Abstract
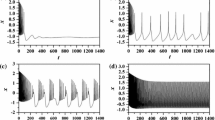
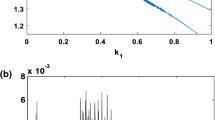
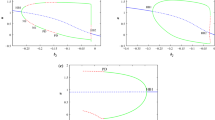
Due to the fluctuation of membrane potential of neuron, there are complex time-varying electromagnetic fields in nervous systems, and the exciting electromagnetic field will further regulate the discharge activities of neurons. In this paper, the coupling of magnetic flux variables to the membrane potential is realised by using a magnetron memristor, and then a 5D extended Hindmarsh–Rose (e-HR) neuron model is established. With the help of Matcont software, the distribution and bifurcation properties of the equilibrium point in the e-HR model is analysed. It is found that there are subcritical Hopf bifurcation, coexisting oscillation modes and hidden limit cycle attractors with period 1 and period 2. In addition, by applying the washout controller, the subcritical Hopf bifurcation point can be transformed into the supercritical Hopf bifurcation point. Thus, the hidden oscillation behaviour of the model can be effectively eliminated. In order to analyse the influence of various parameters on the bifurcation behaviour, numerical simulation of two-parameter bifurcation, single-parameter bifurcation, maximum Lyapunov exponential and time response are given. It is found that the e-HR neuron has a complex bifurcation structure, i.e., the bifurcation structure with period-doubling bifurcations, inverse period-doubling bifurcations, period-adding bifurcations with and without chaos. At the same time, the study also finds that the coexistence behaviour of the periodic cluster discharge and the mixed-mode oscillations (MMOs) can be observed from the bifurcation structure with unique ‘periodic dislocation layer’ on the two-parameter plane. Interestingly, the bursting mode of the system is converted into MMOs when the system parameters are randomly perturbed. The results of this study provide useful insights into the complex discharge patterns and hidden discharge behaviours of neurons under electromagnetic induction.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
E Av-Ron, J H Byrne and D A Baxter, J. Undergrad. Neurosci. Educ. 4, 2 (2006)
G S Wig, B L Schlaggar and S E Petersen, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1224, 1 (2011)
D E Postnov, R N Koreshkov and N A Brazhe, J. Biol. Phys. 35, 4 (2009)
A L Hodgkin and A F Huxley, J. Physiol. 116, 4 (1952)
W E Sherwood and J Guckenheimer, SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 9, 3 (2010)
E M I Izhikevich and R Fitzhugh, Scholarpedia 1, 9 (2006)
P C Rech, Chin. Phys. Lett. 29, 6 (2012)
C Morris and H Lecar, Biophys. J. 35, 1 (1981)
J L Hindmarsh and R M Rose, Proc. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 221, 1222 (1984).
Y Zhao, X Y Sun and Y Liu, Nonlinear Dyn. 93, 1315 (2018)
H G Gu and B B Pan, Nonlinear Dyn. 81, 2107 (2015)
P C Rech, Phys. Lett. A 375, 12 (2011)
G S Yi, J Wang and X L Wei, J. Comput. Neurosci. 36, 3 (2014)
X L Wei, B J Li and M L Lu, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 29, 21 (2015)
J Berzhanskaya, N Chernyy and B J Gluckman, J. Comput. Neurosci. 34, 3 (2012)
H X Qin, J Ma and W Y Jin, Sci. China Technol. Sci. 57, 5 (2014)
D Hu and H Cao, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 26, 11 (2016)
J Ma and J Tang, Sci. China Technol. Sci. 58, 12 (2015)
Y Wang, J Ma and Y Xu, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 27, 02 (2017)
F B Zhan and S Q Liu, Front. Comput. Neurosci. 11, 107 (2017)
M Lv, C-N Wang and G-D Ren, Nonlinear Dyn. 85, 3 (2016)
K M Tang, Z L Wang and X R Shi, Front. Comput. Neurosci. 11, 105 (2017)
X Z Xia, Y C Zeng and Z J Li, Pramana – J. Phys. 91: 82 (2018)
J Wu and S J Ma, Nonlinear Dyn. 96, 1895 (2019)
H Bao, A H Hu and W B Liu, IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31, 2 (2019)
H Fallah, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 26, 09 (2016)
I Bashkirtseva, V Nasyrova and L Ryashko, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 63, 261 (2018)
S Leo Kingston and K Thamilmaran, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 27, 7 (2017)
X B Rao, Y D Chu and L Xu, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 50, 330 (2017)
B Ambrosio, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 27, 05 (2017)
J Rubin and M Wechselberger, Biol. Cybern. 97, 1 (2007)
T Vo, J Tabak and R Bertram, J. Comput. Neurosci. 36, 2 (2014)
M Lv and J Ma, Neurocomputing 205, 4 (2016)
A I Selverston, M I Rabinovich and H D I Abarbanel, J. Physiol. Paris 94, 5 (2000)
E B Megam Ngouonkadi, H B Fotsin and P H Louodop Fotso, Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 24, 05 (2014)
A Moujahid, A d’Anjou and F J Torrealdea, Chaos Solitons Fractals 44, 11 (2011)
E B Megam Ngouonkadi, H B Fotsin and P Louodop Fotso, Chaos Solitons Fractals 85, 2 (2016)
H X Wang, Q Y Wang and Y H Zheng, Sci. China (Technol. Sci.) 57, 872 (2014)
K J Wu, T Q Luo and H W Lu, Neural Comput. Appl. 27, 739 (2016)
J A C Gallas, Mod. Phys. Lett. B 29, 1530018 (2015)
X B Rao, Y D Chu and Y X Chang, Nonlinear Dyn. 88, 4 (2017)
A Wolf, J B Swift and H L Swinney, Physica D 16, 3 (1985)
H Simo, U S Domguia, J K Dutt and P Woafo, Pramana – J. Phys. 92: 3 (2019)
M A Khan, M Nag and S Poria, Pramana – J. Phys. 91, 89 (2018)
Z F Qu, Z D Zhang, P Miao and Q S Bi, Pramana – J. Phys. 91: 72 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (Nos 11962012, 61863022), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2018M633649XB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, S., An, XL. Dynamic response of the e-HR neuron model under electromagnetic induction. Pramana - J Phys 95, 72 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-021-02095-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-021-02095-z
Keywords
- Hopf bifurcation
- hidden attractors
- washout bifurcation control
- two-parameter bifurcation
- mixed-mode oscillations