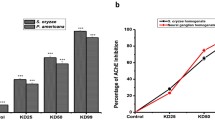
Abstract
The non-target toxicity and resistance problems of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) insecticides, such as organophosphates and carbamates, are of growing concern. To explore the potential targets for achieving inhibitor selectivity, the AChE structures at or near the catalytic pocket of Tetranychus urticae (TuAChE), honey bees, and humans were compared. The entrances to the AChE catalytic pocket differ significantly because of their different peripheral sites. The role of these potential mite-specific sites in AChE function was further elucidated by site-directed mutagenesis of these sites and then examining the catalytic activities of TuAChE mutants. The spider mite E316, H369, and V105 active sites are important for AChE function. By further analyzing their physostigmine inhibitory properties and the detailed interaction between physostigmine and TuAChE, the peripheral site H369 locating near the gorge entrance, and S154 at the oxyanion hole, affects substrate and inhibitor trafficking. The discovery of conserved mite-specific residues in Tetranychus will enable the development of safer, effective pesticides that target residues present only in mite AChEs, potentially offering effective control against this important agricultural pest.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anazawa Y, Tomita T, Aiki Y, Kozaki T, Kono Y (2003) Sequence of a CDNA encoding acetylcholinesterase from susceptible and resistant two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 33:509–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0965-1748(03)00025-0
Barak D, Ordentlich A, Stein D, Yu Q, Greig NH, Shafferman A (2008) Accommodation of physostigmine and its analogues by acetylcholinesterase is dominated by hydrophobic interactions. Biochemical Journal 417:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20081276
Bu C-Y, Feng X-J, Wang X-Q, Cao Y, Wang Y-N, Chen Q, Gao P, Peng B, Li J-L, Han J-Y, Shi G-L (2015a) Cloning and characterization of the acetylcholinesterase1 gene of Tetranychus cinnabarinus (Acari: Tetranychidae). J Econ Entomol 108:769–779. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/tou046
Bu C, Peng B, Cao Y, Wang X, Chen Q, Li J, Shi G (2015b) Novel and selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for Tetranychus cinnabarinus (Acari: Tetranychidae). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 66:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2015.10.012
Cao Y, Li L (2014) Improved protein–ligand binding affinity prediction by using a curvature-dependent surface-area model. Bioinformatics 30(12):1674–1680
Cao Y, Song L, Miao Z, Hu Y, Tian L, Jiang T (2010) Improved side-chain modeling by coupling clash-detection guided iterative search with rotamer relaxation. Bioinformatics 27:785–790. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr009
Carlier PR, Anderson TD, Wong DM, Hsu DC, Hartsel J, Ma M, Wong EA, Choudhury R, Lam PC-H, Totrov MM (2008) Towards a species-selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitor to control the mosquito vector of malaria, Anopheles gambiae. Chem Biol Interact 175:368–375
Cheung J, Mahmood A, Kalathur R, Liu L, Carlier PR (2018) Structure of the g119s mutant acetylcholinesterase of the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae reveals basis of insecticide resistance. Structure 26:130-136.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2017.11.021
Dermauw W, Osborne EJ, Clark RM, Grbić M, Tirry L, Van Leeuwen T (2013) A burst of abc genes in the genome of the polyphagous spider mite Tetranychus urticae. BMC Genomics 14:317. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-317
Dou D, Park JG, Rana S, Madden BJ, Jiang H, Pang Y-P (2013) Novel selective and irreversible mosquito acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for controlling malaria and other mosquito-borne diseases. Sci Rep 3:1068–1068. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01068
Dvir H, Silman I, Harel M, Rosenberry TL, Sussman JL (2010) Acetylcholinesterase: from 3d structure to function. Chem Biol Interact 187:10–22
Goulson D, Nicholls E, Botías C, Rotheray EL (2015) Bee declines driven by combined stress from parasites, pesticides, and lack of flowers. Science 347:1255957. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1255957
Grbić M, Van Leeuwen T, Clark RM, Rombauts S, Rouzé P, Grbić V, Osborne EJ, Dermauw W, Thi Ngoc PC, Ortego F, Hernández-Crespo P, Diaz I, Martinez M, Navajas M, Sucena É, Magalhães S, Nagy L, Pace RM, Djuranović S, Smagghe G, Iga M, Christiaens O, Veenstra JA, Ewer J, Villalobos RM, Hutter JL, Hudson SD, Velez M, Yi SV, Zeng J, Pires-daSilva A, Roch F, Cazaux M, Navarro M, Zhurov V, Acevedo G, Bjelica A, Fawcett JA, Bonnet E, Martens C, Baele G, Wissler L, Sanchez-Rodriguez A, Tirry L, Blais C, Demeestere K, Henz SR, Gregory TR, Mathieu J, Verdon L, Farinelli L, Schmutz J, Lindquist E, Feyereisen R, Van de Peer Y (2011) The genome of Tetranychus urticae reveals herbivorous pest adaptations. Nature 479:487. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10640
Harel M, Kryger G, Rosenberry TL, Mallender WD, Lewis T, Fletcher RJ, Guss JM, Silman I, Sussman JL (2000) Three-dimensional structures of Drosophila melanogaster acetylcholinesterase and of its complexes with two potent inhibitors. Protein Sci 9:1063–1072. https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.9.6.1063
Hetnarski B, O’Brien RD (1975) Electron-donor and affinity constants and their application to the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by carbamates. J Agric Food Chem 23:709–713. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf60200a002
Ilg T, Cramer J, Lutz J, Noack S, Schmitt H, Williams H, Newton T (2011) The characterization of Lucilia cuprina acetylcholinesterase as a drug target, and the identification of novel inhibitors by high throughput screening. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41:470–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2011.04.003
Khajehali J, Van Leeuwen T, Grispou M, Morou E, Alout H, Weill M, Tirry L, Vontas J, Tsagkarakou A (2010) Acetylcholinesterase point mutations in European strains of Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) resistant to organophosphates. Pest Manag Sci 66:220–228. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1884
Khajehali J, Van Nieuwenhuyse P, Demaeght P, Tirry L, Van Leeuwen T (2011) Acaricide resistance and resistance mechanisms in Tetranychus urticae populations from rose greenhouses in The Netherlands. Pest Manag Sci 67:1424–1433. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.2191
Kim S, Chen J, Cheng T, Gindulyte A, He J, He S, Li Q, Shoemaker Benjamin A, Thiessen Paul A, Yu B (2018) Pubchem 2019 update: Improved access to chemical data. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D1102–D1109
Kwon DH, Choi JY, Je YH, Lee SH (2012) The overexpression of acetylcholinesterase compensates for the reduced catalytic activity caused by resistance-conferring mutations in Tetranychus urticae. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 42:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2011.12.003
Lang GJ, Yan Zhu K, Zhang C-X (2012) Can acetylcholinesterase serve as a target for developing more selective insecticides? Curr Drug Targets 13:495–501
Lewis G, Thompson H, Smagghe G (2007) In focus: pesticides and honeybees—the work of the ICP-BR bee protection group. Pest Manag Sci 63:1047–1050
Liu Y, Grimm M, Dai W-T, Hou M-C, Xiao Z-X, Cao Y (2020) CB-dock: a web server for cavity detection-guided protein–ligand blind docking. Acta Pharmacol Sin 41:138–144. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0228-6
Meng X, Li C, Xiu C, Zhang J, Li J, Huang L, Zhang Y, Liu Z (2016) Identification and biochemical properties of two new acetylcholinesterases in the pond wolf spider (Pardosa pseudoannulata). PLoS ONE 11:e0158011. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158011
Migeon A, Ferragut F, Escudero-Colomar LA, Fiaboe K, Knapp M, de Moraes GJ, Ueckermann E, Navajas M (2009) Modelling the potential distribution of the invasive tomato red spider mite, Tetranychus evansi (Acari: Tetranychidae). Exp Appl Acarol 48:199–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-008-9229-8
Pang YP (2007) Species marker for developing novel and safe pesticides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:197–199
Pang YP, Singh SK, Yang G, Leon LT, Mishra RK, Yan ZK, Stephen B, Floyd R (2009) Selective and irreversible inhibitors of aphid acetylcholinesterases: steps toward human-safe insecticides. PLoS ONE 4:e4349
Pang YP, Ekström F, Polsinelli GA, Gao Y, Rana S, Hua DH, Andersson B, Andersson PO, Peng L, Singh SK, Mishra RK, Zhu KY, Fallon AM, Ragsdale DW, Brimijoin S (2009) Selective and irreversible inhibitors of mosquito acetylcholinesterases for controlling malaria and other mosquito-borne diseases. PLoS ONE 4(8):e6851
Pang YP, Brimijoin S, Ragsdale DW, Yan Zhu K, Suranyi R (2012) Novel and viable acetylcholinesterase target site for developing effective and environmentally safe insecticides. Curr Drug Targets 13:471–482
Polsinelli GA, Singh SK, Mishra RK, Suranyi R, Ragsdale DW, Pang Y-P, Brimijoin S (2010) Insect-specific irreversible inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase in pests including the bed bug, the Eastern Yellowjacket, German and American cockroaches, and the confused flour beetle. Chem Biol Interact 187:142–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2010.01.036
Stecker T (2018) Harmful pesticide phaseout calls come as some countries’ use rises. Environment & Energy Report. Bloomberg Inductry Group
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) Autodock vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21334
Van Leeuwen T, Vontas J, Tsagkarakou A, Dermauw W, Tirry L (2010) Acaricide resistance mechanisms in the two-spotted spider mite tetranychus urticae and other important acari: a review. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 40:563–572
Van Leeuwen T, Yamamoto A, Nauen R, Dermauw W (2015) The economic importance of acaricides in the control of phytophagous mites and an update on recent acaricide mode of action research. Pest Biochem Physiol 121:12–21
Wu S, Li M, Tang P-A, Felton GW, Wang J-J (2010) Cloning and characterization of acetylcholinesterase 1 genes from insecticide-resistant field populations of Liposcelis paeta Pearman (Psocoptera: Liposcelididae). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 40:415–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2010.04.001
Xiao-Yue H, Xiao-Feng X, Jin-Jun W, Wei D, Yan-Xuan Z, Han-Jie C, Jin-Yong Z, Gui-Sheng Q, Jun-Hua H, Shao-Li W, Li-Chen Y, Hui-Min S, Rui-Hong S, Jian-Jun G, Wei-Nan W, Ming-Fang G, Jian-Ping Z, Bing-Xu C, Zi-Wei S, Lian-You G (2013) Integrated control techniques for spider mites on important crops. Chin J Appl Entomol 50:321–328
Xu Z, Zhu W, Liu Y, Liu X, Chen Q, Peng M, Wang X, Shen G, He L (2014) Analysis of insecticide resistance-related genes of the carmine spider mite Tetranychus cinnabarinus based on a de novo assembled transcriptome. PLoS ONE 9:e94779–e94779. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0094779
Yang J, Zhang Y (2015) I-TASSER server: new development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res 43:W174–W181
Yang J, Yan R, Roy A, Xu D, Poisson J, Zhang Y (2014) The I-TASSER suite: protein structure and function prediction. Nat Methods 12:7–8
Zhang Y (2008) I-TASSER server for protein 3d structure prediction. BMC Bioinformatics 9:40–40. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-40
Zheng W, Zhang C, Wuyun Q, Pearce R, Li Y, Zhang Y (2019) Lomets 2: improved meta-threading server for fold-recognition and structure-based function annotation for distant-homology proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 47:W429–W436
Acknowledgements
This study was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31670648 and 81973243) and Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 6212004 and 6162004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Cao, Y., Yang, J. et al. Acetylcholinesterase target sites for developing environmentally friendly insecticides against Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Exp Appl Acarol 84, 419–431 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-021-00624-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-021-00624-4