Abstract
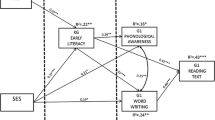
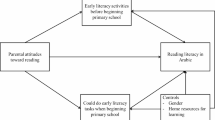
The study focuses on the beliefs of Arabic-speaking mothers in Israel relating to early literacy, and the relations between their beliefs and their children’s actual early literacy skills. Participants included 113 mothers and their 5–6-year-old preschool children. At the families’ homes, mothers reported about the richness of the home literacy environment (HLE), their general beliefs relating to the importance of the literacy environment and their specific estimations of their child’s letter knowledge, phonological awareness, word writing and reading. In preschools, we assessed children’s letter knowledge, phonological awareness, word writing and reading. Results showed that mothers were aware of their children’s early literacy skills yet they over-estimated them. In a series of hierarchical regression analyses, we found that family socio-economic status (SES) significantly explained all of the children’s early literacy skills. Beyond SES, richness of the HLE contributed to most of the assessed literacy skills. Mothers’ general beliefs regarding the importance of the HLE and their estimation of their child’s literacy skills explained children’s skills beyond SES and HLE. The study has educational implications relating to the promotion of children’s early literacy skills in Arabic within the family.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhadi, S., Ibrahim, R., & Eviatar, Z. (2011). Perceptual load in the reading of Arabic: Effects of orthographic visual complexity on detection. Writing Systems Research, 3(2), 117–127. https://doi.org/10.1093/wsr/wsr014
Abu Ahmad, H. (2015). Psycholinguistic and pedagogical aspects of learning to read among speakers of Arabic: An experimental investigation (Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Haifa, Israel). (in Hebrew)
Abu-Rbia, S., & Taha, H. (2006). Reading in Arabic orthography: Characteristics, research findings, and assessment. In P. G. Aaron & M. Joshi (Eds.), Handbook of orthography and literacy (pp. 321–338). Lawrence Erlbaum.
Ahmeida, F. (2009). The impact of a rich print environment on the development of awareness of the written language amongst preschoolers. Jordanian Journal of Science and Education, 5(1), 59–69 (In Arabic).
Alimat, A. L., & M, H. . (2013). The degree of parental practice of reading, writing and emotional readiness skills among pre-school children. Al-Manara Magazine, 19(1), 105–137 (In Arabic).
Al Nab'a Informatics Network. (2018). https://m.annabaa.org/arabic/mediareports/17629.
Al-Bahiri, G., & Mahfouzi, A. (2014). Review of important studies relating to the acquisition of basic skills in reading Arabic. Arab Organization of Education, Culture, and Science, Tunisia. (In Arabic)
Altun, D., Erden, T., Snow, F., & C. . (2018). A multilevel analysis of home and classroom literacy environments in relation to preschoolers’ early literacy development. Psychology in the Schools, 55(9), 1098–1120. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.22153
Amare, M., & Mari, A. (2004). Language education policy towards Arab residents of Israel. Darassat Center for Arabic Literature, Beit Berl. (In Arabic)
Anderson, J., Anderson, A., & Shapiro, J. (2006). Parents’ beliefs about young children’s literacy development and parents’ literacy behaviors. Reading Psychology, 27(1), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/02702710500468708
Aram, D. (2008). Predictors of maternal writing mediation to kindergartners: Analysis via a twins study (pp. 43–68). In Ramirez RN (Ed.) Family relations issues and challenges. NY: Nova Science Publishers.
Aram, D., Korat, O., & Levin, I. (2006). Maternal mediation in a young child’s writing activity: A sociocultural perspective. In R. M. Joshi & P. G. Aaron (Eds.), Handbook of orthographyand literacy (pp. 709–733). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Aram D, Korat O & Hassunah-Arafat, S. (2013). The contribution of early home literacy activities to first grade reading and writing achievements in Arabic. Springer: Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-013-9430-y.
Aram. D, & Levin, I. (2001). Mother-child joint writing in low SES: Sociocultural factors, maternal mediation, and emergent literacy. Cognitive Development, 16, 831–852.
Aram, D., & Levin, I. (2016). Mother-child joint writing as a learning activity. In J. Perera, M. Aparici, E. Rosado & N. Salas (Eds.) and M. Joshi (Series Ed.). Literacy studies. Perspectives from cognitive neurosciences, linguistics, psychology and education (pp. 29–45). Springer: New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21136-7_3.
Ayari, S. (1996). Diglossia and illiteracy in the Arab word. Language Culture and Curriculum, 9, 243–253. https://doi.org/10.1080/07908319609525233
Azazaia, C. (2000). Fluency in reading and reading comprehension—mediating factors. Academic College of Arabic.
Barnyak, N. C. (2011). A qualitative study in a rural community: Investigating the attitudes, beliefs, and interactions of young children and their parents regarding storybook read alouds. Early Childhood Education Journal, 39(2), 149–159
Bentin, S., & Ibrahim, R. (1996). New evidence for phonological processing during visual word recognition: The case of Arabic. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 22(2), 309–323. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.22.2.309
Bingham, G. E. (2007). Exploring the role of maternal literacy beliefs in mother child joint book reading and home literacy environments. Early Education and Development, 18(1), 23–49. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409280701274428
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development. Harvard University Press.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1986). Ecology of the family as a context for human development: Research perspectives. Developmental Psychology, 22, 723–742. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.22.6.723
Burgess, R. B., Hecht, S. A., & Lonigan, C. J. (2002). Relations of the home literacy environment (HLE) to the development of reading-related abilities: A one year longitudinal study. Reading Research Quarterly, 37(4), 408–426. https://doi.org/10.1598/RRQ.37.4.4
Carretti, B., Borella, E., Cornoldi, C., & De Beni, R. (2009). Role of working memory in explaining the performance of individuals with specific reading difficulties: A meta-analysis. Learning and Individual Differences, 19(2009), 246–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2008.10.002
Carroll, J. M., Holliman, A. J., Weir, F., & Baroody, A. E. (2019). Literacy interest, home literacy environment and emergent literacy skills in preschoolers. Journal of Research in Reading, 42(1), 150–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9817.12255
Catts, H. W. (2009). The narrow view of reading promotes a broad view of comprehension. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 40(2), 178–183. https://doi.org/10.1044/0161-1461(2008/08-0035)
Chambré, S. J., Ehri, L. C., & Ness, M. (2017). Orthographic facilitation of first graders’ vocabulary learning: Does directing attention to print enhance the effect? Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 30(5), 1137–1156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-016-9715-z
Chamorro-Premuzic, T., Arteche, A., Furnham, A., & Trickot, N. (2009). Assessing pupils’ intelligence through self, parental, and teacher estimates. Educational Psychology, 29, 83–97. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410802520662
Cunningham, A. E., & Zilbulsky, J. (2010). Tell me a story: Examining the benefits of shared reading. In S. B. Neuman (Ed.), Handbook of early literacy research (3rd ed., pp. 396–411). Guilford Press.
Curenton, S. M., & Justice, L. M. (2008). Children’s pre-literacy skills: Influence of mothers’ education and beliefs about shared-reading interactions. Early Education and Development, 19(2), 261–283. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409280801963939
Daniels, P. T., & Share, D. L. (2018). Writing system variation and its consequences for reading and dyslexia. Scientific Studies of Reading, 22(1), 101–116
Davoodi, S., Akbarnezhad, S., & Sadighi, F. (2017). Home literacy environment and reading achievement: The case of Persian and Arab children. Journal of Applied Linguistics and Language Research, 4(2), 131–138
Davis, H. S., Gonzalez, J. E., Pollard-Durodola, S., Saenz, L. M., Soares, D. A., Resendez, N., Zhu, L., & Hagan-Burke, S. (2016). Home literacy beliefs and practices among low-income Latino families. Early Child Development and Care, 186(7), 1152–1172
DeBaryshe, B. D., Binder, J. C., & Buell, M. J. (2000). Mothers’ implicit theories of early literacy instruction: Implications for children’s reading and writing. Early Child Development and Care, 160, 119–131. https://doi.org/10.1080/0030443001600111
Ehri, L. C., Nunes, S. R., Stahl, S. A., & Willows, D. M. (2001). Systematic phonics instruction helps students learn to read: Evidence from the National Reading Panel’s meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 71(3), 393–447. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543071003393
Elimelech, A., Aram, D., & Levin, I. (2019). Mothers teaching their children the Hebrew written code: The effects on children's early writing and reading skills. In A. Rui, & M. Joshi (Eds.) Reading-writing connections: Towards integrative literacy science.
Eviatar, Z., & Ibrahim, R. (2000). Bilingual is as bilingual does: Metalinguistic abilities of Arabic-speaking children. Applied Psycholinguistics, 21(4), 451–471. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0142716400004021
Eviatar, Z., Ibrahim, R., & Ganayim, D. (2004). Orthography and the hemispheres: Visual and linguistic aspects of letter processing. Neuropsychology, 18(1), 174–184. https://doi.org/10.1037/0894-4105.18.1.174
Gaffen, S. (2011). Strengthening reading: Report of basic Yemenite. Ministry of Education.
Glascoe, F. P. (1999). The value of parents’ concerns to detect and address developmental and behavioural problems. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health, 35, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1754.1999.00342.x
Gough, P. B., Hoover, W. A., & Peterson, C. L. (1996). Some observations on a simple view of reading. In C. Cornoldi, & J. Oakhill (Eds.) Reading comprehension difficulties (pp. 1–13). Erlbaum.
Goodnow, J. J. (2002). Parents’ knowledge and expectations: Using what we know. In M. Bornstein (Ed.), Handbook of parenting: Being and becoming a parent (pp. 439–460). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Guo, Y., Puranik, C., Kelcey, B., Sun, J., Dinnesen, M. S., & Breit-Smith, A. (2020). The role of home literacy practices in kindergarten children’s early writing development: A one-year longitudinal study. Early Education and Development. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409289.2020.1746618
Hadad Haj-Yahya, N. & Bachar Cohen, Y. (2019). The Arab population in Israel in numbers. The Israel Democracy Institute. https://www.idi.org.il/books/26352.
Hassunah-Arafat, S. (2010). Maternal mediation during a shared book-reading activity and contribution to children’ literacy in kindergarten and first grade: Evidence from the Arab family. Unpublished doctoral dissertation. Bar-Ilan University, Israel [Hebrew].
Hassunah Arafat, S., Korat, O., Aram, D., & Saiegh-Haddad, E. (2017). Continuity in literacy development from kindergarten to first grade: A longitudinal study of Arabic speaking children. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 30, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-016-9709-x.
Hassunah Arafat, S., Sarssur., M., Korat, O., Aram, D. (2021). Early literacy among Arab children. In F. Nasser-Abu & M. Israelashvili (Eds.) Education in Arab Society in Israel. Tel Aviv: Mofet [Hebrew].
Hindi, N. (2012). From literacy in preschool to reading in second grade in Arabic (Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Tel Aviv University, Israel). (in Hebrew).
Ibrahim, R., Eviatar, Z., & Aharon-Peretz, J. (2007). Metalinguistic awareness and reading performance: A cross language comparison. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 36(4), 97–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-006-9046-3
Ibrahim, Z. (2010). Some of the mental and social variables related to reading readiness in preschoolers (Unpublished thesis, El-Zakaik University, Egypt).
Ferguson, C. A. (1959). Diglossia. Word, 15(2), 325–340. https://doi.org/10.1080/00437956.1959.11659702
Fernald, A., Marchman, V. A., & Weisleder, A. (2013). SES differences in language processing skill and vocabulary are evident at 18 months. Developmental Science, 16(2), 234–248. https://doi.org/10.1111/desc.12019
Fitzgerald, J., Spiegel, D. L., & Cunningham, J. W. (1991). The relationship between parental literacy level and perceptions of emergent literacy. Journal of Reading Behavior, 23(2), 191–213
Fuchs, H., & Friedman-Wilson, T. (2018). Integration of Arab women in the workforce: Education, employment, and salary. Taub Center for Social Policy Studies in Israel. http://taubcenter.org.il/wp-content/files_mf/arabisraeliwomen.pdf.
Furnham, A., & Valgeirsson, H. (2007). Parents’ estimations of their own intelligence and that of their children: A comparison between English and Icelandic parents. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 48, 289–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9450.2007.00587.x
Israeli Ministry of Education. (2008). Preschool language curriculum. http://cms.education.gov.il/EducationCMS/Units/Tochniyot_Limudim/ArabicKdamYesodi/tochnyot/ChinuchLeshoni.htm.
Jamallah-Nasser, H. (2008). Impact of letter name knowledge on early writing development amongst Arabic-speaking preschoolers: An intervention study (Unpublished Master’s thesis, Tel Aviv University, Israel). (in Hebrew)
Kareeri, M. (2013). The role of visual media in the acquisition of written Arabic for children: The model of the Spacetoon television station (Lecture delivered at the First International Conference on Arabic Language, Beirut, Lebanon).
Kardosh, L. (2016). The development of phonological awareness among native Arabic-speaking kindergarten children (Unpublished Master's thesis, University of Haifa, Israel). (in Hebrew)
Kårstad, S. B., Kvello, Ø., Wichstrøm, L., & Berg‐Nielsen, T. S. (2014). What do parents know about their children's comprehension of emotions? Accuracy of parental estimates in a community sample of pre‐schoolers. Child: Care, Health and Development, 40(3), 346–353.
Koch, H., Kastner-Koller, U., Deimann, P., Kossmeier, C., Koitz, C., & Steiner, M. (2011). The development of kindergarten children as evaluated by their kindergarten teachers and mothers. Psychological Test and Assessment Modeling, 53(2), 241–257
Korat, O. (2004). Mothers' and teachers' attributions of the academic functioning of Israeli second graders: acomparison between social groups. Early Childhood Research Quarterly. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2004.07.001.
Korat, O. (2005). Contextual and non-contextual knowledge in emergent literacy development: A comparison between children from low SES and middle SES communities. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 20(2), 220–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2005.04.009.
Korat, O. (2009). How accurate can mothers and teachers be regarding children's emergent Literacy development? A comparison between mothers with high and low education. Early Child Development and Care, 179(1), 27–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004430600879232.
Korat, O. (2011). Mothers' and teachers' estimations of first graders' literacy level and their relation to the children's actual performance in different SES groups. Education and Treatment of Children, 34(3), 347-371. https://doi.org/10.1353/etc.2011.0021
Korat, O. & Haglili, S. (2007). Maternal evaluations of children’s emergent literacy level, maternal mediation in book reading, and children’s emergent literacy level: A comparison between SES groups. Journal of Literacy Research 39, 249–276. https://doi.org/10.1080/10862960701331993.
Korat, O., Hassunah Arafat, S., Aram, D., & Klein, P. (2012). Book reading mediation, SES, home literacy environment and children’s literacy: Evidence from Arabic-speaking families. First Language, 33(2), 132–154. https://doi.org/10.1177/0142723712455283.
Korat, O., & Levin, I. (2001). Maternal beliefs, mother-child interaction, comparison of independent and collaborative text writing between two social group. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology 22, 397–420.
McBride-Chang, C. (2014). The development of phonological processing and language for reading. In Children’s literacy development (pp. 22–45). Texts in Developmental Psychology, University of London.
Meagher, S. M., Arnold, D. H., Doctoroff, G. L., & Baker, C. N. (2008). The relationship between maternal beliefs and behavior during shared reading. Early Education and Development, 19, 138–160. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409280701839221
Midraj, S., & Midraj, J. (2011). Parental involvement and grade four students’ Arabic reading achievement. European Journal of Educational Studies, 3(2), 245–260
National Institute for Literacy [NIFL]. (2008). Developing early literacy: A scientific synthesis of early literacy development and implications for intervention. Report of the National Early Literacy Panel. http://lincs.ed.gov/publications/pdf/NELPReport09.pdf.
Neuman, S. B., Kaefer, T., & Pinkham, A. M. (2018). A double dose of disadvantage: Language experiences for low-income children in home and school. Journal of Educational Psychology, 110(1), 102–118. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000201
OECD (2010). PISA 2009 key findings. https://www.oecd.org/pisa/pisaproducts/pisa2009keyfindings.htm
Puccioni, J. (2018). Parental beliefs about school readiness, home and school-based involvement, and children’s academic achievement. Journal of Research in Childhood Education, 32(4), 435–454. https://doi.org/10.1080/02568543.2018.1494065
Ravid, D. (2002). Language and literacy in the transition from preschool to school. In P. Klein, & D. Givon (Eds.), Language learning and literacy in early childhood (pp. 43–70). Tel Aviv University.
Robins, S., Treiman, R., & Rosales, N. (2014). Letter knowledge in parent–child conversations. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 27(3), 407–429
Rodriguez, E. T., Tamis-LeMonda, C. S., Spellmann, M. E., Pan, B. A., Raikes, H., Lugo-Gil, J., & Luze, G. (2009). The formative role of home literacy experiences across the first three years of life in children from low-income families. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 30(6), 677–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2009.01.003
Saiegh-Haddad, E. (2018). MAWRID: A model of Arabic word reading in development. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 51, 454–462. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219417720460
Saiegh-Haddad, E. (2017). Learning to read in Arabic. In L. Verhoeven & C. Perfetti (Eds.), Reading acquisition across languages and writing systems: An international handbook (pp. 127–154). Cambridge University Press.
Saiegh-Haddad, E. (2012). Literacy reflexes of Arabic diglossia. In M. Leikin, M. Schwartz, & Y. Tobin (Eds.), Current issues in Bilingualism: Cognitive and sociolinguistic perspectives (pp. 43–55). Springer.
Saiegh-Haddad, E. (2008). The challenge diglossia poses for children acquiring basic reading processes in Arabic: Review and hypothesis. Language and Literacy, 1, 105–126 (in Hebrew).
Saiegh-Haddad, E. (2007). Epilinguistic and metalinguistic phonological awareness may be subject to different constraints: Evidence from Hebrew. First Language, 27(4), 385–405
Sarsour, M. (2013). The impact of learning letter names on alphabet and phonological awareness skills in a diglossic language: A training study amongst Hebrew-speaking preschoolers in Israel (Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Tel Aviv University, Israel).
Sartawi, A., Tibi, S. & Abidat, R. (2006). Level of parents’ involvement in preliteracy skills with their preschoolers in the United Arab Emirates. http://www.gulfkids.com/ar/book34-939.htm.
Sawyer, B. E., Cycyk, L. M., Sandilos, L. E., & Hammer, C. S. (2018). ‘So many books they don’t even all fit on the bookshelf’: An examination of low-income mothers’ home literacy practices, beliefs and influencing factors. Journal of Early Childhood Literacy, 18(3), 338–372. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468798416667542
Segal, A., & Martin-Chang, S. (2018). The apple doesn’t fall from the tree: parents’ reading-related knowledge and children’s reading outcomes. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 31(5), 1231–1247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-018-9837-6
Sénéchal, M., & LeFevre, J. (2002). Parental involvement in the development of children’s reading skill: A five-year longitudinal study. Child Development, 73, 445–460. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00417
Share, D. L., & Daniels, P. T. (2016). Aksharas, alphasyllabaries, abugidas, alphabets and orthographic depth: Reflections on Rimzhim, Katz and Fowler (2014). Writing Systems Research, 8(1), 17–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/17586801.2015.1016395
Skibbe, L. E., Justice, L. M., Zucker, T. A., & McGinty, A. S. (2008). Relations among maternal literacy beliefs, home literacy practices, and the emergent literacy skills of preschoolers with specific language impairment. Early Education and Development, 19, 68–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409280701839015
Sonnenschein, S., Stapleton, L. M., & Metzger, S. R. (2014). What parents know about how well their children are doing in school. The Journal of Educational Research, 17, 152–162. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2013.788987
Sonnenschein, S., & Munsterman, K. (2002). The influence of home based reading interactions 5-years’ reading motivations and early literacy development. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 17(3), 318–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0885-2006(02)00167-9
Taieh, A. (2016). Educational beliefs and literacy practices of Arab kindergarten teachers following the implementation of a new literacy curriculum in Israel (Unpublished Master’s thesis, Tel Aviv University). (in Hebrew).
Taibah, N. J., & Haynes, C. W. (2011). Contributions of phonological processing skills to reading skills in Arabic speaking children. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 24(9), 1019–1042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-010-9273-8
Tibi, S. (2010). Developmental hierarchy of Arabic phonological awareness skills. International Journal of Special Education, 25(1), 27–33
Treiman, R. (2017). Learning to spell words: Findings, theories, and issues. Scientific Studies of Reading, 21(4), 265–276. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888438.2017.1296449
Vasilyeva, M., Dearing, E., Lvanova, A., Shen, C., & Kardanova, E. (2018). Testing the family investment model in Russia: Estimating indirect effects of SES and parental beliefs on the literacy skills of first-graders. Journal of Early Childhood Literacy, 42, 11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2017.08.003
Weigel, D. J., Martin, S. S., & Bennett, K. K. (2006). Contributions of the home literacy environment to preschool-aged children’s emerging literacy and language skills. Early Child Development and Care, 176(3–4), 357–378. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004430500063747
Yassin, R., Share, D. L., & Shalhoub-Awwad, Y. (2020). Learning to spell in Arabic: The impact of script-specific visual-orthographic features. Frontiers in Psychology, 11(2059), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.02059
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Suha Atamna for her contribution in thinking about the course of the research and collecting the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassunah-Arafat, S.M., Aram, D. & Korat, O. Early literacy in Arabic: the role of SES, home literacy environment, mothers’ early literacy beliefs and estimation of their children’s literacy skills. Read Writ 34, 2603–2625 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10158-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10158-1