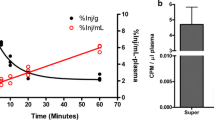
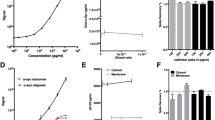
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder. Alpha-synuclein misfolding and aggregation resulting in neurototoxicity is a hallmark of PD. The prion properties of alpha-synuclein are still under discussion. Exosomes (extrcellular vesicles 40–100 nm in size) can play a key role in the transport of pathogenic forms of alpha-synuclein. The most frequent inherited forms of the disease are PD associated with mutation in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2-PD) and glucocerebrosidase (GBA-PD) genes. The aim of our work is to evaluate the concentration and size of exosomes derived from blood plasma of patients with GBA-PD, asymptomatic GBA mutation carriers, and the effect of GBA and LRRK2 mutations on alpha-synuclein level in exosomes derived from peripheral blood plasma. Plasma extracellular vesicles were isolated via chemical precipitation and sequential ultracentrifugation and characterized by transmission electron microscopy, nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), and flow cytometry. Total alpha-synuclein level in plasma exosomes was estimated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Patients with sporadic PD, PD with dementia, patients with inherited PD (GBA-PD, LRRK2-PD), and GBA mutation carriers were included in the study. The concentration on plasma exosomes was higher in GBA-PD patients that in sporadic PD patients, asymptomatic carriers of mutations on GBA gene, and control (p = 0.004, 0.019 and 0.0001 respectively). The size of plasma exosomes was higher in GBA-PD patients compared to asymptomatic carriers of GBA mutations and control (p = 0.009 and 0.0001, respectively). No significant difference was found for exosomal alpha-synuclein levels in the studied groups. Our results allowed us to suggest that a decrease in GBA activity may affect the pool of plasma exosomes, and mutations in the LRRK2 and GBA genes do not influence the level of plasma exosomal alpha-synuclein.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Emelyanov A.K., Usenko T.S., Tesson C., Senkevich K.A., Nikolaev M.A., Miliukhina I.V., Kopytova A.E., Timofeeva A.A., Yakimovsky A.F., Lesage S., Brice A., Pchelina S.N. 2018. Mutation analysis of Parkinson’s disease genes in a Russian data set. Neurobiol. Aging. 71, 272.
Pchelina S.N., Ivanova O.N., Emel’yanov A.K., Yakimovskii A.F.2011. Clinical course of LRRK2-associated Parkinson’s disease. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatrii im. S.S. Korsakova. 12 (111), 56–62.
Lesage S., Anheim M., Condroyer C., Pollak P., Durif F., Dupuits C., Viallet F., Lohmann E., Corvol J.C., Honore A., Rivaud S., Vidailhet M., Durr A., Brice A., French Parkinson’s Disease Genetics Study Group. 2011. Large-scale screening of the Gaucher’s disease-related glucocerebrosidase gene in Europeans with Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 20 (1), 202–210.
Balestrino R., Schapira A. 2019. Parkinson disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 27, 27–42.
Bieri G., Gitler A.D., Brahic M. 2018. Internalization, axonal transport and release of fibrillar forms of alpha-synuclein. Neurobiol. Dis. 109, 219–225.
Danzer K.M., Krebs S.K., Wolff M., Birk G., Hengerer B. 2009. Seeding induced by alpha-synuclein oligomers provides evidence for spreading of alpha-synuclein pathology. J. Neurochem. 111 (1), 192–203.
Shvarzman A.L., Senkevich K.A., Emelyanov A.K., Pchelina S.N. 2019. Prion properties of alpha-synuclein. Mol. Biol. (Moscow). 53 (3), 335–341.
Greening D., Simpson R. 2018. Understanding extracellular vesicle diversity – current status. Expert. Rev. Proteomics. 15, 887–910.
Shi M., Liu C., Cook T.J., Bullock K.M., Zhao Y., Ginghina C., Li Y., Aro P., Dator R., He C., Hipp M.J., Zabetian C.P., Peskind C.P., Hu S.-C., Quinn S.F., et al. 2014. Plasma exosomal α-synuclein is likely CNS-derived and increased in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 128, 639–650.
Stuendl A., Kunadt M., Kruse N., Bartels C., Moebius W., Danzer K.M., Mollenhauer B., Schneider A. 2016. Induction of α-synuclein aggregate formation by CSF exosomes from patients with Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain. 139, 481–494.
Cao Z., Wu Y., Liu G., Jiang Y., Wang X., Wang Z., Feng T. 2019. α-Synuclein in salivary extracellular vesicles as a potential biomarker of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 696, 114–120.
Eitan E., Suire C., Zhang S., Mattson M.P. 2016. Impact of lysosome status on extracellular vesicle content and release. Ageing Res. Rev. 32, 65–74.
Orenstein S.J., Kuo S.H., Tasset I., Arias E., Koga H., Fernandez-Carasa I., Cortes E., Honig L.S., Dauer W., Consiglio A., Raya A., Sulzer D., Cuervo A.M. 2013. Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy. Nat. Neurosci. 16 (4), 394–406.
Fraser K.B., Rawlins A.B., Clark R.G., Alcalay R.N., Standaert D.G., Liu N. 2016. Ser(P)-1292 LRRK2 in urinary exosomes is elevated in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 31 (10), 1543–1550.
Magalhaes J., Gegg M.E., Migdalska-Richards A., Doherty M.K., Whitfield P.D., Schapira A.H. 2016. Autophagic lysosome reformation dysfunction in glucocerebrosidase deficient cells: relevance to Parkinson disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 25, 3432–3445.
Shtam T., Naryzhny S., Kulabukhova D., Garaeva L., Senkevich K., Landa S., Varfolomeeva E., Salogub G., Verlov N., Kopylov A., Zorina E., Kamyshinsky R., Usenko T., Shwartsman A., Zakharova E., et al. 2020. Altered level of plasma exosomes in patients with Gaucher disease. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 63 (11), 104038.
Postuma R.B., Berg D., Stern M., Poewe W., Olanow C.W., Oertel W., Obeso J., Marek K., Litvan I., Lang A.E., Halliday G., Goetz C.G., Gasser T., Dubois B., Chan P., et al. 2015. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 30, 1591–1601.
Aharon-Peretz J., Rosenbaum H., Gershoni-Baruch R. 2004. Mutations in the glucocerebrosidase gene and Parkinson’s disease in Ashkenazi Jews. N. Engl. J. Med. 351 (19), 1972–1977.
Alcalay R.N., Levy O.A., Waters C.C., Fahn S., Ford B., Kuo S-H., Mazzoni P., Pauciulo M.W., Nichols W.C., Gan-Or Z., Rouleau G.A., Chung W.K., Wolf P., Oliva P., Keutzer J., et al. 2015. Glucocerebrosidase activity in Parkinson’s disease with and without GBA mutations. Brain. 138 (9), 2648–2658.
Pchelina S.N., Yakimovskii A.F., Emelyanov A.K., Ivanova O.N., Schwarzman A.L., Singleton A.B. 2008. Screening for LRRK2 mutations in patients with Parkinson’s disease in Russia: identification of a novel LRRK2 variant. 15 (7), 692–696.
Hashad D.I., Abou-Zeid A.A., Achmawy G.A., Allah H.M., Saad M.A. 2011. G2019S mutation of the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 gene in a cohort of Egyptian patients with Parkinson’s disease. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomarkers. 15 (12), 861–866.
Fedick A., Su J., Jalas C., Northrop L., Devkota B., Ekstein J., Treff N.R. 2013. High-throughput carrier screening using TaqMan allelic discrimination. PLoS One. 8 (3), e59722.
Pchelina S., Emelyanov A., Baydakova G., Andoskin P., Senkevich K., Nikolaev M., Miliukhina I., Yakimovskii A., Timofeeva A., Fedotova E., Abramycheva N., Usenko T., Kulabukhova D., Lavrinova A., Kopytova A., et al. 2017. Oligomeric α-synuclein and glucocerebrosidase activity levels in GBA-associated Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 636, 70–76.
Guedes L.C., Chan R.B., Gomes M.A., Conceiçao V.A., Machado R.B., Soares T., Xu Y., Gaspar P., Carriço J.A., Alcalay R.N., Ferreira J.J., Outeiro T.F., Miltenberger-Miltenyi G. 2017. Serum lipid alterations in GBA-associated Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 44, 58–65.
Pchelina S., Baydakova G., Nikolaev M., Senkevich K., Emelyanov A., Kopytova A., Miliukhina I., Yakimovskii A., Timofeeva A., Berkovich O., Fedotova E., Illarioshkin S., Zakharova E. 2018. Blood lisosphingolipids accumulation in patients with Parkinson’s disease with glucocerebrosidase 1 mutations. Mov. Disord. 33 (8), 1325–1330.
Miao Y., Li G., Zhang X., Xu H., Abraham S.N. 2015. A TRP channel senses lysosome neutralization by pathogens to trigger their expulsion. Cell. 161 (6), 1306–1319.
Papadopoulos V.E., Nikolopoulou G., Antoniadou I., Karachaliou A., Arianoglou G., Emmanouilidou E., Sardi S.P., Stefanis L., Vekrellis K. 2018. Modulation of β-glucocerebrosidase increases α-synuclein secretion and exosome release in mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 27 (10), 1696–1710.
Aflaki E., Stubblefield B.K., Maniwang E., Lopez G., Moaven N., Goldin E., Marugan J., Patnaik S., Dutra A., Southall N., Zheng W., Tayebi N., Sidransky E. 2016. Macrophage models of Gaucher disease for evaluating disease pathogenesis and candidate drugs. Sci. Transl. Med. 6, 240–273.
Lachenal G., Pernet-Gallay K., Chivet M., Hemming F.G., Belly A., Bodon G., Blot B., Haase G., Goldberg Y., Sadoul R. 2011. Release of exosomes from differentiated neurons and its regulation by synaptic glutamatergic activity. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 46 (2), 409–418.
Han C., Xiong N., Guo X., Huang J., Ma K., Liu L., Xia Y., Shen Y., Li J., Jiang H., Wang L., Guo S., Xu X., Zhang G., Liu J., et al. 2019. Exosomes from patients with Parkinson’s disease are pathological in mice. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.). 97 (9), 1329–1344.
Cerri S., Ghezzi C., Sampieri M., Avenali M., Dornini G., Zangaglia R., Minafra B., Blandini F. 2018. The exosomal/total α-synuclein ratio in plasma is associated with glucocerebrosidase activity and correlates with measures of disease severity in PD patients. Front. Cell Neurosci. 12, 125.
de la Torre Gomez C., Goreham R.V., Bech Serra J.J., Nann T., Kussmann M. 2018. “Exosomics” : A review of biophysics, biology and biochemistry of exosomes with a focus on human breast milk. Front. Genet. 9, 92.
Tomlinson P.R., Zheng Y., Fischer R., Heidasch R., Gardiner C., Evetts S., Hu M., Wade-Martins R., Turner M.R., Morris J., Talbot K., Kessler B.M., Tofaris G.K. 2015. Identification of distinct circulating exosomes in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2(4), 353–361.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to express our gratitude to A.N. Gorshkov (Smorodintsev Research Institute of Influenza) for conducting experiments with transmission electron microscopy.
Funding
The study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project nos. 18-015-00262A (screening of mutations in genes GBA and LRRK2 and assessing the concentration of alpha-synuclein in blood plasma exosomes; 19-315-90059 Postgraduate students (characterization of extracellular vesicles by flow cytometry, Western blotting) and the Russian Science Foundation no. 19-15-00315 (characterization of vesicles by the NTA method in groups of asymptomatic carriers of mutations GBA, patients with GBA-PD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of compliance with standards of research involving humans as subjects. All procedures performed in this work are in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional committee on research ethics and the Declaration of Helsinki 1964 and its subsequent amendments or comparable standards of ethics. Informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Additional information
Abbreviations: PD, Parkinson’s disease; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; LRRK2, leucine repeat enriched kinase 2; GBA, glucocerebrosidase; PDD, PD with dementia; GBA-PD, PD associated with mutations in the GBA gene; LRRK2-PD, PD associated with mutations in the with mutations in the LRRK2 gene; sPD, sporadic PD; AC-GBA, asymptomatic carriers of mutations in the GBA gene; SU, sequential ultracentrifugation; CP, chemical precipitation; NTA, nanoparticle trajectory analysis; TEM, Transmission Electron Microscopy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kulabukhova, D.G., Garaeva, L.A., Emelyanov, A.K. et al. Plasma Exosomes in Inherited Forms of Parkinson’s Disease. Mol Biol 55, 297–303 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S002689332101009X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S002689332101009X