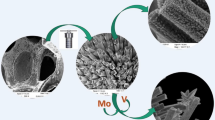
The article investigates the influence of the reduction modes of hollow nickel oxide microspheres synthesized by the pyrolysis of ultrasonic aerosols on the ratio of the oxide and metallic forms of nickel in their structure. The synthesis of microspheres from an aerosol of an aqueous solution of nickel nitrate was carried out; their composition and morphology were studied. The reduction of microspheres was carried out in a stream of hydrogen at different temperatures. The ratio of metallic nickel and oxide was determined by two different methods: according to the data of thermogravimetric analysis and by the Rietveld method based on the results of x-ray phase analysis. It is shown that the proportion of metallic nickel increases with an increase in the reduction temperature to approximately 375°C and then changes insignificantly. The fractional composition of microspheres was determined.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Feng, X. M. Chen, P. Qiu, et al., “Copper oxide hollow spheres: synthesis and catalytic application in hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane,” Int. J. Hydrogen Energ., 43(45), 20875 – 20881 (2018).
X. Tan, Yi. Wan, Ya. Huang, et al., “Three-dimensional MnO2 porous hollow microspheres for enhanced activity as ozonation catalysts in degradation of bisphenol A,” J. Hazard. Mater., 321, 162 – 172 (2017).
S. Zhai, M. Li, D. Wang, and S. Fu, “Fabrication of hollow-catalytic microspheres (HCMs) with double-sided materials and their application on wastewater treatment,” J. Clean. Prod., 253, 119956 (2020).
H. Chen, Yi. Zheng, B. Cheng, J. Yu, and C. Jiang, “Chestnut husk-like nickel cobaltite hollow microspheres for the adsorption of Congo red,” J. Alloy. Compd., 735, 1041 – 1051 (2018).
H. Chen, S. Wageh, A. A. Al-Ghamdi, et al., “Hierarchical C/NiO-ZnO nanocomposite fibers with enhanced adsorption capacity for Congo red,” J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 537, 736 – 745 (2019).
H. Li, H. Ma, M. Yang, et al., “Highly controlled synthesis of multi-shelled NiO hollow microspheres for enhanced lithium storage properties,” Mater. Res. Bull., 87, 224 – 229 (2017).
J. Wang, Y. Cui, and D. Wang, “Design of hollow nanostructures for energy storage, conversion and production,” Adv. Mater., 31(38), 1801993 (2019).
C. Zhang, F. Ke, H. Xiao, et al., “Well-designed hollow and porous Co3O4 microspheres used as an anode for Li-ion battery,” J. Solid State Electr., 23(8), 2477 – 2482 (2019).
I. Burmistrov, N. Gorshkov, N. Kovyneva, et al., “High seebeck coefficient thermoelectrochemical cell using nickel hollow microspheres electrodes,” Renew. Energ., 157, 1 – 8 (2020).
I. Burmistrov, N. Kovyneva, N. Gorshkov, et al., “Development of new electrode materials for thermo-electrochemical cells for waste heat harvesting,” Renew. Energ. Focus, 29, 42 – 48 (2019).
C. B. Ong, L. Y. Ng, and A. W. Mohammad, “A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: synthesis, mechanisms and applications,” Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 81, 536 – 551 (2018).
A. Yudin, N. Shatrova, B. Khaydarov, et al., “Synthesis of hollow nanostructured nickel oxide microspheres by ultrasonic spray atomization,” J. Aerosol Sci., 98, 30 – 40 (2016).
M. Thirumoorthi and J. Thomas Joseph Prakash, “Structure, optical and electrical properties of indium tin oxide ultra thin films prepared by jet nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique,” J. Asian Ceram. Soc., 4(1), 124 – 132 (2016).
M. L. Zeggar, L. Chabane, M. S. Aida, et al., “Solution flow rate influence on properties of copper oxide thin films deposited by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis,” Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc., 30, 645 – 650 (2015).
S. J. Shih and W. L. Tzeng, “Manipulation of morphology of strontium titanate particles by spray pyrolysis,” Powder Technol., 264, 291 – 297 (2014).
S. Edinger, J. Bekacz, M. Richter, et al., “Influence of the acetic acid concentration on the growth of zinc oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis of aqueous solutions,” Thin Solid Films, 594, 238 – 244 (2015).
S. J. Shih, W. L. Tzeng, and W. L. Kuo, “Fabrication of ceria particles using glycine nitrate spray pyrolysis,” Surf. Coat. Tech., 259, 302 – 309 (2014).
G. V. Trusov, D. O. Moskovskikh, A. S. Rogachev, et al., “High porous cellular materials by spray solution combustion synthesis and spark plasma sintering,” J. Alloy. Compd., 779, 557 – 565 (2019).
B. H. Min and K. Y. Jung, “Enhanced upconversion luminescence of GdVO4:Er3+/Yb3+ prepared by spray pyrolysis using organic additives,” RSC Adv., 9(35), 20002 – 20008 (2019).
N. V. Y. Scarlett, I. C. Madsen, L. M. D. Cranswick, et al., “Outcomes of the International Union of Crystallography Commission on powder diffraction round robin on quantitative phase analysis: samples 2, 3, 4, synthetic bauxite, natural granodiorite and pharmaceuticals,” J. Appl. Crystallogr., 35(4), 383 – 400 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Novye Ogneupory, No. 12, pp. 49 – 53, December, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taganova, A.A., Boychenko, E.A., Kiselev, N.V. et al. Synthesis and Study of the Composition of Hollow Microspheres of NiO and NiO/Ni Composition for Thermoelectrochemical Energy Converters of Low-Potential Temperature Gradients of Thermal Units Into Electricity. Refract Ind Ceram 61, 715–719 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11148-021-00548-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11148-021-00548-x