Abstract
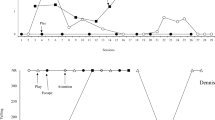
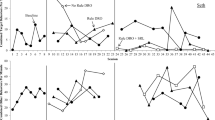
Differential reinforcement of other behavior (DRO) is a commonly used reinforcement-based system for reducing problem behavior. DRO systems are particularly useful in that they are effective for the treatment of maladaptive behavior and can be individualized based on the needs of the learner. One possible way to enhance the effectiveness of DRO systems is the use of signaled delays. In the present study, the effectiveness of signaled and unsignaled DRO systems was compared for the treatment of stereotypical behavior in three adolescents and adults diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Results from this study suggested that while the unsignaled DRO condition was effective at reducing stereotypical behavior for one of three participants, the signaled DRO condition was effective for all three participants.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association 2013 Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders 5 American Psychiatric Publishing
Bergstrom, R., Tarbox, J., & Gutshall, K. A. (2011). Behavioral intervention for domestic pet mistreatment in a young child with autism. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 5, 218–211.
Campbell, J. M. (2003). Efficacy of behavioral interventions for reducing problem behavior in persons with autism: A quantitative synthesis of single-subject research. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 24, 120–138.
DeLeon, I. G., & Iwata, B. (1996). Evaluation of a multiple-stimulus presentation format for assessing reinforcer preferences. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 29(4), 519–533.
Della Rosa, K. A., Fellman, D., DeBiase, C., DeQuinzio, J. A., & Taylor, B. A. (2015). The effects of using a conditioned stimulus to cue DRO schedules. Behavioral Interventions, 30, 219–230.
Hagopian, L. P., Bruzek, J. L., Bowman, L. G., & Jennett, H. K. (2007). Assessment and treatment of problem behavior occasioned by interruption of free-operant behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 40(1), 89–103.
Hammond, J. L., Iwata, B. A., Fritz, J. N., & Dempsey, C. M. (2011). Evaluation of fixed momentary DRO schedules under signaled and unsignaled arrangements. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 44(1), 69–81.
Harris, S. L., & Wolchik, S. A. (1979). Suppression of self-stimulation: Three alternative strategies. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 12(2), 185–198.
Hill, A. P., Zuckerman, K. E., Hagen, A. D., Kriz, D. J., Duvall, S. W., van Santen, J., & Fombonne, E. (2014). Aggressive behavior problems in children with autism spectrum disorders: Prevalence and correlates in a large clinical sample. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 8(9), 1121–1133.
Homer, A. L., & Peterson, L. (1980). Differential reinforcement of other behavior: A preferred response elimination procedure. Behavior Therapy, 11, 449–471.
Iwata, B., Dorsey, M. F., Slifer, K. J., Bauman, K. E., & Richman, G. S. (1982). Toward a functional analysis of self-injury. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 2(1), 3–20.
Jessel, J., & Ingvarsson, E. T. (2016). Recent advances in applied research on DRO procedures. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 49(4), 991–995.
Kahng, S., Abt, K. A., & Schonbachler, H. E. (2001). Assessment and treatment of low-rate high-intensity problem behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 34(2), 225–228.
Kelley, M. E., Lerman, D. C., Fisher, W. W., Roane, H. S., & Zangrillo, A. N. (2011). Reinforcement delay fading during differential reinforcement of communication: The effects of signals on response maintenance. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 96(1), 107–122.
Lennox, D. B., Miltenberger, R. G., Spengler, P., & Erfanian, N. (1988). Decelerative treatment practices with persons who have mental retardation: A review of five years of literature. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 92(6), 492–501.
Nuernberger, J. E., Vargo, K. K., & Ringdahl, J. E. (2013). An application of differential reinforcement of other behavior and self-monitoring to address repetitive behavior. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 25, 105–117.
Querim, A. C., Iwata, B. A., Roscoe, E. M., Schlichenmeyer, K. J., Ortega, J. V., & Hurl, K. E. (2013). Functional analysis screening for problem behavior maintained by automatic reinforcement. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 46(1), 47–60.
Rapp, J. T., Cook, J. L., McHugh, C., & Mann, K. R. (2017). Decreasing stereotypy using NCR and DRO with functionally matched stimulation: Effects on targeted and non-targeted stereotypy. Behavior Modification, 41(1), 45–83.
Repp, A. C., Barton, L. E., & Brulle, A. R. (1983). A comparison of two procedures for programming the differential reinforcement of other behaviors. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 16(4), 435–445.
Rozenblat, E., Brown, J. L., Brown, A. K., Reeve, S. A., & Reeve, K. F. (2009). Effects of adjusting DRO schedules on the reduction of stereotypic vocalizations in children with autism. Behavioral Interventions, 24, 1–15.
Schaal, D. W., & Branch, M. N. (1988). Responding of pigeons under variable-interval schedules of unsignaled, briefly signaled, and completely signaled delays to reinforcement. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 50, 33–54.
Schaal, D. W., & Branch, M. N. (1990). Responding of pigeons under variable-interval schedules of signaled-delayed reinforcement: Effects of delay-signal duration. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 53, 103–121.
Schaal, D. W., & Branch, M. N. (1992). Key pecking of pigeons under variable-interval schedules of briefly signaled delayed reinforcement: Effects of variable-interval value. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 58, 277-286.Scheuermann, B., Webber, J., Boutat, E. A., & Goodwin, M. (2003). Problems with personnel preparation in autism spectrum disorders. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 18(3), 197-206
Sisson, L. A., Van Hasselt, V. B., Hersen, M., & Aurand, J. C. (1988). Tripartite behavioral intervention to reduce stereotypic behaviors in young multi-handicapped children. Behavior Therapy, 19, 503–526.
Watts, A. C., Wilder, D. A., Gregory, M. K., Leon, Y., & Ditzian, K. (2013). The effect of rules on differential reinforcement of other behavior. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 3(46), 680–684.
Weston, R., Hodges, A., & Davis, T. N. (2018). Differential reinforcement of other behaviors to treat challenging behaviors among children with autism: A systematic and quality review. Behavior Modification, 42(4), 584–609.
Funding
No funding was received for the current study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Confict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The procedures involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maraventano, J.C., Kishel, C.B., LaRue, R.H. et al. The Effects of Signaled Delays on the Effectiveness of Differential Reinforcement of Other Behavior (DRO) Reinforcement Systems. J Behav Educ 32, 51–63 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-021-09441-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-021-09441-6