cycle topology. Moreover, we contribute the first large-scale dataset for visible light polarization image desmogging evaluation, which contains 17,216 visible light polarization images, to validate our proposed method. On this dataset, extensive experiments demonstrate that our method can achieve the best performance in comparison with the state-of-the-art baselines.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Data is available at https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Z-imyNuL6sNIS8OoiHHVNg (passwd: iy2q).
References
Wang, J., Wang, W., Wang, R., Gao, W.: Csps: An adaptive pooling method for image classification. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 18(6), 1000–1010 (2016)
He, K., Sun, J., Tang, X.: Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33(12), 2341–2353 (2010)
Zhang, W., Man, Z., Ge, X., Xing, F.: Fast dehazing method based on polarization optics. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 56(14), 141103–1–141103–6 (2019)
Zhao, L., Gao, J., Bi, R., Fan, Z.: Polarization defogging method based on maximum and minimum intensity images. J. Appl. Opt. 38(3), 415–420 (2017)
Dai, Q., Fan, Z., Song, Q., Chen, Y.: Polarization and desmogging of color image based on automatic estimation of global parameters. J. Appl. Opt. 39(4), 511–517 (2015)
Shen, L., Zhao, Y., Peng, Q., Chan, J.C.-W., Kong, S.G.: An iterative image dehazing method with polarization. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 21(5), 1093–1107 (2018)
Xia, P., Liu, X.-B.: Study on the polarization spectral image dehazing. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 37(8), 2331–2338 (2017)
Zhang, W., Ren, L., Xing, F., Zhang, F., Ge, X., Guomei, W., Shenggui, F.: Novel polarimetric dehazing method using discrete cosine transform based laplacian pyramid. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 57(6), 061102–1–061102–7 (2020)
Xiao-ning, L., Yang-yang, L., Zheng, T., Qun-bo, L.: A polarizing universal multi-scale and real-time image defogging algorithm. Acta Photonica Sinica 48(8), 810003–0810003 (2019)
Zhao, C., Duan, J., Li, G., Peng, J.: Polarization image defogging algorithm based on atmosphere scattering model. J. Changchun Univ. Sci. Technol. (Natural Science Edition) 03, 111–115 (2015)
Narasimhan, S.G., Nayar, S.K.: Vision and the atmosphere. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 48(3), 233–254 (2002)
Mei, K., Jiang, A., Li, J., Wang, M.: Progressive feature fusion network for realistic image dehazing, in: Asian conference on computer vision, Springer, pp. 203–215 (2018)
Yu-Long, Y., Sun, X.-B., Song, M.-X., Chen, W., Chen, F.-N.: Phase delay error analysis of wave plate of division-of-amplitude full stokes simultaneous polarization imaging system. Acta Physica Sinica 68(2), 024203–1–024203–12 (2019)
McCartney, E.J.: Optics of the atmosphere: scattering by molecules and particles. Physics Today 30(5), 76 (1977).
Zhang, S., Zhan, J., Fu, Q., Duan, J.: Polarization detection defogging technology based on multi-wavelet fusion. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 55(12), 122602–1–122602–7 (2018)
Hu, H., Zhao, L., Li, X., Wang, H., Yang, J., Li, K., Liu, T.: Polarimetric image recovery in turbid media employing circularly polarized light. Opt. Express 26(19), 25047–25059 (2018)
Ju, H., Liang, J., Zhang, W., Bai, Z., Ren, L., Qu, E.: Simultaneous, real-time, chromatic polarimetric imaging technology with full-polarization-state detection. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 36(6), 744–748 (2017)
Hui, W., Jin, W., Xiaobo, L., Haofeng, H., Tiegen, L.: Optimization for a polarimetic dehazing imaging method based on the circularly polarized light. Infrared Laser Eng. 48(11), 1126001–1126001 (2019)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 25, 1097–1105 (2012)
Gao, J., Xu, C.: Ci-gnn: Building a category-instance graph for zero-shot video classification. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 22(12), 3088–3100 (2020)
Dong, H., Pan, J., Xiang, L., Hu, Z., Zhang, X., Wang, F., Yang, M.-H.: Multi-scale boosted dehazing network with dense feature fusion, in: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2157–2167 (2020)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster r-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(6), 1137–1149 (2016)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition, in: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.-J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recogn. 2009, 248–255 (2009)
Chen, Q., Wang, Y., Yang, T., Zhang, X., Cheng, J., Sun, J.: You only look one-level feature, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, (2021)
Romano, Y., Elad, M.: Boosting of image denoising algorithms. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 8(2), 1187–1219 (2015)
Afouras, T., Chung, J. S., Zisserman, A.: My lips are concealed: Audio-visual speech enhancement through obstructions, arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.04975
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization, arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980
Jun, G., Bi, R., Zhao, L., Fan, Z.: Global optimized hazed image reconstruction based onpolarization information. Opt. Precis. Eng. 25(8), 2212–2220 (2017)
Li, B., Peng, X., Wang, Z., Xu, J., Feng, D.: Aod-net: All-in-one dehazing network, in: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 4770–4778 (2017)
Ren, W., Ma, L., Zhang, J., Pan, J., Cao, X., Liu, W., Yang, M.-H.: Gated fusion network for single image dehazing, In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3253–3261 (2018)
Cai, B., Xu, X., Jia, K., Qing, C., Tao, D.: Dehazenet: an end-to-end system for single image haze removal. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(11), 5187–5198 (2016)
Zhu, J.-Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks, In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 2223–2232 (2017)
Liu, X., Ma, Y., Shi, Z., Chen, J.: Griddehazenet: Attention-based multi-scale network for image dehazing, In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 7314–7323 (2019)
Engin, D., Genç, A., Kemal Ekenel, H.: Cycle-dehaze: Enhanced cyclegan for single image dehazing, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 825–833 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (NSF) of China (No. 61902104), the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province (No. GXXT-2019-048), the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 2008085QF295) and the Talent Research Foundation of Hefei University (No. 18-19RC54), the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 1908085J25), Key Laboratory of Polarization Imaging Detection Technology Anhui Province (No. 2019KJS030009), and Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (No. 1808085MF209).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Gao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix (Additional qualitative examples)
Appendix (Additional qualitative examples)
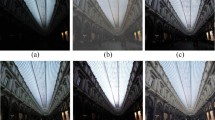
To demonstrate that our model achieves robust and superior performance on different scenes, we visualize more examples (Fig. 9) on the constructed dataset using the proposed method.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Zhang, X., Li, T. et al. Visible light polarization image desmogging via Cycle Convolutional Neural Network. Multimedia Systems 28, 45–55 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-021-00802-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-021-00802-9