Abstract
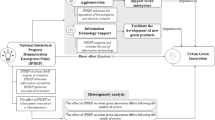
With the global economy increasingly dependent on innovation, urban discourse has shifted to consider what kinds of spatial designs may best nurture innovation. We examined the relationship between the built environment and the spatial heterogeneity of regional innovation productivity (RIP) using the example of China’s Pearl River Delta (PRD). Based on a spatial database of 522 546 patent data from 2017, this study proposed an innovation-based built environment framework with the following five aspects: healthy environment, daily interaction, mixed land use, commuting convenience, and technology atmosphere. Combining negative binomial regression and Geodetector to examine the impact of the built environment on RIP, the results show that the spatial distribution of innovation productivity in the PRD region is extremely uneven. The negative binomial regression results show that the built environment has a significant impact on the spatial differentiation of RIP, and, specifically, that healthy environment, mixed land use, commuting convenience, and technology atmosphere all demonstrate significant positive impacts. Meanwhile, the Geodetector results show that the built environment factor impacts the spatial heterogeneity of RIP to varying degrees, with technology atmosphere demonstrating the greatest impact intensity. We conclude that as regional development discourse shifts focus to the knowledge and innovation economy, the innovation-oriented design and updating of built environments will become extremely important to policymakers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler P, Florida R, King K et al., 2019. The city and high-tech startups: the spatial organization of Schumpeterian entrepreneurship. Cities, 87: 121–130. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2018.12.013
Albahari A, Barge-Gil A, Pérez-Canto S et al., 2018. The influence of Science and Technology Park characteristics on firms’ innovation results. Papers in Regional Science, 97(2): 253–279. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/pirs.12253
Aragón Amonarriz C, Iturrioz C, Narvaiza L et al., 2019. The role of social capital in regional innovation systems: creative social capital and its institutionalization process. Papers in Regional Science, 98(1): 35–51. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/pirs.12329
Bathelt H, Malmberg A, Maskell P, 2004. Clusters and knowledge: local buzz, global pipelines and the process of knowledge creation. Progress in Human Geography, 28(1): 31–56. doi: https://doi.org/10.1191/0309132504ph469oa
Bereitschaft B, Cammack R, 2015. Neighborhood diversity and the creative class in Chicago. Applied Geography, 63: 166–183. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2015.06.020
Bergek A, Hekkert M, Jacobsson S et al., 2015. Technological innovation systems in contexts: conceptualizing contextual structures and interaction dynamics. Environmental Innovation and Societal Transitions, 16: 51–64. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eist.2015.07.003
Boschma R, 2005. Proximity and innovation: a critical assessment. Regional Studies, 39(1): 61–74. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340052000320887
Boschma R, Fritsch M, 2009. Creative class and regional growth: empirical evidence from seven European countries. Economic Geography, 85(4): 391–423. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1944-8287.2009.01048.x
Capello R, Lenzi C, 2015. The knowledge-innovation nexus. Its spatially differentiated returns to innovation. Growth and Change, 46(3): 379–399. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/grow.12098
Capello R, Lenzi C, 2016. Innovation modes and entrepreneurial behavioral characteristics in regional growth. Small Business Economics, 47(4): 875–893. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-016-9741-x
Capello R, 2017. Towards a new conceptualization of innovation in space: territorial patterns of innovation. International Journal of Urban and Regional Research, 41(6): 976–996. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-2427.12556
Capello R, Lenzi C, 2018. Regional innovation patterns from an evolutionary perspective. Regional Studies, 52(2): 159–171. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2017.1296943
Carlino G A, Chatterjee S, Hunt R M, 2007. Urban density and the rate of invention. Journal of Urban Economics, 61(3): 389–419. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jue.2006.08.003
Casares Blanco J, Fernández-Aracil P, Ortuño-Padilla A, 2019. Built environment and tourism as road safety determinants in Benidorm (Spain). European Planning Studies, 27(7): 1314–1328. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09654313.2019.1579784
Chen X F, Liu Z Y, Ma C L, 2017. Chinese innovation-driving factors: regional structure, innovation effect, and economic development-empirical research based on panel data. The Annals of Regional Science, 59(1): 43–68. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-017-0818-5
Cooke P, Uranga M G, Etxebarria G, 1997. Regional innovation systems: institutional and organisational dimensions. Research Policy, 26(4–5): 475–491. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-7333(97)00025-5
Crossan M M, Apaydin M, 2010. A multi-dimensional framework of organizational innovation: a systematic review of the literature. Journal of Management Studies, 47(6): 1154–1191. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6486.2009.00880.x
Duan D Z, Du D B, Liu C L et al., 2016. Spatio-temporal evolution of urban innovation structure based on zip code geodatabase: an empirical study from Shanghai and Beijing. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 26(12): 1707–1724. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-016-1354-4
Esmaeilpoorarabi N, Yigitcanlar T, Guaralda M, 2018a. Place quality in innovation clusters: an empirical analysis of global best practices from Singapore, Helsinki, New York, and Sydney. Cities, 74: 156–168. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2017.11.017
Esmaeilpoorarabi N, Yigitcanlar T, Guaralda M et al., 2018b. Does place quality matter for innovation districts? Determining the essential place characteristics from Brisbane’s knowledge precincts. Land Use Policy, 79: 734–747. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.09.016
Esmaeilpoorarabi N, Yigitcanlar T, Guaralda M et al., 2018c. Evaluating place quality in innovation districts: a Delphic hierarchy process approach. Land Use Policy, 76: 471–486. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.02.027
Ewing R, Hamidi S, Grace J B et al., 2016. Does urban sprawl hold down upward mobility? Landscape and Urban Planning, 148: 80–88. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2015.11.012
Fagerberg J, Srholec M, 2008. National innovation systems, capabilities and economic development. Research Policy, 37(9): 1417–1435. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2008.06.003
Florida R, 2002. The Rise of the Creative Class. New York: Basic Books.
Florida R, Mellander C, Stolarick K, 2008. Inside the black box of regional development: human capital, the creative class and tolerance. Journal of Economic Geography, 8(5): 615–649. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/jeg/lbn023
Florida R, Adler P, Mellander C, 2017. The city as innovation machine. Regional Studies, 51(1): 86–96. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2016.1255324
Freeman C, 2002. Continental, national and sub-national innovation systems: complementarity and economic growth. Research Policy, 31(2): 191–211. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-7333(01)00136-6
Furman J L, Porter M E, Stern S, 2002. The determinants of national innovative capacity. Research Policy, 31(6): 899–933. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-7333(01)00152-4
Giuliano G, Kang S, Yuan Q, 2019. Agglomeration economies and evolving urban form. The Annals of Regional Science, 63(3): 377–398. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-019-00957-4
Hamidi S, Ewing R, 2015. Is sprawl affordable for Americans? Exploring the association between housing and transportation affordability and urban sprawl. Transportation Research Record, 2500(1): 75–79. doi: https://doi.org/10.3141/2500-09
Hamidi S, Zandiatashbar A, 2018. Does urban form matter for innovation productivity? A national multi-level study of the association between neighbourhood innovation capacity and urban sprawl. Urban Studies, 56(8): 1576–1594. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098018767002
Hamidi S, Zandiatashbar A, Bonakdar A, 2019. The relationship between regional compactness and regional innovation capacity (RIC): empirical evidence from a national study. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 142: 394–402. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.07.026
Jacobs J, 1969. The Economy of Cities. New York: Vintage.
Katz B, Wagner J, 2014. The Rise of Innovation Districts: A New Geography of Innovation in America. Washington, DC: Metropolitan Policy Program at Brookings.
Kiuru J, Inkinen T, 2017. Predicting innovative growth and demand with proximate human capital: a case study of the Helsinki metropolitan area. Cities, 64: 9–17. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2017.01.005
Lee H K, Kim H B, 2019. Regional preferences for the living environment and mobility of researchers and general workers: the case of Korea. Annals of Regional Science, 62(1): 169–186. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-018-0892-3
Li H, Wei Y D, Wu Y Y, 2019. Urban amenity, human capital and employment distribution in Shanghai. Habitat International, 91: 102025. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2019.102025
Li Y C, Phelps N A, 2018. Articulating China’s science and technology: knowledge collaboration networks within and beyond the Yangtze River Delta megalopolis in China. Chinese Geographical Science, 28(2): 247–260. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-018-0944-8
Liu Q Q, Wang S J, Zhang W Z et al., 2017. China’s municipal public infrastructure: estimating construction levels and investment efficiency using the entropy method and a DEA model. Habitat International, 64: 59–70. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.04.010
Liu Y, Shen J F, 2014. Jobs or amenities? Location choices of interprovincial skilled migrants in China, 2000–2005. Population, Space and Place, 20(7): 592–605. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/psp.1803
Luo W, Jasiewicz J, Stepinski T et al., 2016. Spatial association between dissection density and environmental factors over the entire conterminous United States. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(2): 692–700. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2015gl066941
Lv Lachang, Sun Feixiang, Huang Ru, 2019. Innovation-based urbanization: evidence from 270 cities at the prefecture level or above in China. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 29(8): 1283–1299. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-019-1659-1
Ma Haitao, Fang Chuanglin, Pang Bo et al., 2015. Structure of Chinese city network as driven by technological knowledge flows. Chinese Geographical Science, 25(4): 498–510. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-014-0731-0
Malerba F, 2004. Sectoral Systems of Innovation: Concepts, Issues and Analyses of Six Major Sectors in Europe. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Marshall A, 1890. Principles of Economics. London: Macmillan.
National bureau of statistics of China, 2018. China Statistical Year Book. In: Beijing Chinese Statistics Bureau.
Ozgen C, Nijkamp P, Poot J, 2017. The elusive effects of workplace diversity on innovation. Papers in Regional Science, 96: S29–S50. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/pirs.12176
Peiró-Palomino J, 2019. The geography of social capital and innovation in the European Union. Papers in Regional Science, 98(1): 53–73. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/pirs.12337
Porter M E, 1998. Competitive Advantage of Nations. New York: Free Press.
Proksch D, Haberstroh M M, Pinkwart A, 2017. Increasing the national innovative capacity: identifying the pathways to success using a comparative method. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 116: 256–270. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2016.10.009
Qian H F, 2013. Diversity versus tolerance: the social drivers of innovation and entrepreneurship in US cities. Urban Studies, 50(13): 2718–2735. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098013477703
Rammer C, Kinne J, Blind K, 2019. Knowledge proximity and firm innovation: a microgeographic analysis for Berlin. Urban Studies, 57(5): 996–1014. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098018820241
Schoenberger E, Walker R A, 2017. Beyond exchange and agglomeration: resource flows and city environments as wellsprings of urban growth. Journal of Economic Geography, 17(5): 935–958. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/jeg/lbw012
Scott A J, 2000. Economic geography: the great half-century. Cambridge Journal of Economics, 24(4): 483–504. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/cje/24.4.483
Shannon C E, 1948. A mathematical theory of communication. The Bell System Technical Journal, 27(3): 379–423. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x
Souzanchi Kashani E, Roshani S, 2019. Evolution of innovation system literature: intellectual bases and emerging trends. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 146: 68–80. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.05.010
Spencer G M, 2015. Knowledge neighbourhoods: urban form and evolutionary economic geography. Regional Studies, 49(5): 883–898. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2015.1019846
Storper M, Scott A J, 2009. Rethinking human capital, creativity and urban growth. Journal of Economic Geography, 9(2): 147–167. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/jeg/lbn052
Sun B D, Yin C, 2018. Relationship between multi-scale urban built environments and body mass index: a study of China. Applied Geography, 94: 230–240. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2018.03.012
Van Winden W, de Carvalho L, van Tuijl E et al., 2012. Creating Knowledge Locations in Cities. London: Routledge.
Wang J F, Li X H, Christakos G et al., 2010. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun Region, China. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 24(1): 107–127. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/13658810802443457
Wang J F, Zhang T L, Fu B J, 2016. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecological Indicators, 67: 250–256. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.02.052
Wang Yuming, Wang Ruikang, 2018. Reasons for the increasing information entropy of suburban land use structure during the period of urbanization. Acta Geographica Sinica, 73(9): 1647–1657. (in Chinese)
Wixe S, 2018. Neighbourhood related diversity, human capital and firm innovation. Papers in Regional Science, 97(2): 217–253. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/pirs.12255
Wood S, Dovey K, 2015. Creative multiplicities: urban morphologies of creative clustering. Journal of Urban Design, 20(1): 52–74. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/13574809.2014.972346
Wu Kangmin, Zhang Hongou, Wang Yang et al., 2016. Identify of the multiple types of commercial center in Guangzhou and its spatial pattern. Progress in Geography, 35(8): 963–974. (in Chinese). doi: https://doi.org/10.18306/dlkxjz.2016.08.005
Wu K M, Wang Y, Ye Y Y et al., 2019. Relationship between the built environment and the location choice of high-tech firms: evidence from the Pearl River Delta. Sustainability, 11(13): 3689. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133689
Yang C, 2012. Restructuring the export-oriented industrialization in the Pearl River Delta, China: institutional evolution and emerging tension. Applied Geography, 32(1): 143–157. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2010.10.013
Yang C, 2013. From strategic coupling to recoupling and decoupling: restructuring global production networks and regional evolution in China. European Planning Studies, 21(7): 1046–1063. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09654313.2013.733852
Yang C, 2014. State-led technological innovation of domestic firms in Shenzhen, China: evidence from liquid crystal display (LCD) industry. Cities, 38: 1–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2013.12.005
Yang J W, Zhou P L, 2020. The obesity epidemic and the metropolitan-scale built environment: examining the health effects of polycentric development. Urban Studies, 57(1): 39–55. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0042098019844177
Ye Y Y, Wu K M, Xie Y C et al., 2019. How firm heterogeneity affects foreign direct investment location choice: micro-evidence from new foreign manufacturing firms in the Pearl River Delta AppliedGeography, 106:11–21. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2019.03.005
Yu W H, Ai T H, Shao S W, 2015. The analysis and delimitation of Central Business District using network kernel density estimation. Journal of Transport Geography, 45: 32–47. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2015.04.008
Zandiatashbar A, Hamidi S, 2018. Impacts of transit and walking amenities on robust local knowledge economy. Cities, 81: 161–171. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2018.04.005
Zhang F Z, Wu F L, 2019. Rethinking the city and innovation: a political economic view from China’ s biotech. Cities, 85: 150–155. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2018.09.003
Zhang H, Yin L, 2019. A meta-analysis of the literature on the association of the social and built environment with obesity: identifying factors in need of more in-depth research. American Journal of Health Promotion, 33(5): 792–805. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0890117118817713
Zheng W, 2010. A social capital perspective of innovation from individuals to nations: where is empirical literature directing us? International Journal of Management Reviews, 12(2): 151–183. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2370.2008.00247.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item
Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41871150), GDAS’ Project of Science and Technology Development (No. 2021GDASYL-20210103004), National Key Research and Development Program (No. 2019YFB2103-101), Special Construction Project of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area Strategic Research Institute (No. 2020GDA-SYL-20200201001), Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou) (No. GML2019ZD0301)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, K., Wang, Y., Zhang, H. et al. Impact of the Built Environment on the Spatial Heterogeneity of Regional Innovation Productivity: Evidence from the Pearl River Delta, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 31, 413–428 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-021-1198-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-021-1198-4