Abstract
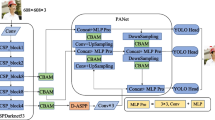
Moving object detection (MOD) is a crucial research topic in the field of computer vision, but it faces some challenges such as shadows, illumination, and dynamic background in practical application. In the past few years, the rise of deep learning (DL) has provided fresh ideas to conquer these issues. Inspired by the existing successful deep learning framework, we design a novel pyramid attention-based architecture for MOD. On the one hand, we propose a pyramid attention module to get pivotal target information, and link different layers of knowledge through skip connections. On the other hand, the dilated convolution block (DCB) is dedicated to obtain multi-scale features, which provides sufficient semantic information and geometric details for the network. In this way, contextual resources are closely linked and get more valuable clues. It helps to obtain a precise foreground in the end. Compared with the existing conventional techniques and DL approaches on the benchmark dataset (CDnet2014), the experiments indicate that the performance of our algorithm is better than previous methods.







Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Huang, R., Zhou, M., Xing, Y., Zou, Y., Fan, W.: Change detection with various combinations of fluid pyramid integration networks. Neurocomputing 437, 84 (2021)
Teng, S., Zhang, S., Huang, Q., Sebe, N.: Multi-view spatial attention embedding for vehicle Re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Vid. 31(2), 816–827 (2021)
Akilan, T., Wu, Q.J., Safaei, A., Huo, J., Yang, Y.: A 3D CNN-LSTM-based image-to-image foreground segmentation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. 21(3), 959–971 (2020)
Chen, Y., Sun, Z., Lam, K.: An effective subsuperpixel-based approach for background subtraction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 67(1), 601–609 (2020)
Minaeian, S., Liu, J., Son, Y.: Effective and efficient detection of moving targets from a UAV’s camera. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. 19(2), 497–506 (2018)
Nie, J., Qu, S., Wei, Y., Zhang, L., Deng, L.: An infrared small target detection method based on multiscale local homogeneity measure. Infrared Phys. Techn. 90, 186–194 (2018)
ElTantawy, A., Shehata, M.S.: Local null space pursuit for real-time moving object detection in aerial surveillance. Signal Image Video Process. 14(1), 87–95 (2020)
Chiu, C., Ku, M., Liang, L.: A robust object segmentation system using a probability-based background extraction algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Vid. 20(4), 518–528 (2010)
Choudhury, S.K., Sa, P.K., Bakshi, S., Majhi, B.: An evaluation of background subtraction for object detection vis-a-vis mitigating challenging scenarios. IEEE Access 4, 6133–6150 (2016)
Zhang, H., Qu, S., Li, H., Luo, J., Xu, W.: A moving shadow elimination method based on fusion of multi-feature. IEEE Access 8, 63971–63982 (2020)
Yu, Y., Kurnianggoro, L., Jo, K.: Moving object detection for a moving camera based on global motion compensation and adaptive background model. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 17(7), 1866–1874 (2019)
Ke, X., Shi, L., Guo, W., Chen, D.: Multi-dimensional traffic congestion detection based on fusion of visual features and convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. 20(6), 2157–2170 (2019)
Sakkos, D., Liu, H., Han, J., Shao, L.: End-to-end video background subtraction with 3d convolutional neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 77(17), 23023–23041 (2018)
Mandal, M., Dhar, V., Mishra, A., Vipparthi, S.K.: 3DFR: a swift 3D feature reductionist framework for scene independent change detection. IEEE Signal Proc. Let. 26(12), 1882–1886 (2019)
C. Stauffer and W.E.L. Grimson.: Adaptive background mixture models for real-time tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 246–252 (1999)
Z. Zivkovic.: Improved adaptive Gaussian mixture model for background subtraction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference Pattern Recognit (ICPR), pp. 28–31 (2004)
A. Elgammal and D. Harwood.: Non-parametric Model for Background Subtraction. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp.751–767 (2000)
S. Liao, G. Zhao, V. Kellokumpu, M. Pietikäinen and S.Z. Li.: Modeling pixel process with scale invariant local patterns for background subtraction in complex scenes. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Third IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1301–1306 (2010)
Barnich, O., Van Droogenbroeck, M.: ViBe: a universal background subtraction algorithm for video sequences. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(6), 1709–1724 (2011)
X. Yiming.: An optimized Vibe target detection algorithm based on gray distribution and Minkowski distance. In: Proceedings of the 32nd Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese Association of Automation, pp. 66–71 (2017)
M. Hofmann, P. Tiefenbacher and G. Rigoll.: Background segmentation with feedback: the pixel-based adaptive segmenter. In: Proceedings of the Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 38–43 (2012)
P. Li and Y. Wang.: An improved vibe algorithm based on visual saliency. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Technology, Electronics and Communication, pp. 603–607 (2017)
St-Charles, P., Bilodeau, G., Bergevin, R.: SuBSENSE: a universal change detection method with local adaptive sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(1), 359–373 (2015)
P. St-Charles, G. Bilodeau and R. Bergevin.: A self-adjusting approach to change detection based on background word consensus. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 990–997 (2015)
Bianco, S., Ciocca, G., Schettini, R.: Combination of video change detection algorithms by genetic programming. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 21(6), 914–928 (2017)
Sajid, H., Cheung, S.S.: Universal multimode background subtraction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(7), 3249–3260 (2017)
M. Braham and M.V. Droogenbroeck.: Deep background subtraction with scene-specific convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing, pp. 1–4 (2016)
Wang, Y., Luo, Z., Jodoin, P.: Interactive deep learning method for segmenting moving objects. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 96, 66–75 (2017)
Patil, P.W., Murala, S.: MSFgNet: a novel compact end-to-end deep network for moving object detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. 20(11), 4066–4077 (2019)
Babaee, M., Dinh, D.T., Rigoll, G.: A deep convolutional neural network for video sequence background subtraction. Pattern Recogn. 76, 635–649 (2018)
R. Wang, Filiz Bunyak, Guna Seetharaman and K. Palaniappan.: Static and moving object detection using flux tensor with split Gaussian models. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 420–424 (2014)
Yang, L., Li, J., Luo, Y., Zhao, Y., Cheng, H., Li, J.: Deep background modeling using fully convolutional network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. 19(1), 254–262 (2018)
Chen, Y., Wang, J., Zhu, B., Tang, M., Lu, H.: Pixelwise deep sequence learning for moving object detection. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Vid. 29(9), 2567–2579 (2017)
S. Ioffe and C. Szegedy.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift, (2015)
Li, A., Qi, J., Lu, H.: Multi-attention guided feature fusion network for salient object detection. Neurocomputing 411, 416–427 (2020)
O. Ronneberger, P. Fischer and T. Brox.: U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the MICCAI, pp. 234–241 (2015)
Y. Wang, P. Jodoin, F. Porikli, J. Konrad, Y. Benezeth and P. Ishwar.: CDnet 2014: an expanded change detection benchmark dataset. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, pp. 393–400 (2014)
V. Mondéjar-Guerra, J. Rouco and J. Novo.: an end-to-end deep learning approach for simultaneous background modeling and subtraction. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, pp. 1–12 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61673190/F030101, and in part by the Self-Determined Research Funds of Central China Normal University (CCNU) from the Colleges’ Basic Research and Operation of the Ministry of Education (MOE) under Grant CCNU18TS042.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, S., Zhang, H., Wu, W. et al. Symmetric pyramid attention convolutional neural network for moving object detection. SIViP 15, 1747–1755 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01920-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01920-7