Abstract
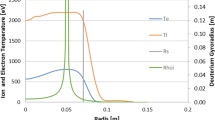
The interaction between graphite particles and argon plasma in the arc torch is investigated by numerical simulations. The addition of carbon vapor improves the specific heat capacity, electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity of plasma, and decreases its viscosity. It is important to note that the changes in the thermodynamic and transport properties of the plasma substantially affect the arc plasma temperature and the spatial distribution of the carbon vapor concentration. As the graphite particle feed rate increases, the arc will be continuously contracted and the arc electric current density will be increased. The carbon vapor enhances the plasma electrical conductivity, but the heat absorption by the particles reduces the temperature of the plasma, eventually leading to decreased the electrical conductivity. Both result in ascent of the electric field of the arc, so that increase the arc voltage. In addition, the heat flux radial distribution of radiation-absorption of the particles is much less than the thermal conduction, but the particles near the wall absorb radiation from arc region, so that reduce energy loss of the radiation of the arc column.














Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
All data and materials as well as software application support their published claims and comply with field standards.
Code Availability
Custom code support their published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Liu SH, Trelles JP, Murphy AB, Li L, Zhang SL, Yang GJ, Li CX, Li CJ (2019) J Phys D Appl Phys 52:335203
Chen J, Cheng Y (2009) J Chem Eng Jpn 42:s103–s110
Yugeswaran S, Selvarajan V, Seo D, Ogawa K (2008) Surf Coat Technol 203:129–136
Wan YP, Fincke JR, Sampath S, Prasad V, Herman H (2002) Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:1007–1015
Yang K, Rong J, Feng JW, Zhuang Y, Zhao HY, Wang L, Ni JX, Tao SY, Shao F, Ding CX (2017) Surf Coat Technol 326:96–102
Gulyaev I (2015) Ceram Int 41:101–107
Ye R, Proulx P, Boulos MI (2000) J Phys D Appl Phys 33:2154
Ye R, Ishigaki T, Jurewicz J, Proulx P, Boulos M (2004) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 24:555–571
Shigeta M, Watanabe T, Nishiyama H (2004) Thin Solid Films 457:192–200
http://www.mettech.com/coating-equipment/axial-III-plasma-spray-system.php
Ma J, Su BG, Wen GD, Yang QW, Ren QL, Yang YW, Xing HB (2017) Fuel Process Technol 167:721–729
Wang C, Cui HC, Li WW, Liao MR, Xia WL, Xia WD (2017) Chin Phys B 26:025202
Todorović-Marković B, Marković Z, Mohai I, Nikolić Z, Farkas Z, Szépvölgyi J, Kováts É, Scheier P, Feil S (2006) J Phys D Appl Phys 39:320
Wang C, Imahori T, Tanaka Y, Sakuta T, Takikawa H, Matsuo H (2001) Thin Solid Films 390:31–36
Szépvölgyi J, Marković Z, Todorović-Marković B, Nikolić Z, Mohai I, Farkas Z, Tóth M, Kováts É, Scheier P, Feil S (2006) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 26:597–608
Delbos C, Fazilleau J, Rat V, Coudert JF, Fauchais P, Pateyron B (2006) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 26:393–414
Saito H, Suzuki T, Fujino T, Suzuki M (2018) Mater Trans 59:1791–1797
Gawne D, Liu B, Bao Y, Zhang T (2005) Surf Coat Technol 191:242–254
Lee Y, Pfender E (1987) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 7:1–27
Mostaghimi-Tehrani J, Pfender E (1984) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 4:129–139
Chen X, Chyou Y, Lee YC, Pfender E (1985) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 5:119–141
Proulx P, Mostaghimi J, Boulos MI (1985) Int J Heat Mass Transfer 28:1327–1336
Suzuki T, Saito H, Fujino T (2018) IEEE T Plasma Sci 47:688–700
Bauchire J, Gonzalez J, Proulx P (1999) J Phys D Appl Phys 32:675
Proulx P, Mostaghimi J, Boulos MI (1987) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 7:29–52
Li HP, Chen X (2002) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 22:27–58
Xu DY, Wu XC, Chen X (2003) Surf Coat Technol 171:149–156
Pan ZH, Ye L, Qian SL, Sun Q, Wang C, Ye TH, Xia WD (2019) Plasma Sci Technol 22:025401
Wilke C (1950) J Chem Phys 18:517–519
ANSYS 2009 ANSYS FLUENT 12.0 Theory Guide (Canonsburg, PA)
Huang R, Fukanuma H, Uesugi Y, Tanaka Y (2012) J Therm Spray Technol 21:636–643
Han P, Chen X (2001) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 21:249–264
Bauchire J, Gonzalez J, Gleizes A (1997) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 17:409–432
Godin D, Trépanier J (2004) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 24:447–473
Wang WZ, Rong MZ, Murphy AB, Wu Y, Spencer JW, Yan JD, Fang MT (2011) J Phys D Appl Phys 44:355207
Pan WX, Meng X, Wu CK (2006) Plasma Sci Technol 8:416
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11675177 and 11875256).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11675177 and No. 11875256).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Z., Chen, X., Yuan, X. et al. The Effects of Graphite Particles on arc Plasma Characteristics. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 41, 1183–1203 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-021-10177-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-021-10177-4