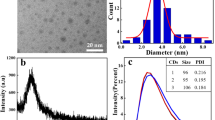
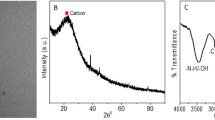
Abstract
Carbon dots (CDots) are characterized by their optical properties including strong absorptions, bright fluorescence emissions, and electron acceptor and donor behaviors in the visible spectrum. In this study, aconitic acid and oligomeric polyethyleneimine were used as precursors to prepare PEI/AA-CDots by vigorous microwave-assisted thermal carbonization. The as-prepared CDots exhibit excitation wavelength-dependent fluorescence with a quantum yield of 44.2% at the excitation wavelength of 380 nm. In addition, the fluorescence in the visible spectrum can be selectively and efficiently quenched by Cu2+ or Hg2+ ions via electron transitions due to the electron donor behaviors of the as-prepared CDots. The detection limits of Cu2+ and Hg2+ ions are 70 and 84 nM, respectively. The quenched fluorescence can be recovered by introducing aspartic acid or L-cysteine into the PEI/AA-CDots-Cu2+ or the PEI/AA-CDots-Hg2+ systems. Furthermore, the as-prepared PEI/AA-CDots can be successfully applied for detecting Cu2+ and Hg2+ ions in real water and can serve as a potential candidate as a probe for detecting these metal ions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.P. Sun, B. Zhou, Y. Lin, W. Wang, K.A.S. Fernando, P. Pathak, M.J. Meziani, B.A. Harruff, X. Wang, H. Wang, P.G. Luo, H. Yang, M.E. Kose, B. Chen, L.M. Veca, S.Y. Xie, Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 7756–7757 (2006)
Y.P. Sun, Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles. U.S. Patent 7,829,772 (2010)
L. Cao, M.J. Meziani, S. Sahu, Y.P. Sun, Photoluminescence properties of graphene versus other carbon nanomaterials. Acc. Chem. Res. 46, 171–180 (2013)
G.E. LeCroy, S.T. Yang, F. Yang, Y. Liu, K.A.S. Fernando, C.E. Bunker, Y. Hu, P.G. Luo, Y.P. Sun, Functionalized carbon nanoparticles: syntheses and applications in optical bioimaging and energy conversion. Coord. Chem. Rev. 320, 66–81 (2016)
H. Li, X. Yan, D.S. Kong, R. Jin, C. Sun, D. Du, Y. Lin, G. Lu, Recent advances in carbon dots for bioimaging applications. Nanoscale Horiz. 5, 218–234 (2020)
D. Wang, X. Mei, S. Wang, J. Li, C. Dong, A one-pot synthesis of fluorescent N, P-codoped carbon dots for vitamin B12 determination and bioimaging application. New J. Chem. 45, 3508–3514 (2021)
N. Dhenadhayalan, K.C. Lin, T.A. Saleh, Recent advances in functionalized carbon dots toward the design of efficient materials for sensing and catalysis applications. Small 16, 1905767 (2020)
X. Yue, Z. Zhou, Y. Wu, M. Jie, Y. Li, H. Guo, Y. Bai, A green carbon dots-based fluorescent sensor for selective and visual detection of nitrite triggered by the nitrite-thiol reaction. New J. Chem. 44, 8503–8511 (2020)
Z. Zhang, G. Yi, P. Li, X. Zhang, H. Fan, Y. Zhang, X. Wang, C. Zhang, A minireview on doped carbon dots for photocatalytic and electrocatalytic applications. Nanoscale 12, 13899–13906 (2020)
Z. Zhu, P. Yang, X. Li, M. Luo, W. Zhang, M. Chen, Green preparation of palm powder-derived carbon dots co-doped with sulfur/chlorine and their application in visible-light photocatalysis. Spectrochim. Acta. Part A 227, 117659 (2020)
T. Feng, S. Tao, D. Yue, Q. Zeng, W. Chen, B. Yang, Recent advances in energy conversion applications of carbon dots: from optoelectronic devices to electrocatalysis. Small 16, 2001295 (2020)
E.A. Stepanidenko, E.V. Ushakova, A.V. Fedorov, A.L. Rogach, Applications of carbon dots in optoelectronics. Nanomaterials 11, 364 (2021)
F. Zhao, J. Qian, F. Quan, C. Wu, Y. Zheng, L. Zhou, Aconitic acid derived carbon dots as recyclable “on–off–on” fluorescent nanoprobes for sensitive detection of mercury(II) ions, cysteine and cellular imaging. RSC Adv. 7, 44178–44185 (2017)
S. Dinç, M. Kara, M.D. Kars, F. Aykül, H. Çiçekci, M. Akkuş, Biocompatible yogurt carbon dots: evaluation of utilization for medical applications. Appl. Phys. A 123, 572 (2017)
Y. Park, Y. Kim, H. Chang, S. Won, H. Kim, W. Kwon, Biocompatible nitrogen-doped carbon dots: synthesis, characterization, and application. J. Mater. Chem. B 8, 8935–8951 (2020)
H. Eskalen, Influence of carbon quantum dots on eletro-optical performance of nematic liquid crystal. Appl. Phys. A 126, 708 (2020)
R. Wang, K.-Q. Lu, Z.-R. Tang, Y.-J. Xu, Recent progress in carbon quantum dots: synthesis, properties and applications in photocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 3717–3734 (2017)
S.Y. Lim, W. Shen, Z. Gao, Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 362–381 (2015)
A. Verhagen, A. Kelarakis, Carbon dots for forensic applications: a critical review. Nanomaterials 10, 1535 (2020)
M.J. Molaei, Principles, mechanisms, and application of carbon quantum dots in sensors: a review. Anal. Methods 12, 1266–1287 (2020)
G.E. LeCroy, S.K. Sonkar, F. Yang, L.M. Veca, P. Wang, K.N.I.I. Tackett, J.J. Yu, E. Vasile, H. Qian, Y. Liu, P. Luo, Y.-P. Sun, Toward structurally defined carbon dots as ultracompact fluorescent probes. ACS Nano 8, 4522–4529 (2014)
C. Zhang, M. Liu, T. Li, S. Liu, Q. Chen, J. Zhang, K. Zhang, One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of dual-emission fluorescent carbon dots for hypochlorous acid detection. Dyes Pigments 180, 108507 (2020)
T.N.J.I. Edison, R. Atchudan, N. Karthik, D. Xiong, Y.R. Lee, Facile hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen rich blue fluorescent carbon dots for cell bio-imaging of Candida Albicans. Process Biochem. 88, 113–119 (2020)
J. Xu, L. Dai, C. Zhang, Y. Gui, L. Yuan, Y. Lei, B. Fan, Ionic liquid-aided hydrothermal treatment of lignocellulose for the synergistic outputs of carbon dots and enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 305, 123043 (2020)
K. Qin, D. Zhang, Y. Ding, X. Zheng, Y. Xiang, J. Hua, Q. Zhang, X. Ji, B. Li, Y. Wei, Applications of hydrothermal synthesis of escherichia coli derived carbon dots in in Vitro and in Vivo imaging and p-nitrophenol detection. Analyst 145, 177–183 (2020)
P. Brachi, Synthesis of carbon dots (CDs) through the fluidized bed thermal treatment of residual biomass assisted by γ-alumina. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 263, 118361 (2020)
P.D. Khavlyuk, E.A. Stepanidenko, D.P. Bondarenko, D.V. Danilov, A.V. Koroleva, A.V. Baranov, V.G. Maslov, P. Kasak, A.V. Fedorov, E.V. Ushakova, A.L. Rogach, The influence of thermal treatment conditions (solvothermal versus microwave) and solvent polarity on the morphology and emission of phloroglucinol-based nitrogen-doped carbon dots. Nanoscale 13, 3070–3078 (2021)
G. Sayan, D. Poushali, I. Ella, H. Elad, G. Aharon, M. Shlomo, Microwave-synthesized polysaccharide-derived carbon dots as therapeutic cargoes and toughening agents for elastomeric gels. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 46, 51940–51951 (2020)
D. Qu, Z. Sun, The formation mechanism and fluorophores of carbon dots synthesized via a bottom-up route. Mater. Chem. Front. 4, 400–420 (2020)
M.J. Krysmann, A. Kelarakis, P. Dallas, E.P. Giannelis, Formation mechanism of carbogenic nanoparticles with dual photoluminescence emission. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 747–750 (2012)
L. Ge, N. Pan, J. Jin, P. Wang, G.E. LeCroy, W. Liang, L. Yang, L.R. Teisl, Y. Tang, Y.P. Sun, Systematic comparison of carbon dots from different preparations: consistent optical properties and photoinduced redox characteristics in visible spectrum and structural and mechanistic implications. J. Phys. Chem. C 12, 21667–21676 (2018)
H.A. Nguyen, I. Srivastava, D. Pan, M. Gruebele, Unraveling the fluorescence mechanism of carbon dots with sub-single-particle resolution. ACS Nano 14, 6127–6137 (2020)
M. Fu, F. Ehrat, Y. Wang, K.Z. Milowska, C. Reckmeier, A.L. Rogach, J.K. Stolarczyk, A.S. Urban, J. Feldmann, Carbon dots: a unique fluorescent cocktail of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Nano Lett. 15, 6030–6035 (2015)
Y. Song, S. Zhu, S. Zhang, Y. Fu, L. Wang, X. Zhao, B. Yang, Investigation from chemical structure to photoluminescent mechanism: a type of carbon dots from the pyrolysis of citric acid and an amine. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 5976–5984 (2015)
Q. Dan, Z. Sun, The formation mechanism and fluorophores of carbon dots synthesized via a bottom-up. Mater. Chem. Front. 4, 400–420 (2020)
L. Shi, J.H. Yang, H.B. Zeng, Y.M. Chen, S.C. Yang, C. Wu, H. Zeng, O. Yoshihito, Q. Zhang, Carbon dots with high fluorescence quantum yield: the fluorescence originates from organic fluorophores. Nanoscale 8, 14374–14378 (2016)
K. Jiang, Y. Wang, Z. Li, H. Lin, Afterglow of carbon dots: mechanism, strategy and applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 4, 386–399 (2020)
F. Ehrat, S. Bhattacharyya, J. Schneider, A. Löf, R. Wyrwich, A.L. Rogach, J.K. Stolarczyk, A.S. Urban, J. Feldmann, Tracking the source of carbon dot photoluminescence: aromatic domains versus molecular fluorophores. Nano Lett. 17, 7710–7716 (2017)
U.S. Enviromental Protetcion Agency. Health effects of overexposure to the Sun. Air and radiation, EPA 430-F-10-026 (2021). https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/documents/healtheffects_1.pdf
D. Li, J. Huang, R. Li, P. Chen, D. Chen, M. Cai, H. Liu, Y. Feng, W. Lv, G. Liu, Synthesis of a carbon dots modified g-C3N4/SnO2 Z-scheme photocatalyst with superior photocatalytic activity for PPCPs degradation under visible light irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 401, 123257 (2021)
U.S. Enviromental Protetcion Agency. National primary drinking water regulations. Ground water and drinking water, EPA 916-F-09-004 (2009). https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2016-06/documents/npwdr_complete_table.pdf
W. Liang, E.B. Christopher, Y.P. Sun, Carbon dots: zero-dimensional carbon allotrope with unique photoinduced redox characteristics. ACS Omega 5, 965–971 (2020)
H.R.H. Ali, A.I. Hassan, Y.F. Hassan, M.M. EI-Wekil, Development of dual function polyamine-functionalized carbon dots derived from one step green synthesis for quantitation of Cu2+ and S2− ions in complicated matrices with high selectivity. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 412, 1353–1363 (2020)
M. Pajewska-Szmyt, B. Buszewki, R. Gadzała-Kopciuch, Carbon dots as rapid assays for detection of mercury (II) ions based on turn-off mode and breast milk. Spectrochim. Acta A 236, 118320 (2020)
K. Patir, S.K. Gogoi, Nitrogen-doped carbon dots as fluoresence on–off–on sensor for parallel detection of copper (II) and mercury (II) ions in solutions as well as in filter paper-based. Nanoscale Adv. 1, 591–601 (2019)
X. Ren, W. Liang, P. Wang, C.E. Bunker, M. Coleman, L.R. Teisl, L. Cao, Y.-P. Sun, A new approach in functionalization of carbon nanoparticles for optoelectronically relevant carbon dots and beyond. Carbon 141, 553–560 (2019)
I.B. Berlman, Handbook of Fluoresence Spectra of Aromatic Molecules, 2nd edn. (Academic Press, 1971).
S. Zhu, Q. Meng, L. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Song, H. Jin, K. Zhang, H. Sun, H. Wang, B. Yang, Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit 125, 4045–4049 (2013)
Y. Sun, S. Liu, L. Sun, S. Wu, G. Hu, X. Pang, A.T. Smith, C. Hu, S. Zeng, W. Wang, Y. Liu, M. Zheng, Ultralong lifetime and efficient room temperature phosphorescent carbon dots through multi-confinement structure design. Nat. Commun. 11, 5591 (2020)
G. Qiao, L. Liu, X. Hao, J. Zheng, W. Liu, J. Gao, C.C. Zhang, Q. Wang, Signal transduction from small particles: sulfur nanodots featuring mercury sensing, cell entry mechanism and in vitro tracking performance. Chem. Eng. J. 382, 122907 (2020)
F. Yang, G.E. LeCroy, P. Wang, W. Liang, J. Chen, K.A.S. Fernando, C.E. Bunker, H. Qian, Y.P. Sun, Functionalization of carbon nanoparticles and defunctionalization-toward structural and mechanistic elucidation of carbon “Quantum” dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 25604–25611 (2016)
Y. Hu, M.M. Al Awak, F. Yang, S. Yan, Q. Xiong, P. Wang, Y. Tang, L. Yang, G.E. LeCroy, X. Hou, C.E. Bunker, H. Qian, Y.-P. Sun, Photoexcited state properties of carbon dots from thermally induced functionalization of carbon nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 10554–10561 (2016)
S. Liu, J. Tian, L. Wang, H. Li, Y. Zhang, X. Sun, Stable aqueous dispersion of graphene nanosheets: noncovalent functionalization by a polymeric reducing agent and their subsequent decoration with Ag nanoparticles for enzymeless hydrogen peroxide detection. Macromolecules 43, 10078–10083 (2021)
T. Lai, E. Zheng, L. Chen, X. Wang, L. Kong, C. You, Y. Ruan, X. Weng, Hybrid carbon source for producing nitrogen-doped polymer nanodots: one-pot hydrothermal synthesis, fluorescence enhancement and highly selective detection of Fe(III). Nanoscale 5, 8015–8021 (2013)
S. Fleutot, J.C. Dupin, G. Renaudin, H. Martinez, Intercalation and grafting of benzene derivatives into zinc–aluminum and copper–chromium layered double hydroxide hosts: an XPS monitoring study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13, 17564–17578 (2011)
M. Sevilla, A.B. Fuertes, Chemical and structural properties of carbonaceous products obtained by hydrothermal carbonization of saccharides. Chem. Eur. J. 15, 4195–4203 (2009)
J. Peng, W. Gao, B.K. Gupta, Z. Liu, R. Romero-Aburto, L. Ge, L. Song, B.L. Alemany, X. Zhan, G. Gao, S.A. Vithayathil, B.A. Kaipparettu, A.A. Marti, T. Hayashi, J.J. Zhu, P.M. Ajayan, Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano. Lett. 2, 844–849 (2012)
D.I.A. Rabe, M.M.A. Awak, F. Yang, P.A. Okonjo, X. Dong, L.R. Teisl, P. Wang, Y. Tang, N. Pan, Y.-P. Sun, L. Yang, The dominant role of surface functionalization in carbon dots’ photo-activated antibacterial activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 14, 2655–2665 (2019)
F. Yang, X. Ren, G.E. LeCroy, J. Song, P. Wang, L. Beckerle, C.E. Bunker, Q. Xiong, Y.P. Sun, Zero-dimensional carbon allotropes—carbon nanoparticles versus fullerenes in functionalization by electronic polymers for different optical and redox properties. ACS Omega 3, 5685–5691 (2018)
Y. Chen, Z. Rosenzweig, Luminescent CdS quantum dots as selective ion probes. Anal. Chem. 74, 5132–5138 (2002)
F. Wang, Z. Gu, W. Lei, W. Wang, X. Xia, Q. Hao, Graphene quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing platform for highly efficient detection of copper (II) ions. Sensor Actuat. B Chem. 190, 516–522 (2014)
G. Hu, L. Ge, Y. Li, M. Mukhtar, B. Shen, D. Yang, Carbon dots derived from flax straw for highly sensitive and selective detections of cobalt, chromium, and ascorbic acid. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 579, 96–108 (2020)
L. Sun, D. Hao, W. Shen, Z. Qian, C. Zhu, Highly sensitive fluorescent sensor for copper (II) based on amplified fluorescence quenching of a water-soluble NIR emitting conjugated polymer. Microchim. Acta 177, 357–364 (2012)
J.M. Liu, L.P. Lin, X.X. Wang, S.Q. Lin, W.L. Cai, L.H. Zhang, Z.Y. Zheng, Highly selective and sensitive detection of Cu2+ with lysine enhancing bovine serum albumin modified-carbon dots fluorescent probe. Chem. Eng. J. 137, 2637–2642 (2012)
Acknowledgments
Gansu Province Science Foundation for Youths (20JR10RA104) and Gansu Province Science Foundation for Youth Teachers (2020B-092) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, L., Hu, G., Zhao, F. et al. Carbon dots prepared by thermal reactions and selective detections of copper and mercury ions in visible spectrum. Appl. Phys. A 127, 388 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04545-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04545-2