Abstract
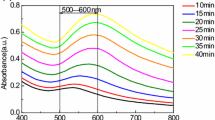
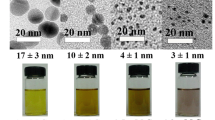
A series of gold nanoparticles were synthesized by stepwise growth method under the condition of citrate as a reducing agent and stabilizer. The optical properties with the maximum absorption wavelength (λmax) and electrochemical properties of the oxidation potential (Ep) dependence on the particle size were analyzed. The method of calculating the particle size from the UV-visible spectrum and the electrochemical oxidation peak was deduced, following the theoretical prediction trend and consistent with previous observations. Furthermore, we investigated the application performance based on the electrochemical catalytic activity and the aggregation of the spherical gold nanoparticles using L-cysteine as a target. The results indicated that the optical and electrochemical properties of the gold nanoparticles to L-cysteine were closely related to the particle size of gold nanoparticles. With the increased size of the nanoparticles, the full width at half maximum in the UV-visible absorption spectrum increased and the electrochemical oxidation potential was positively shifted.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beisl S, Miltner A, Friedl A (2017) Lignin from micro-to nanosize: production methods. Int J Mol Sci 18:1244
Xu T, Zhang NH, Nichols L, Shi D, Wen X (2007) Modification of nanostructured materials for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C 27:579–594
Hashmi ASK, Hutchings GJ (2006) Gold catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:7896–7936
Wang N, Zhao W, Zhang M, Cao P, Sun S, Ma H, Lin M (2021) Bismuth-induced synthesis of Au-X (X=Pt, Pd) nanoalloys for electrocatalytic reactions. Chem Commun 57:391–394
Kooij ES, Poelsema B (2006) Shape and size effects in the optical properties of metallic nanorods. Phys Chem Chem Phys 8:3349–3357
Dutta J, Hofmann H (2003) Nanomaterials. Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, E-book:9–20
Yang XY, Hu WY, Liu FS, Li Y (2012) Atomistic simulation for the size-dependent melting behaviour of vanadium nanowires. J Phys D Appl Phys 45:485304–485312
Cui ZX, Zhao MZ, Lai WP, Xue YQ (2011) Thermodynamics of size effect on phase transition temperatures of dispersed phases. J Phys Chem C 115:22796–22803
Wei XC, Bhojappa S, Lin LS, Viadero RC (2012) Performance of nano-magnetite for removal of selenium from aqueous solutions. Environ Eng Sci 29:526–532
Okubo M, Hosono E, Kudo T, Zhou HS, Honma I (2009) Size effect on electrochemical property of nanocrystalline LiCoO2 synthesized from rapid thermal annealing method. Solid State Ionics 180:612–615
Mogensen KB, Kneipp K (2014) Size-dependent shifts of plasmon resonance in silver nanoparticle films using controlled dissolution: monitoring the onset of surface screening effects. J Phys Chem C 118:28075–28083
McGuire MM, Edwards KJ, Banfield JF, Hamers RJ (2001) Kinetics, surface chemistry, and structural evolution of microbially mediated sulfide mineral dissolution. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:1243–1258
Haiss W, Thanh NTK, Aveyard J, Fernig DG (2007) Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-Vis spectra. Anal Chem 79:4215–4221
Masitas RA, Allen SL, Zamborini FP (2016) Size-dependent electrophoretic deposition of catalytic gold nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 138:15295–15298
Plieth WJ (1982) Electrochemical properties of small clusters of metal atoms and their role in the surface enhanced Raman scattering. J Phys Chem 86:3166–3170
Redmond PL, Hallock AJ, Brus LE (2005) Electrochemical Ostwald ripening of colloidal Ag particles on conductive substrates. Nano Lett 5:131–135
Henglein A (1993) Physicochemical properties of small metal particles in solution: “microelectrode” reactions, chemisorption, composite metal particles, and the atom-to-metal transition. J Phys Chem 97:5457–5471
Frens G (1973) Nature. Phys Sci 241:20–22
Kimling J, Maier M, Okenve B, Kotaidis V, Ballot H, Plech A (2006) Turkevich method for gold nanoparticle synthesis revisited. J Phys Chem B 110:15700–15707
Bastús NG, Comenge J, Puntes V (2011) Kinetically controlled seeded growth synthesis of citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: size focusing versus ostwald ripening. Langmuir. 27:11098–11105
Ivanova OS, Zamborini FP (2010) Electrochemical size discrimination of gold nanoparticles attached to glass/indium-tin-oxide electrodes by oxidation in bromide-containing electrolyte. Anal Chem 82:5844–5850
Shelley EJ, Ryan D, Johnson SR, Couillard M, Fitzmaurice D, Nellist PD, Chen Y, Palmer RE, Preece JA (2002) Dialkyl sulfides: novel passivating agents for gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 18:1791–1795
Hasan M, Bethell D, Brust M (2002) The fate of sulfur-bound hydrogen on formation of self-assembled thiol monolayers on gold: 1H-NMR spectroscopic evidence from solutions of gold clusters. J Am Chem Soc 125:1132–1133
Zhang X, Deng J, Shi G, Zhou T (2015) Valence-tautomeric infinite coordination polymer nanoparticles for encapsulation of rhodamine B and its potential application for colorimetric and fluorescence dual sensing of hypochlorite. RSC Adv 5:107964–107969
Brown KR, Walter DG, Natan MJ (2000) Seeding of colloidal Au nanoparticle solutions. 2. Improved control of particle size and shape. Chem Mater 12:306–313
Khanna PK, Gokhale R, Subbarao VVVS, Vishwanath AK, Das BK, Satyanarayana CVV (2005) PVA stabilized gold nanoparticles by use of unexplored albeit conventional reducing agent. Mater Chem Phys 92:229–233
Qiu H, Xue L, Ji G, Zhou G, Huang X, Qu Y, Gao P (2009) Enzyme-modified nanoporous gold-based electrochemical biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 24:3014–3018
Liu Z, Zhang H, Hou S, Ma H (2012) Highly sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of l-cysteine using nanoporous gold. Microchim Acta 177:427–433
Fawcett WR, Fedurco M, Kovácová Z, Borkowska Z (1994) Oxidation of cysteine, cysteinesulfinic acid cysteic acid on a polycrystalline gold electrode. J Electroanal Chem 368:265–274
Koryta J, Pradac J (1968) Electrode processes of the sulfhydryl-disulfide system: II. Cystine at a gold electrode J Electroanal Chem 17:177–183
Wain AJ (2013) Imaging size effects on the electrocatalytic activity of gold nanoparticles using scanning electrochemical microscopy. Electrochim Acta 92:383–391
Rhee CK, Kim BJ, Ham C, Kim YJ, Song K, Kwon K (2009) Size effect of Pt nanoparticles on catalytic activity in oxidation of methanol and formic acid: comparison to Pt (111), Pt (100), and polycrystalline Pt electrodes. Langmuir. 25:7140–7147
Funding
This work was supported by the Young Scholars Program of Shandong University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, P., Wang, N., Chen, D. et al. Size-dependent optical and electrochemical properties of gold nanoparticles to L-cysteine. Gold Bull 54, 97–103 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13404-021-00296-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13404-021-00296-3