Abstract
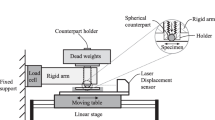
We used Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) for 3D printing of Polylactic acid (PLA) samples, with variation of the printing infill (20% and 100%). Tribological testing was performed on a nanotribometer, under low loads (5, 10, and 15 mN), with a rotating module (ball-on-flat). We studied the friction and wear of PLA samples in two different positions: along the printing direction and normal to the printed direction. The tribological contacts along the printing direction had lower friction coefficient than the contacts that were normal to the printing direction. Samples with 20% infill produced a significantly higher friction coefficient than those with 100% infill. A higher wear factor was exhibited for a dense structure (100% infill) than for a porous material (20% infill). The load increase showed a slight transitional behavior for all types of contacts. The wear factor was on the order of 10–3 mm3/(N m) for all tests.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Narayanan, G., Vernekar, V.N., Kuyinu, E.L., and Laurencin, C.T., Poly (lactic acid)-based biomaterials for orthopaedic regenerative engineering, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2016, vol. 107, pp. 247–276.
Tappa, K., Jammalamadaka, U., Weisman, J.A., Ballard, D.H., Wolford, D.D., Pascual-Garrido, C., Wolford, L.M., Woodard, P.K., and Mill, D.K., 3D printing custom bioactive and absorbable surgical screws, pins, and bone plates for localized drug delivery, J. Funct. Biomater., 2019, vol. 10, no. 2, p. 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb10020017
Upex, P., Jouffroy, P., and Riouallon, G., Application of 3D printing for treating fractures of both columns of the acetabulum: benefit of pre-contouring plates on the mirrored healthy pelvis, Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res., 2017, vol. 103, no. 3, pp. 331–334.
Eutionnat-Diffo, P.A., Chen, Y., Guan, J., Cayla, A., Campagne, C., Zeng, X., and Nierstrasz, V., Stress, strain and deformation of poly-lactic acid filament deposited onto polyethylene terephthalate woven fabric through 3D printing process, Sci. Rep., 2019, vol. 9, art. ID 14333. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50832-7
Hanon, M.M., Kovács, M., and Zsidai, L., Tribology behaviour investigation of 3D printed polymers, Int. Rev. Appl. Sci. Eng., 2019, vol. 10, no. 2, art. ID 173181.
Zhang, P., Hu, Z., Xie, H., et al., Friction and wear characteristics of polylactic acid (PLA) for 3D printing under reciprocating sliding condition, Ind. Lubr. Tribol., 2020, vol. 72, no. 4, pp. 533–539. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-11-2016-0280
Briscoe, B.J. and Sinha, S.K., Wear of polymers, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Part J, 2002, vol. 216, no. 6, pp. 401–413.
Prozhega, M.V., Reschikov, E.O., Shirshov, A.D., and Yakovenko, N.G., Frictional properties of 3D printing polymers in vacuum, J. Frict. Wear, 2020, vol. 41, no. 6, pp. 565–570. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068366620060173
Panda, S., Sarangi, M., and Chowdhury, S.K.R., An analytical model of mechanistic wear of polymers, J. Tribol., 2018, vol. 140, no. 1, art. ID 011609. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4037136
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by A. Muravev
About this article
Cite this article
Zivic, F., Mitrovic, S., Grujovic, N. et al. The Influence of the 3D Printing Infill and Printing Direction on Friction and Wear of Polylactic Acid (PLA) under Rotational Sliding. J. Frict. Wear 42, 106–111 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068366621020124
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068366621020124