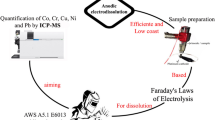
Abstract
In Lead-acid batteries, there are significant efforts to enhance battery performance, mainly by reducing metal impurities that negatively affect battery performance. Currently implemented impurity analysis requires significant time and effort. Wet chemical preparation method is not only hazardous due to the extensive use of acids, but generates environmental pollutants and hazardous waste which require more costly and comprehensive disposal processes. In industry, it is desirable to reduce sample processing and analysis time to improve productivity and efficiency. Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (LA-ICP-MS) is a technique that has the potential to overcome the above issues. In this work, we demonstrate an analysis of impurities (Cu, As, Cd, Co, Se, and Te) in lead-based samples at the ppm/sub-ppm level by the LA-ICP-MS method and verify with matrix matching an accurate quantification of the impurity concentrations of interest. The resulting data, which determines to reduce analysis time more than 50% due to simple preparation step while not as accurate concentration as traditional ICP-MS with at least two times increment of relative standard deviation, provides a reasonable level of accuracy and precision in a substantially quick, cost-effective method that is viable for a high throughput industrial setting.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gad-Allah AG, Salih SA, Mokhtar AA, El-Rahman HAA (2013) Effect of As, Cu and Sb impurities on performance of Pb-Ca-Sn grids of lead-acid batteries. Mater Werkst 44:832–838. https://doi.org/10.1002/mawe.201300071
Nakamura K, Shiomi M, Takahashi K, Tsubota M (1996) Failure modes of valve-regulated lead/acid batteries. J Power Sources 59:153–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-7753(95)02317-8
Ronglong C, Shousong W (1993) Lead alloys for maintenance-free and sealed lead/acid batteries. J Power Sources 46:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-7753(93)90029-Z
Kwiecien M, Schröer P, Kuipers M, Sauer DU (2017) Current research topics for lead–acid batteries. In: Garche J, Karden E, Moseley PT, Rand DAJ (eds) Lead-acid batteries for future automobiles. Elsevier, pp 133–146
Clough TJ, Wertz JA (2001) Life and capacity improvements in lead acid batteries through metal control additives. In: Sixteenth annual battery conference on applications and advances. Proceedings of the conference, pp 87–92
David Prengaman R (1993) Metallurgy of recycled lead for recombinant batteries. J Power Sources 42:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-7753(93)80134-B
Buldini PL, Laghi A, Saxena P et al (1989) The influence of traces of impurities in the lead-acid battery electrolytes. In: Conference Proceedings. Eleventh international telecommunications energy conference, vol 2, pp 17.1/1–17.1/7
Kubaszewski Ł, Zioła-Frankowska A, Frankowski M et al (2014) Atomic absorption spectrometry analysis of trace elements in degenerated intervertebral disc tissue. Med Sci Monit Int Med J Exp Clin Res 20:2157–2164. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.890654
Palisoc ST, Bentulan JMO, Natividad MT (2019) Determination of trace heavy metals in canned food using Graphene/AuNPs/[Ru(NH3)6]3+/Nafion modified glassy carbon electrodes. J Food Meas Charact 13:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-018-9930-1
Hong YS, Choi JY, Nho EY et al (2019) Determination of macro, micro and trace elements in citrus fruits by inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), ICP–mass spectrometry and direct mercury analyzer. J Sci Food Agric 99:1870–1879. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9382
Bussan D, Harris A, Douvris C (2019) Monitoring of selected trace elements in sediments of heavily industrialized areas in Calcasieu Parish, Louisiana, United States by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES). Microchem J 144:51–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.08.053
Solovyev N, Ala A, Schilsky M et al (2019) Biomedical copper speciation in relation to Wilson’s disease using strong anion exchange chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.11.033
Arı B, Can SZ, Bakırdere S (2019) Traceable and accurate quantification of iron in seawater using isotope dilution calibration strategies by triple quadrupole ICP-MS/MS: characterization measurements of iron in a candidate seawater CRM. Talanta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120503
Lorenc W, Markiewicz B, Kruszka D et al (2019) Study on speciation of As, Cr, and Sb in bottled flavored drinking water samples using advanced analytical techniques IEC/SEC-HPLC/ICP-DRC-MS and ESI-MS/MS. Molecules 24:668. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040668
Kinoshita M, Fuyuto T, Akatsuka H (2019) Measurement of vibrational and rotational temperature in spark-discharge plasma by optical emission spectroscopy: change in thermal equilibrium characteristics of plasma under air flow. Int J Engine Res 20:746–757. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468087418791684
Peng X, Guo X, Ge F, Wang Z (2019) Battery-operated portable high-throughput solution cathode glow discharge optical emission spectrometry for environmental metal detection. J Anal At Spectrom 34:394–400. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8JA00369F
Zhang J, Zhou T, Tang Y et al (2018) Rapid and quantitative analysis of impurities in silicon powders by glow discharge mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:7195–7201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1324-z
Stehrer T, Heitz J, Pedarnig JD et al (2010) LA-ICP-MS analysis of waste polymer materials. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:415–424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3963-6
Resano M, García-Ruiz E, Vanhaecke F (2005) Laser ablation–inductively coupled plasma–dynamic reaction cell–mass spectrometry for the multi-element analysis of polymers. Spectrochim Acta Part B At Spectrosc 60:1472–1481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2005.09.006
East Penn Manufacturing | Sustainability in design and manufacturing. In: East Penn Manuf. https://www.eastpennmanufacturing.com/about/sustainability/
Hydrochloric acid 339253. In: 7647-01-0. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sigald/339253
Nitric acid 695041. In: 7697-37-2. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sial/695041
Somenath M, Roman B (2014) Sample preparation: an analytical perspective. In: Somenath M (ed) Sample preparation techniques in analytical chemistry, Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/sepspec.462education
Wilschefski S, Baxter M (2019) Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: introduction to analytical aspects. Clin Biochem Rev 40:115–133. https://doi.org/10.33176/AACB-19-00024
Liu Y, Hu Z, Li M, Gao S (2013) Applications of LA-ICP-MS in the elemental analyses of geological samples. Chin Sci Bull 58:3863–3878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-013-5901-4
Sussulini A, Becker JS, Becker JS (2017) Laser ablation ICP-MS: application in biomedical research. Mass Spectrom Rev 36:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1002/mas.21481
Salit ML, Turk GC (2005) Traceability of single-element calibration solutions. Anal Chem 77:136 A-141 A. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac053354n
Hibbert DB (2006) Metrological traceability: I make it 42; you make it 42; but is it the same 42? Accredit Qual Assur 11:543–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00769-006-0177-x
Imai H (2013) Expanding needs for metrological traceability and measurement uncertainty. Measurement 46:2942–2945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2013.04.046
Raimondo T, Payne J, Wade B et al (2017) Trace element mapping by LA-ICP-MS: assessing geochemical mobility in garnet. Contrib Mineral Petrol 172:17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-017-1339-z
Russo RE, Mao X, Liu H et al (2002) Laser ablation in analytical chemistry—a review. Talanta 57:425–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(02)00053-X
Kroll WJ (1945) Melting and evaporating metals in a vacuum. Trans Electrochem Soc 87:571–587. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.3071666
MacDougall D, Crummett WB et al (1980) Guidelines for data acquisition and data quality evaluation in environmental chemistry. Anal Chem 52:2242–2249. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac50064a004
Nič M, Jirát J, Košata B et al (2009) Limit of detection in analysis. In: IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2.1.0. IUPAC, Research Triangle Park, NC
Long GL, Winefordner JD (1983) Limit of detection a closer look at the IUPAC definition. Anal Chem 55:712A–724A. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00258a724
Müller W, Shelley M, Miller P, Broude S (2009) Initial performance metrics of a new custom-designed ArF excimer LA-ICPMS system coupled to a two-volume laser-ablation cell. J Anal Spectrom 24:209–214. https://doi.org/10.1039/B805995K
Lehmann EL, Arruda MAZ (2019) Minimalist strategies applied to analysis of forensic samples using elemental and molecular analytical techniques—a review. Anal Chim Acta 1063:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.02.003
Russo R (2002) Laser ablation in analytical chemistry—a review. Talanta 57:425–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(02)00053-X
Evertz M, Schwieters T, Börner M et al (2017) Matrix-matched standards for the quantification of elemental lithium ion battery degradation products deposited on carbonaceous negative electrodes using pulsed-glow discharge-sector field-mass spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 32:1862–1867. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7JA00129K
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Center for Resource Recovery and Recycling (CR3) at WPI. We acknowledge helpful discussions with Brian Rauch from East Penn Manufacturing Co, Camille Fleuriault, Joe Grogan, and Benjamin Rodrigue from Gopher Resource, Paul Kennedy from Global Mineral Recovery, Mark Bauer from GM, and Bert Coletti from Metallo-Belgium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
The contributing editor for this article was Hiromichi Takebe.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bong, S., Azhari, L. & Wang, Y. Laser Ablation Inductive Coupled Plasma Mass Spectroscopy (LA-ICP-MS) Analysis on Lead-Acid Battery System: Development of Evaluation Method of Sub-ppm Metal Impurity Elements. J. Sustain. Metall. 7, 610–619 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-021-00369-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40831-021-00369-9