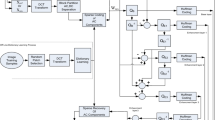
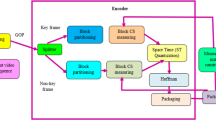
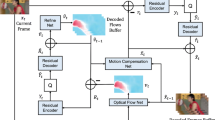
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a novel video reconstruction methodology built based on a generalization of alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) named Plug-and-Play. The motivation of the proposed technique is the improvement in visual quality performance of the video frames and decreasing the reconstruction error in comparison with the former video reconstruction methods. The proposed algorithm is an end-to-end embedding tool to integrate video reconstruction techniques with denoiser methods. Correspondingly, we use compressive sensing (CS)-based Gaussian mixture models (GMM) as a sub-problem regarding the proposed framework which is used as a method to model spatiotemporal video patches for video reconstruction. On the other hand, sparse 3D transform-domain block matching is applied as the denoiser of the proposed methodology to remove the remaining artifacts and noise in the reconstructed video frames. Consequently, by considering both online and offline CS-based GMM frameworks, we are able to make two forms of GMM-based embedding video reconstruction algorithms. The outcome has been compared with the result of CS-based GMM algorithm, GAP, TwIST and KSVD-OMP on the same datasets considering PSNR, SSIM, VSNR, WSNR, NQM, UQI, VIF and IFC as the evaluation metrics. It has been experimentally proved that the proposed online and offline GMM-based Plug-and-Play algorithms have more suitable results in comparison with their conventional CS-based online and offline GMM counterparts as well as other state-of-the-art techniques. The general quantitative results (considering all the datasets) for online proposed method regarding PSNR and SSIM metrics are 29.84 and 0.891, respectively, which is higher than the results of other techniques.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The complete database is available in http://dyntex.univ-lr.fr/database_pro.html.
References
Chi, X., Makihara, Y., Yagi, Y., Jianfeng, L.: Gait-based age progression/regression: a baseline and performance evaluation by age group classification and cross-age gait identification. Machine Vision and Applications 30(4), 629–644 (2019)
Setty, S., Mudenagudi, U.: Example-based 3d inpainting of point clouds using metric tensor and christoffel symbols. Machine Vision and Applications 29(2), 329–343 (2018)
Padalkar, M.G., Joshi, M.V.: Auto-inpainting heritage scenes: a complete framework for detecting and infilling cracks in images and videos with quantitative assessment. Machine Vision and Applications 26(2–3), 317–337 (2015)
Howie, R.M., Paxman, J., Bland, P.A., Towner, M.C.: Absolute time encoding for temporal super-resolution using de bruijn coded exposures. Machine Vision and Applications 31(1), 1 (2020)
Chen, Y., Liu, L., Tao, J., Chen, X., Xia, R., Zhang, Q., Xiong, J., Yang, K., Xie, J.: The image annotation algorithm using convolutional features from intermediate layer of deep learning. Multimedia Tools and Applications 80(3), 4237–4261 (2021)
Li, C., Chen, Z., Wu, Q.M.J., Liu, C.: Saliency object detection: integrating reconstruction and prior. Machine Vision and Applications 30(3), 397–406 (2019)
Citraro, L., Márquez-Neila, P., Savarè, S., Jayaram, V., Dubout, C., Renaut, F., Hasfura, A., Shitrit, H.B., Fua, P.: Real-time camera pose estimation for sports fields. Machine Vision and Applications 31(3), 1–13 (2020)
Z. Fan, J. Yin, Y. Song, and Z. Liu: Real-time and accurate abnormal behavior detection in videos. Machine Vision and Applications 31(7), 1–13 (2020)
Venator, M., Aklanoglu, S., Bruns, E., Maier, A.: Enhancing collaborative road scene reconstruction with unsupervised domain alignment. Machine Vision and Applications 32(1), 1–16 (2020)
Pellicanò, N., Aldea, E., Le Hégarat-Mascle, S.: Wide baseline pose estimation from video with a density-based uncertainty model. Machine Vision and Applications 30(6), 1041–1059 (2019)
Zeng, Y., van der Lubbe, J.C.A., Loog, M.: Multi-scale convolutional neural network for pixel-wise reconstruction of van gogh’s drawings. Machine Vision and Applications 30(7–8), 1229–1241 (2019)
Li, H., Zeng, Y., Yang, N.: Image reconstruction for compressed sensing based on joint sparse bases and adaptive sampling. Machine Vision and Applications 29(1), 145–157 (2018)
Chen, Y., Liu, L., Tao, J., Xia, R., Zhang, Q., Yang, K., Xiong, J., Chen, X.: The improved image inpainting algorithm via encoder and similarity constraint. Vis. Comput. 1–15 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-020-01932-3
Chen, Y., Zhang, H., Liu, L., Tao, J., Zhang, Q., Yang, K., Xia, R., Xie, J.: Research on image inpainting algorithm of improved total variation minimization method. J. Ambient Intell. Human. Comput. 1–10 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02778-2
J Su, H Cheng, L Yang, and A Luo. : Robust spatial-temporal bayesian view synthesis for video stitching with occlusion handling. Machine Vision and Applications 29(2), 219–232 (2018)
Yang, J., Yuan, X., Liao, X., Llull, P., Brady, D.J., Sapiro, G., Carin, L.: Video compressive sensing using gaussian mixture models. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 23(11), 4863–4878 (2014)
Yu, G., Sapiro, G., Mallat, S.: Solving inverse problems with piecewise linear estimators: From gaussian mixture models to structed sparsity. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 21(5), 2481–2499 (2012)
Zhang, J., Zhao, D., Gao, W.: Group-based sparse representation for image restoration. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 23(8), 3336–3351 (2014)
Fessler, J.A.: Penalized weighted least-squares image reconstruction for positron emission tomography. IEEE Trans. on Medical Imaging 13(2), 290–300 (1994)
Hitomi, Y., Gu, J., Gupta, M., Mitsunaga, T., Nayar, S.K.: Video from a single coded exposure photograph using a learned over-complete dictionary. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. 287–294 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126254
Venkatakrishnan, S., Bouman, C., Wohlberg, B.: Plug-and-play priors for model based reconstruction. In: Proc. IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing, pp. 945–948 (2013)
Xia, Y., Zhang, Z.: Rank-sparsity balanced representation for subspace clustering. Machine Vision and Applications 29(6), 979–990 (2018)
Chan, S.H., Wang, X., Elgendy, O.A.: Plug-and-play admm for image restoration: Fixed point convergence and applications. IEEE Trans. on Computational Imaging 3(1), 84–98 (2017)
Sreehari, S., Venkatakrishnan, S.V., Wohlberg, B., Buzzard, G.T., Drummy, L.F., Simmons, J.P., Bouman, C.A.: Plug-and-play priors for bright field electron tomography and sparse interpolation. IEEE Trans. on Computational Imaging 2(4), 408–423 (2016)
Matthews, C.E., Kuncheva, L.I., Yousefi, P.: Classification and comparison of on-line video summarisation methods. Machine Vision and Applications 30(3), 507–518 (2019)
Risojević, V., Momić, S., Babić, Z.: Gabor descriptors for aerial image classification. In: International Conference on Adaptive and Natural Computing Algorithms, pp. 51–60. Springer (2011)
Ojala, T., Pietikainen, M., Maenpaa, T.: Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 24(7), 971–987 (2002)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International journal of computer vision 60(2), 91–110 (2004)
Zheng, X., Yuan, Y., Xiaoqiang, L.: A deep scene representation for aerial scene classification. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 57(7), 4799–4809 (2019)
Fergus, R., Singh, B., Hertzmann, A., Roweis, S.T., Freeman, W.T.: Removing camera shake from a single photograph. In: ACM SIGGRAPH 2006 Papers, pp. 787–794 (2006)
Krishnan, D., Tay, T., Fergus, R.: Blind deconvolution using a normalized sparsity measure. In: CVPR 2011, pp. 233–240. IEEE (2011)
Sun, L., Cho, S., Wang, J., Hays, J.: Edge-based blur kernel estimation using patch priors. In: IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2013)
Xu, L., Zheng, S., Jia, J.: Unnatural l0 sparse representation for natural image deblurring. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1107–1114 (2013)
Lai, W.-S., Ding, J.-J., Lin, Y.-Y., Chuang, Y.-Y.: Blur kernel estimation using normalized color-line prior. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 64–72 (2015)
Pan, J., Sun, D., Pfister, H., Yang, M.-H.: Deblurring images via dark channel prior. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 40(10), 2315–2328 (2017)
Jin, M., Meishvili, G., Favaro, G.: Learning to extract a video sequence from a single motion-blurred image. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6334–6342 (2018)
Purohit, K., Shah, A., Rajagopalan, A.N.: Bringing alive blurred moments. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6830–6839 (2019)
Kokaram, A.C., Morris, R.D., Fitzgerald, W.J., Rayner, P.J.W.: Interpolation of missing data in image sequences. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 4(11), 1509–1519 (1995)
Hirani, A., Totsuka, T.: Combining frequency and spatial domain information for fast interactive image noise removal. SIGGRAPH 96, 269–276 (1996)
Ma, Y., Zhu, J., Baron, D.: Approximate message passing algorithm with universal denoising and gaussian mixture learning. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing 64(21), 5611–5622 (2016)
Donoho, D.L.: Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. on Information Theory 52(4), 1289–1305 (2006)
Donoho, D.L., Maleki, A., Montanari, A.: The noise-sensitivity phase transition in compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. on Information Theory 57(11), 6920–6940 (2011)
Liu, Z., Elezzabi, A.Y., Zhao, H.V.: Maximum frame rate video acquisition using adaptive compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. on Circuits Syst. Video Technol 21(11), 1704–1718 (2011)
Guerrero-Colon, J.A., Mancera, L., Portilla, J.: Image restoration using space-variant gaussian scale mixtures in overcomplete pyramids. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 17(1), 27–41 (2008)
Metzler, C.A., Maleki, A., Baraniuk, R.G.: From denoising to compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. on Information Theory 62(9), 5117–5144 (2016)
Danielyan, A., Katkovnik, V., Egiazarian, K.: Bm3d frames and variational image deblurring. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 21(4), 1715–1728 (2012)
Niu, Y., Ke, L., Guo, W.: Evaluation of visual saliency analysis algorithms in noisy images. Machine Vision and Applications 27(6), 915–927 (2016)
Levin, A., Nadler, B.: Natural image denoising: optimality and inherent bounds. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2833–2840 (2011)
Levin, A., Nadler, B., Durand, F., Freeman, W.: Patch complexity, finite pixel correlations and optimal denoising. In: Proc. 12th European. Conf. Computer Vision (ECCV), vol. 7576, pp. 73–86 (2012)
Aharon, M., Elad, M., Bruckstein, A.: K-svd: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing 54(11), 4311–4322 (2006)
Zhou, M., Chen, H., Paisley, J., Ren, L., Li, L., Xing, Z., Dunson, D., Sapiro, G., Carin, L.: Nonparametric bayesian dictionary learning for analysis of noisy and incomplete images. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 21(1), 130–144 (2012)
Hao, W., Li, Y., Xiong, J., Bi, X., Zhang, L., Bie, R., Guo, J.: Weighted-learning-instance-based retrieval model using instance distance. Machine Vision and Applications 30(1), 163–176 (2019)
Haskins, G., Kruger, U., Yan, P.: Deep learning in medical image registration: a survey. Machine Vision and Applications 31(1), 8 (2020)
Reddy, D., Veeraraghavan, A., Chellappa, R.: P2c2: programmable pixel compressive camera for high speed imaging. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 329–336 (2011)
Rangappa, S., Matharu, R., Petzing, J., Kinnell, P.: Establishing the performance of low-cost lytro cameras for 3d coordinate geometry measurements. Machine Vision and Applications 30(4), 615–627 (2019)
Dempster, A.P., Laird, N.M., Rubin, D.B.: Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the em algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological 39(1), 1–28 (1997)
Eldar, Y.C., Kuppinger, P., Bolcskei, H.: Block-sparse signals: Uncertainty relations and efficient recovery. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(6), 3042–3054 (2010)
Ezhilarasan, M., Thambidurai, P.: Simplified block matching algorithm for fast motion estimation in video compression. J. Comput. Sci. 4(4), 282–289 (2008)
Fowler, J.E., Mun, S., Tramel, E.W.: Block-based compressed sensing of images and video. Found. Trends Signal Process. 4(4), 297–416 (2012)
Hsieh, C.-H., Lin, T.-P.: Vlsi architecture for block-matching motion estimation algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2(2), 169–175 (1992)
Mun, S., Fowler, J.E.: Residual reconstruction for block-based compressed sensing of video. In: Proc. Data Compress. Conf., pp. 183–192 (2011)
Pizurica, A., Philips, W., Lemahieu, I., Acheroy, M.: A joint inter- and intrascale statistical model for bayesian wavelet based image denoising. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 11(5), 545–557 (2002)
Portilla, J., Strela, V., Wainwright, M., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image denoising using a scale mixture of gaussians in the wavelet domain. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 12(11), 1338–1351 (2003)
Sendur, L., Selesnick, I.W.: Bivariate shrinkage functions for wavelet-based denoising exploiting interscale dependency. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing 50(11), 2744–2756 (2002)
Dabov, K., Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., Egiazarian, K.: Color image denoising via sparse 3d collaborative filtering with grouping constraint in luminance-chrominance space. In: IEEE Int. Conf. on Image Processing, pp. 313–316 (2007)
Gersho, A.: On the structure of vector quantizers. IEEE Trans. on Information Theory 28(2), 157–166 (1982)
Dabov, K., Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., Egiazarian, K.: Image denoising by sparse 3d transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 16(8), 2080–2095 (2007)
Kervrann, C., Boulanger, J.: Optimal spatial adaptation for patchbased image denoising. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 15(10), 2866–2878 (2006)
Huynh-Thu, Q., Ghanbari, M.: The accuracy of psnr in predicting video quality for different video scenes and frame rates. Telecommunication Systems 49(1), 35–48 (2012)
Thomos, N., Boulgouris, N.V., Strintzis, M.G.: Optimized transmission of jpeg2000 streams over wireless channels. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 15(1), 54–67 (2006)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Chandler, D.M., Hemami, S.S.: Vsnr: A wavelet-based visual signal-to-noise ratio for natural images. IEEE transactions on image processing 16(9), 2284–2298 (2007)
Damera-Venkata, N., Kite, T.D., Geisler, W.S., Evans, B.L., Bovik, A.C.: Image quality assessment based on a degradation model. IEEE transactions on image processing 9(4), 636–650 (2000)
Han, Yu., Cai, Y., Cao, Y., Xiaoming, X.: A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity. Inf. Fusion 14(2), 127–135 (2013)
Sheikh, H.R., Bovik, A.C., De Veciana, G.: An information fidelity criterion for image quality assessment using natural scene statistics. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 14(12), 2117–2128 (2005)
Chen, M., Silva, J., Paisley, J., Wang, C., Dunson, D., Carin, L.: Compressive sensing on manifolds using a nonparametric mixture of factor analyzers: Algorithm and performance bounds. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing 58(12), 6140–6155 (2010)
Liao, X., Li, H., Carin, L.: Generalized alternating projection for weighted-\(\ell _{2,1}\) minimization with applications to model-based compressive sensing. SIAM J. Imag. Sci. 7(2), 797–823 (2014)
Bioucas-Dias, J.M., Figueiredo, M.A.T.: A new twist: Two-step iterative shrinkage/thresholding algorithms for image restoration. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing 16(12), 2992–3004 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The completion of this research was made possible thanks to the Natural Sciences and Engineering research Council of Canada (NSERC). In addition, the authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments that lead to the clarification and general improvement of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khorasani Ghassab, V., Bouguila, N. Plug-and-Play video reconstruction using sparse 3D transform-domain block matching. Machine Vision and Applications 32, 76 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-021-01201-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-021-01201-w