Abstract
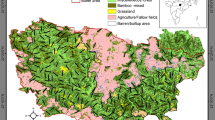
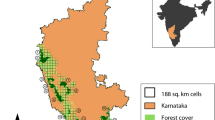
Baseline data on intrinsic–extrinsic determinants of spatial distribution of flagship species helps wildlife managers develop their management strategies. Globally, large herbivores are in range contraction due to the expansion of human habitation. Of late, alien invasion is raising management concerns due to its detrimental effect on native biota. This study evaluating the determinants of spatial detectability and density distribution of blackbuck Antilope cervicapra, an endemic species of the Indian subcontinent, demonstrates the negative influence of Prosopis juliflora, an alien invasive, on the native blackbuck at three reserves—Point Calimere Wildlife Sanctuary, Guindy National Park and Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve, Tamil Nadu, India. Using distance sampling technique, the study has surveyed blackbuck from 26 grid-based, spatially replicated line-transects between January 2018 and July 2019. Furthermore, 27 covariates related to climate, habitat and anthropogenic pressure were evaluated to determine their effect on spatial detectability and density distribution. Regression by Empirical Variable Selection showed that blackbuck spatial detectability and density distribution increase significantly with the extent of grassland, habitat openness and grass biomass, but decreases with Prosopis cover, shrub cover, percentage of woodland and distance to water, thus revealing their negative effect on the blackbuck. Besides, the Prosopis cover also decreases significantly the key positive predictors of the density distribution of blackbuck, namely the extent of grassland, habitat openness and grass productivity. Thus, the study concludes that the alien invasive species has a negative effect on the native blackbuck population. This raises the need for controlling or eliminating the invasive species in order to conserve, in the long run, the endemic blackbuck at the three reserves.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrestani FS, Sankaran M (eds) (2016) The ecology of large herbivores in south and Southeast Asia, vol 225. Springer, Dordrecht
Ali R (2005) Field studies for the conservation and management of point Calimere complex. FERAL, Pondicherry
Arandhara S, Sathishkumar S, Baskaran N (2020) Modelling the effect of covariates on the detectability and density of native blackbucks and invasive feral-horse using multiple covariate distance sampling at point Calimere wildlife sanctuary, southern India. Mamm Biol:1–14
Bailey DW, Gross JE, Laca EA, Rittenhouse LR, Coughenour MB, Swift DM, Sims PL (1996) Mechanisms that result in large herbivore grazing distribution patterns. J Range Manag 49:386–400
Barrette C (2004) Barking deer or muntjac. In: Sankar K, Goyal SP (eds) Ungulates of India. ENVIS Bulletin: Wildlife and Protected Areas (Vol. 7, No. 1). Wildlife Institute of India, Dehradun, pp 17–28
Baskaran N, Desai AA, Udhayan A (2009) Population distribution and conservation of the four-horned antelope (Tetracerus quadricornis) in the tropical forest of southern India. Journal of Scientific Transaction in Environment Technovation 2(3):139–144
Baskaran N, Kannan V, Thiyagesan K, Desai AA (2011) Behavioural ecology of four-horned antelope (Tetracerus quadricornis Blainville, 1816) in the tropical forests of southern India. Mamm Biol 76:741–747
Baskaran N, Anbarasan U, Agoramoorthy G (2012) India’s biodiversity hotspot under anthropogenic pressure: a case study of Nilgiri biosphere reserve. J Nat Conserv 20(1):56–61
Baskaran N, Ramkumaran K, Karthikeyan G (2016) Spatial and dietary overlap between blackbuck (Antilope cervicapra) and feral horse (Equus caballus) at point Calimere wildlife sanctuary, southern India: competition between native versus introduced species. Mamm Biol 81(3):295–302
Baskaran N, Arandhara S, Sathishkumar S and Gupta S (2019) Assessing the changes in land use and land cover by invasive species and its influence on native flora & ungulates in selected protected areas of Tamil Nadu, India using GIS and remote sensing. Technical report submitted to SERB, Government of India
Baskaran N, Arandhara S, and Sathishkumar S, (2020). Project competition technical report submitted to DST-SERB Delhi
Bayless SR (1969) Winter food habits, range use, and home range of antelope in Montana. J Wildl Manag:538–551
Bethune S, Griffin M, Joubert D (2004) National review of invasive alien species, Namibia. Ministry of Environment and Tourism, Windhoek
Bibby CJ, Burgess ND, Hillani DA, Mustoe S (2000) Bird census techniques, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, New York, USA
Birkett A, Stevens-Wood B (2005) Effect of low rainfall and browsing by large herbivores on an enclosed savannah habitat in Kenya. Afr J Ecol 43(2):123–130
Bleich VC (2009) Factors to consider when reprovisioning water developments used by mountain sheep. California Fish and Game 95(4):153–159
Boulinier T, Nichols JD, Sauer JR, Hines JE, Pollock KH (1998) Estimating species richness: the importance of heterogeneity in species detectability. Ecology 79(3):1018–1028
Buckland ST, Anderson DR, Burnham KP, Laake JL, Borchers DL., & Thomas L (2001) Introduction to distance sampling: estimating abundance of biological populations
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (1976) Mathematical models for nonparametric inferences from line transect data. Biometrics 32(2):325–336
Ceradini JP, Chalfoun AD (2017) Species’ traits help predict small mammal responses to habitat homogenization by an invasive grass. Ecol Appl 27(5):1451–1465
Cochard R, Edwards PJ (2011) Structure and biomass along an Acacia zanzibarica woodland–savanna gradient in a former ranching area in coastal Tanzania. J Veg Sci 22(3):475–489
Crawley MJ (1987) Benevolent herbivores? Trends Ecol Evol 2(6):167–168
De Vos A (1969) Ecological conditions affecting the production of wild herbivorous mammals on grasslands. In Advances in ecological research. Academic Press. 6, 137-183
Dean WRJ, Anderson MD, Milton SJ, Anderson TA (2002) Avian assemblages in native Acacia and alien Prosopis drainage line woodland in the Kalahari, South Africa. J Arid Environ 51(1):1–19
Ewel JJ (1978) Ecology of Schinus. In Anon. Schinus: technical proceedings of techniques for control of Schinus in south Florida: a workshop for natural area managers (pp. 7-21)
Ferdinands K, Beggs K, Whitehead P (2005) Biodiversity and invasive grass species: multiple-use or monoculture? Wildl Res 32(5):447–457
Fryxell JM (1991) Forage quality and aggregation by large herbivores. Am Nat 138(2):478–498
Goodenough AE, Hart AG, Stafford R (2012) Regression with empirical variable selection: description of a new method and application to ecological datasets. PLoS One 7(3):e34338
Gorini L, Linnell JD, May R, Panzacchi M, Boitani L, Odden M, Nilsen EB (2012) Habitat heterogeneity and mammalian predator–prey interactions. Mammal Rev 42(1):55–77
Grime JP (2001) Plant strategies. Vegetation processes and ecosystem properties (Second Edition)–John Wiley and Sons, Chichester
Hardy MA (1993). Regression with dummy variables (Vol. 93). Sage
Hejda M, Pyšek P, Jarošík V (2009) Impact of invasive plants on the species richness, diversity and composition of invaded communities. J Ecol 97(3):393–403
Hobbs RJ, Huenneke LF (1992) Disturbance, diversity, and invasion: implications for conservation. Conserv Biol 6(3):324–337
Hoffmann M, Belant JL, Chanson JS, Cox NA, Lamoreux J, Rodrigues AS, Stuart SN (2011) The changing fates of the world’s mammals. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 366(1578):2598–2610
Hopcraft JGC, Anderson TM, Pérez-Vila S, Mayemba E, Olff H (2012) Body size and the division of niche space: food and predation differentially shape the distribution of Serengeti grazers. J Anim Ecol 81(1):201–213
Isvaran K (2007) Intraspecific variation in group size in the blackbuck antelope: the roles of habitat structure and forage at different spatial scales. Oecologia 154(2):435–444
Isvaran K, Jhala Y (2000) Variation in lekking costs in blackbuck (Antilope cervicapra): relationship to lek-territory location and female mating patterns. Behaviour 137(5):547–563
Jadeja S, Prasad S, Quader S, Isvaran K (2013) Antelope mating strategies facilitate invasion of grasslands by a woody weed. Oikos 122(10):1441–1452
Jarman P (1974) The social organisation of antelope in relation to their ecology. Behaviour 48(1-4):215–267
Jhala (1997) Seasonal effects on the nutritional ecology of blackbuck Antelope cervicapra. J Appl Ecol 1997:1348–1358
Jhala YV, Isvaran K (2016) Behavioural ecology of a grassland antelope, the blackbuck Antilope cervicapra: linking habitat, ecology and behaviour. In: The ecology of large herbivores in South and Southeast Asia (pp. 151-176). Springer, Dordrecht
Jhala YV, Giles RH Jr, Bhagwat AM (1992) Water in the ecophysiology of blackbuck. J Arid Environ 22(3):261–269
Johnsingh AJT, Raghunath R, Pillay R, Madhusudan MD (2010) Ensuring the future of the tiger and other large mammals in the southern portion of the Nilgiri biosphere reserve, southern India. J Bombay Nat Hist Soc 107(2):77
Jose S, Cox J, Miller DL, Shilling DG, Merritt S (2002) Alien plant invasions: the story of cogon grass in southeastern forests. J For 100(1):41–44
Kaufmann JH (1974) Social ethology of the whiptail wallaby, Macropus parryi, in northeastern New South Wales. Anim Behav 22(2):281–369
Kebede AT, Coppock DL (2015) Livestock-mediated dispersal of Prosopis juliflora imperils grasslands and the endangered Grevy’s zebra in northeastern Ethiopia. Rangel Ecol Manag 68(5):402–407
Kebede A, Coppock DL, Authority EWC (2009) Pastoral livestock facilitate dispersal of Prosopis juliflora in an Ethiopian wildlife reserve
Krishna YC, Krishnaswamy J, Kumar NS (2008) Habitat factors affecting site occupancy and relative abundance of four horned antelope. J Zool 276(1):63–70
Krishna YC, Kumar A, Isvaran K, Avilés JM (2016) Wild ungulate decision-making and the role of tiny refuges in human-dominated landscapes. PLOS ONE 11(3):e0151748
Krishna PSSBS, Revanth RTRTT, Masthan KY (2019) Experimental study of partially replacement of cement by Prosopis juliflora concrete
Leopold A (1933). Game management Charles Scribner’s sons. New York, 481
Levine JM, D’ Antonio CM (1999) Elton revisited: a review of evidence linking diversity and invasibility. Oikos:15–26
Lingle S, Wilson WF (2001) Detection and avoidance of predators in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) and mule deer (O. hemionus). Ethology 107(2):125–147
Lodge DM (1993) Biological invasions: lessons for ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 8(4):133–137
Lumley T, (2013) Package ‘leaps’. Regression subset selection. Thomas Lumley Based on Fortran Code by Alan Miller. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=leaps (Accessed on 18 March 2018)
Mack RN (1989) Temperate grasslands vulnerable to plant invasions: characteristics and consequences. Biological invasions: a global perspective
Management Plan for Sathiyamangalam Wildlife Sanctuary (2010 to 2020). (2017). 1st ed. [ebook] Chennai: Tamil Nadu Forest Department, pp.1-139. Available at: http://str-tn.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/Management-Plan-of-Sathiyamangalam.pdf [Accessed 2 May 2017]
Mannheimer C, Curtis B (2010) Le Roux and Muller’s trees and shrubs of Namibia
Marques FF, Buckland ST, Goffin D, Dixon CE, Borchers DL, Mayle BA, Peace AJ (2001) Estimating deer abundance from line transect surveys of dung: sika deer in southern Scotland. J Appl Ecol 38(2):349–363
Mills ML, Retief PF (1984) The response of ungulates to rainfall along the riverbeds of the southern Kalahari. Koedoe 27(2):129–141
Moe SR, Wegge P (1997) The effects of cutting and burning on grass quality and axis deer (Axis axis) use of grassland in lowland Nepal. J Trop Ecol 13:279–292v
Mullin BH (1998) The biology and management of purple loosestrife (Lythrum salicaria). Weed Technol 12:397–401
Mungall EC (1978) The Indian blackbuck antelope: a Texas view (No. QL737. M86 1978.)
Muturi GM, Poorter L, Mohren GMJ, Kigomo BN (2013) Ecological impact of Prosopis species invasion in Turkwel riverine forest, Kenya. J Arid Environ 92:89–97
Nishanth B, Srinivasan SR, Jayathangaraj MG, Sridhar R (2012) Incidence of endoparasotism in free - ranging elephants of Tamil Nadu state. Tamil Nadu Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences 8(3):171–173
Odden M, Wegge P, Storaas T (2005) Hog deer Axis porcinus need threatened tallgrass floodplains: a study of habitat selection in lowland Nepal. Anim Conserv 8:99–104
Ogutu JO, Owen-Smith N (2003). ENSO, rainfall and temperature influences on extreme population declines among African savanna ungulates
Owen-Smith N (1988) Megaherbivores. The influence of very large body size on ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Owen-Smith N, Ogutu J (2012) Changing rainfall and obstructed movements: impact on African ungulates. Wildlife conservation in a changing climate, 153
Paredes OSL, Norris D, De Oliveira TG, Michalski F (2017) Water availability not fruitfall modulates the dry season distribution of frugivorous terrestrial vertebrates in a lowland Amazon forest. PLoS One 12(3):e0174049
Pienaar UDV (1974) Habitat-preference in south African antelope species and its significance in natural and artificial distribution patterns. Koedoe 17(1):185–195
Pollock KH, Nichols JD, Simons TR, Farnsworth GL, Bailey LL, Sauer JR (2002) Large scale wildlife monitoring studies: statistical methods for design and analysis. Environmetrics: The official journal of the International Environmetrics Society 13(2):105–119
Pollock KH, Marsh H, Bailey LL., Farnsworth GL, Simons TR, & Alldredge MW (2004). Separating components of detection probability in abundance estimation: an overview with diverse examples. Island Press
Prater SH (1948) The book of Indian mammals. Bombay Natural History Society
Pyšek P, Jarošík V, Hulme PE, Pergl J, Hejda M, Schaffner U, Vilà M (2012) A global assessment of invasive plant impacts on resident species, communities and ecosystems: the interaction of impact measures, invading species’ traits and environment. Glob Chang Biol 18(5):1725–1737
Rahmani AR, Sankaran R (1991) Blackbuck and Chinkara in the Thar Desert: a changing scenario. J Arid Environ 21(3):379–391
Rajasekhar B (1992) Observations on the vegetation of Guindy National Park. Blackbuck 8(2):38–42
Raman TRS (1996) Ecology and management of chital and blackbuck in Guindy National Park, Madras. J Bombay Nat Hist Soc 93(2):178–192
Ranjitsinh MK (1989) Indian blackbuck. Natraj Publishers, New Delhi
Rathore D (2017) Blackbuck Occupancy in Moyar Valley, Tamil Nadu. M.Sc. Environmental studies and resource management. Submitted to Department of Natural Resource. TERI University
R Core Team (2019) A language and environment for statistical computing”: 201
Redfern JV, Grant R, Biggs H, Getz WM (2003) Surface water constraints on herbivore foraging in the Kruger National Park, South Africa. Ecology 84:2092–2107
Richardson DM (2001) 16 commercial forestry and agroforestry as sources of invasive alien trees and shrubs. Invasive species and biodiversity management 24:237
Ripple WJ, Newsome TM, Wolf C (2015) Collapse of the world’s largest herbivores. Sci Adv. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1400103
Ritchie EG, Martin JK, Krockenberger AK, Garnett S, Johnson CN (2008) Large-herbivore distribution and abundance: intra-and interspecific niche variation in the tropics. Ecol Monogr 78(1):105–122
Rodriguez LF (2006) Can invasive species facilitate native species? Evidence of how, when, and why these impacts occur. Biol Invasions 8(4):927–939
Schipper J, Chanson JS, Chiozza F, Cox NA, Hoffmann M, Katariya V, Baillie J (2008) The status of the world’s land and marine mammals: diversity, threat, and knowledge. Science 322(5899):225–230
Senft RL, Coughenour MB, Bailey DW, Rittenhouse LR, Sala OE, Swift DM (1987) Large herbivore foraging and ecological hierarchies. BioScience 37(11):789–799
Shackleton RT, Le Maitre DC, Van Wilgen BW, Richardson DM (2015) The impact of invasive alien Prosopis species (mesquite) on native plants in different environments in South Africa. S Afr J Bot 97:25–31
Shapiro SS, Wilk MB (1965) An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 52(3/4):591–611
Sharma K, Chundawat RS, Van Gruisen J (2014) Understanding the patchy distribution of four-horned antelope Tetracerus quadricornis in a tropical dry deciduous forest in Central India. J Trop Ecol 30:45–54
Silori CS, Mishra BK (2001) Assessment of livestock grazing pressure in and around the elephant corridors in Mudumalai wildlife sanctuary, South India. Biodivers Conserv 10(12):2181–2195
Sinclair ARE (1995) Equilibria in plant-herbivore interactions. Serengeti II: dynamics, management, and conservation of an ecosystem. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 91-113
Steenkamp HE, Chown SL (1996) Influence of dense stands of an exotic tree, Prosopis glandulosa Benson, on a savanna dung beetle (Coleoptera: Scarabaeinae) assemblage in southern Africa. Biol Conserv 78(3):305–311
Tyson M J (2007) The ecology of muntjac deer (Muntiacus muntjak) in Baluran National Park, Java and their interactions with other mammal species. Doctoral dissertation submitted to Manchester Metropolitan University
Valentine LE, Roberts B, Schwarzkopf LIN (2007) Mechanisms driving avoidance of non-native plants by lizards. J Appl Ecol 44(1):228–237
Wardle DA (2001) Experimental demonstration that plant diversity reduces invasibility–evidence of a biological mechanism or a consequence of sampling effect? Oikos 95:161–170
Wickham H, Francois R, Henry L (2018) Müller, K. dplyr: A grammar of data manipulation. R package version 0.7. 6
Williams D, Pettorelli N, Henschel J, Cowlishaw G, Douglas CM (2014) Impact of alien trees on mammal distributions along an ephemeral river in the Namib Desert. Afr J Ecol 52(4):404–413
Williamson M (1996) Biological invasions. Chapman and Hall, London
Acknowledgements
Our sincere thanks are also due to the Tamil Nadu Forest Department, especially the former Chief Wildlife Warden, Mr. P.C. Tyagi, I.F.S., the present Chief Wildlife Warden, Mr. Sanjay Kumar Srivastava, I.F.S., and Chief Conservator of Forests, Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve, Erode, the Wildlife Wardens of Nagapattinam and Chennai, for granting permission and for logistic support. We also thank the management and the Principal of A.V.C. College for the constant encouragement and support to this project.
Funding
The Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, funded this study under SERB Extramural Research Category.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 129 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arandhara, S., Sathishkumar, S., Gupta, S. et al. Influence of invasive Prosopis juliflora on the distribution and ecology of native blackbuck in protected areas of Tamil Nadu, India. Eur J Wildl Res 67, 48 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-021-01485-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-021-01485-3