Abstract
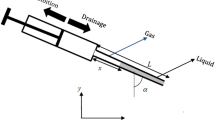
In this paper, we investigate experimentally and numerically the dynamics of the drainage of a transparent capillary tube (radius 0.4 mm). A non-wetting fluid (gas) displaces a wetting fluid (oil). The gas phase is continuously injected at an extremity of the capillary tube (inlet section) at a constant injection-rate \(Q_{inj}\), ranging from 0.1 to 10 ml/h, corresponding to capillary numbers Ca varying between \(5 \cdot 10^{ - 4}\) and \(5 \cdot 10^{ - 2}\). Oil phase, initially filling the tube, leaves the system at the second opened extremity (outlet section).We consider in this work the compressibility of non-wetting fluid (gas), viscous forces in the liquid column, capillary forces and gravity. The effect of several parameters, such as \(Q_{inj}\) j and gravity, on the progress of the gas–liquid interface has been investigated.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birkholzer, J.T., Zhou, Q., Tsang, C.-F.: Large-scale impact of CO2 storage in deep saline aquifers: a sensitivity study on pressure response in stratified systems. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 3, 181–194 (2009)
Cox, B.G.: On driving a viscous fluid out of a tube. J. Fluid Mech. 14, 81 (1962)
Dentz, M., Tartakovsky, D.M.: Abrupt-interface solution for carbon dioxide injection into porous media. Transp. Porous Media 79, 15–27 (2009)
Fallah Abbasi, M., Shokouhmand, H.: Experimental Investigation on Effect of EDL on Heat Transfer of Micro Heat Pipe. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 31, 317–326 (2019)
Frette, V., Feder, J., Jossang, T., Meakin, P., Maloy, K.J.: Fast, immiscible fluid-fluid displacement in three dimensional porous media at finite viscosity contrast. Phys. Rev. E 50, 2881–2890 (1994)
Fries N.: Capillary Transport Processes in Porous Materials – Experiment and Model, CuvillierVerlagGöttingen (2010)
Geistlinger, H., Krauss, G., Lazik, D., Luckner, L.: Direct gas injection into saturated glass beads: transition from incoherent to coherent gas flow pattern. Water Resour. 42, W07403 (2006)
Guo, F., Aryana, S.A.: A Microfluidic Study of Immiscible Drainage Two-Phase Flow Regimes in Porous Media. In: Banerjee S., Barati R., Patil S. (eds) Advances in Petroleum Engineering and Petroleum Geochemistry. Conf. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 2018. Advances in Science, Technology & Innovation (IEREK Interdisciplinary Series for Sustainable Development). Springer, Cham (2019)
Lavi, B., Marmur, A., Bachmann, J.: Capillary Extraction. Langmuir 24(5), 1918–1923 (2008)
Lenormand, R., Touboul, E., Zarcone, C.: Numerical models and experiments on immiscible displacements in porous media. J. Fluid Mech. 189, 165–187 (1988)
Li, P., Fan, M., Sun, L., et al.: Numerical Simulation of Bubble Formation in a Co-Flowing Liquid in Microfluidic Chip. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 32, 1–9 (2020)
Louriou, C., Ouerfelli, H., Prat, M., Najjari, M., Bennasrallah, S.: Gas Injection in a Liquid Saturated Porous Medium. Influence of Gas Pressurization and Liquid Films, Transp. Porous Media 91(1), 153–171 (2012)
Louriou, C.: Modélisation instationnaire des transferts de masse et de chaleur au sein des évaporateurs capillaires. PhD thesis (in French), INPT (2010)
Lucas R.: Ueber das Zeitgesetz des Kapillaren Aufstiegs von Flussigkeiten, KolloidZeitshrift 23, 15–22 (1918)
Masoodi, R., Pillai, K.M.: A general formula for capillary section-pressure in porous media. J. Porous Media 15(8), 775–783 (2012)
Masoodi, R., Pillai, K.M., Varanasi, P.P.: Role of hydraulic and capillary radii in improving the effectiveness of capillary model in wicking, ASME Summer Conference, Jacksonville, FL, USA, August, 0–14 (2008)
Melean, Y., Broseta, D., Blossey, R.: Imbibition fronts in porous media: effects of initial wetting fluid saturation and flow rate. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 39, 327–336 (2003)
Misra, J.C., Mallick, B., Steinmann, P.: Temperature distribution and entropy generation during Darcy–Forchheimer–Brinkman electrokinetic flow in a microfluidic tube subject to a prescribed heat flux. Meccanica 55, 1079–1098 (2020)
Nishikawara, M., Ueda, Y., Yanada, H.: Static and Dynamic Liquid-Vapor Phase Distribution in the Capillary Evaporator of a Loop Heat Pipe. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 31, 61–71 (2019)
Ouerfelli, H., Najjari, M., Bouab, Z., Ben Nasrallah S.: Experimental study of the influence of gravity and injection gas flow rate on drainage in two-dimensional porous media, J. Porous Media 11(8), 781–789 (2008)
Prokopev, S., Vorobev, A., Lyubimova, T.: Phase-field modeling of an immiscible liquid-liquid displacement in a capillary. Phys. Rev. E 99, 033113 (2019)
Serizawa, A., Feng, Z., Kawara, Z.: Two-phase flow in micro-channels. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 26, 703–714 (2002)
Stange, M., Dreyer, M.E., Rath, H.J.: Capillary driven flow in circular cylindrical tubes. Phys. Fluids 15(9), 2587–2601 (2003)
Stark, J., Manga, M.: The motion of long bubbles in a network of tubes. Transp. Porous Media 40, 201–218 (2000)
Taylor, G.I.: Deposition of a viscous fluid on the wall of a tube. J. Fluid Mech. 10, 161 (1961)
Tiwari, A., Chauhan, S.S.: Effect of varying viscosity on a two-layer model of the blood flow through porous blood vessels. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 134, 41 (2019)
Vilarrasa, V., Bolster, D., Dentz, M., Olivella, S., Carrera, J.: Effects of CO2 Compressibility on CO2 Storage in Deep Saline Aquifers. Transp. Porous Media 85(2), 619–639 (2010)
Vorobev, A., Prokopev, S., Lyubimov, T.: Phase-field modelling of a liquid/liquid immiscible displacement through a network of capillaries. J. Comput. Phys. 421, 109747 (2020)
Walls, P.L.L., Dequidt, G., Bird, J.C.: Capillary Displacement of Viscous Liquids. Langmuir 32(13), 3186–3190 (2016)
Wang, T., Li, H.X., Zhao, J.F., Guo, K.K.: Numerical simulation of quasistatic bubble formation from a submerged orifice by the axisymmetric VOSET method. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 31, 1–14 (2019)
Washburn, E.W.: The dynamics of capillary flow. Phys. Rev. 17, 273–283 (1921)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khemili, F., Bahrini, I. & Najjari, M. Oil Drainage in a Capillary Tube: Experimental and Numerical Study. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 33, 33 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-021-09882-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-021-09882-8