Abstract
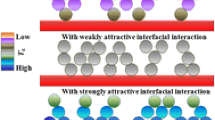
We use coarse grained Molecular Dynamics simulations to determine the effect of diblock copolymers and inorganic sheet like compatibilizers at polymer blend interfaces. Previous studies have shown that the interfacial region is prone to slip if an external shear force is applied to the polymer blend. While a number of theoretical and computational studies have examined the effect of copolymer compatibilizers, the effect of adding sheet-like compatilibilizers (for e.g. nanoclay) has not been investigated computationally. Thus, while experiments have shown that sheet-like filler are effective, the exact mechanisms are unknown. Our results indicate that sheet like fillers that have equal affinity to either polymer in a binary blend can produce a larger reduction of interfacial tension when compared to diblock copolymers at equal volume fractions. However, the localization of sheet fillers at the interface can be a possible limiting factor. We also show that sheet fillers reduce slip, thus providing for improved stress transfer across the interface, leading to a stronger blend.
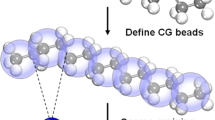
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Avaliability
Data has been archived and will be made available on request.
Code Availability
LAMMPS is an open source software that is available for free download.
References
Paul, D.R.: Polymer Blends, vol. 1. Academic Press Inc, London (1978)
Gan, Z., Yu, D., Zhong, Z., Liang, Q., Jing, X.: Enzymatic degradation of poly(ε-caprolactone)/poly(dl-lactide) blends in phosphate buffer solution. Polymer 40(10), 2859–2862 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(98)00549-7
Gazotti, W.A., Jr., Casalbore-Miceli, G., Mitzakoff, S., Geri, A., Gallazzi, M.C., De Paoli, M.A.: Conductive polymer blends as electrochromic materials. Electrochim. Acta 44(12), 1965–1971 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(98)00305-3
Mano, J.F., Koniarova, D., Reis, R.L.: Thermal properties of thermoplastic starch/synthetic polymer blends with potential biomedical applicability. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 14(2), 127–135 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022015712170
Wu, S.: Phase structure and adhesion in polymer blends: A criterion for rubber toughening. Polymer 26(12), 1855–1863 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-3861(85)90015-1
Song, J., Baker, A.M., Macosko, C.W., Ewoldt, R.H.: Reactive coupling between immiscible polymer chains: acceleration by compressive flow. AIChE J. 59(9), 3391–3402 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.14092
Lizymol, P.P., Thomas, S.: Thermal behaviour of polymer blends: a comparison of the thermal properties of miscible and immiscible systems. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 41(1), 59–64 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-3910(93)90061-M
Porter, R.S., Wang, L.-H.: Compatibility and transesterification in binary polymer blends. Polymer 33(10), 2019–2030 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-3861(92)90866-U
Lyatskaya, Y., Gersappe, D., Balazs, A.C.: Effect of copolymer architecture on the efficiency of compatibilizers. Macromolecules 28(18), 6278–6283 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1021/ma00122a040
Lyatskaya, Y., Gersappe, D., Gross, N.A., Balazs, A.C.: Designing compatibilizers to reduce interfacial tension in polymer blends. J. Phys. Chem. 100(5), 1449–1458 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp952422e
Barsky, S., Robbins, M.O.: Bulk and interfacial shear thinning of immiscible polymers. Phys. Rev. E 65(2), 021808 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.65.021808
Ge, T., Grest, G.S., Robbins, M.O.: Structure and strength at immiscible polymer interfaces. ACS Macro Lett. 2(10), 882–886 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/mz400407m
Ge, T., Grest, G.S., Robbins, M.O.: Tensile fracture of welded polymer interfaces: miscibility, entanglements, and crazing. Macromolecules 47(19), 6982–6989 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/ma501473q
Ge, T., Pierce, F., Perahia, D., Grest, G.S., Robbins, M.O.: Molecular dynamics simulations of polymer welding: strength from interfacial entanglements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(9), 098301 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.098301
Xanthos, M.: Interfacial agents for multiphase polymer systems: Recent advances. Polym. Eng. Sci. 28(21), 1392–1400 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.760282108
Elias, L., Fenouillot, F., Majesté, J.C., Alcouffe, P., Cassagnau, P.: Immiscible polymer blends stabilized with nano-silica particles: rheology and effective interfacial tension. Polymer 49(20), 4378–4385 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2008.07.018
Chen, C.C., White, J.L.: Compatibilizing agents in polymer blends: interfacial tension, phase morphology, and mechanical properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 33(14), 923–930 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.760331409
Fenouillot, F., Cassagnau, P., Majesté, J.C.: Uneven distribution of nanoparticles in immiscible fluids: morphology development in polymer blends. Polymer 50(6), 1333–1350 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2008.12.029
Yousfi, M., Soulestin, J., Vergnes, B., Lacrampe, M.-F., Krawczak, P.: Compatibilization of immiscible polymer blends by organoclay: effect of nanofiller or organo-modifier? Macromol. Mater. Eng 298(7), 757–770 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201200138
Si, M., Araki, T., Ade, H., Kilcoyne, A.L.D., Fisher, R., Sokolov, J.C., Rafailovich, M.H.: Compatibilizing bulk polymer blends by using organoclays. Macromolecules 39(14), 4793–4801 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/ma060125+
Sinha Ray, S., Bousmina, M.: Effect of organic modification on the compatibilization efficiency of clay in an immiscible polymer blend. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 26(20), 1639–1646 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.200500447
Guo, Y., He, S., Yang, K., Xue, Y., Zuo, X., Yu, Y., Liu, Y., Chang, C.-C., Rafailovich, M.H.: Enhancing the mechanical properties of biodegradable polymer blends using tubular nanoparticle stitching of the interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(27), 17565–17573 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b05698
Cao, Y., Zhang, J., Feng, J., Wu, P.: Compatibilization of immiscible polymer blends using graphene oxide sheets. ACS Nano 5(7), 5920–5927 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn201717a
Goveas, J.L., Fredrickson, G.H.: Apparent slip at a polymer-polymer interface. Eur. Phys. Journal B 2(1), 79–92 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050228
Lam, Y.C., Jiang, L., Yue, C.Y., Tam, K.C., Li, L., Hu, X.: Interfacial slip between polymer melts studied by confocal microscopy and rheological measurements. J. Rheol. 47(3), 795–807 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1122/1.1566035
Brochard, F., De Gennes, P.G.: Shear-dependent slippage at a polymer/solid interface. Langmuir 8(12), 3033–3037 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1021/la00048a030
Adhikari, N.P., Goveas, J.L.: Effects of slip on the viscosity of polymer melts. J. Polym. Sci. B 42(10), 1888–1904 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.20066
Zhao, R., Macosko, C.W.: Slip at polymer–polymer interfaces: rheological measurements on coextruded multilayers. J. Rheol. 46(1), 145–167 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1122/1.1427912
Zhang, W., Lin, M., Winesett, A., Dhez, O., Kilcoyne, A.L., Ade, H., Rubinstein, M., Shafi, K.V.P.M., Ulman, A., Gersappe, D., Tenne, R., Rafailovich, M., Sokolov, J., Frisch, H.L.: The use of functionalized nanoparticles as non-specific compatibilizers for polymer blends. Polym. Adv. Technol. 22(1), 65–71 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.1875
Plimpton, S.: Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 117(1), 1–19 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcph.1995.1039
Barsky, S., Robbins, M.O.: Molecular dynamics study of slip at the interface between immiscible polymers. Phys. Rev. E 63(2), 021801 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.63.021801
Kremer, K., Grest, G.S.: Dynamics of entangled linear polymer melts: a molecular-dynamics simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 92(8), 5057–5086 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.458541
Kremer, K., Grest, G.S., Carmesin, I.: Crossover from rouse to reptation dynamics: a molecular-dynamics simulation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 61(5), 566–569 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.61.566
Chremos, A., Nikoubashman, A., Panagiotopoulos, A.Z.: Flory-Huggins parameter χ, from binary mixtures of Lennard–Jones particles to block copolymer melts. J. Chem. Phys. 140(5), 054909 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4863331
Xu, D., Bhatnagar, D., Gersappe, D., Sokolov, J.C., Rafailovich, M.H., Lombardi, J.: Rheology of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)–clay nanocomposite hydrogels. Macromolecules 48(3), 840–846 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/ma502111p
Xu, D., Gersappe, D.: Structure formation in nanocomposite hydrogels. Soft Matter 13(9), 1853–1861 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SM02543A
Verlet, L.: Computer “experiments” on classical fluids. I. Thermodynamical properties of Lennard-Jones molecules. Phys. Rev. 159(1), 98–103 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.159.98
Jaber, E., Luo, H., Li, W., Gersappe, D.: Network formation in polymer nanocomposites under shear. Soft Matter 7(8), 3852–3860 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/C0SM00990C
Lobe, V.M., White, J.L.: An experimental study of the influence of carbon black on the rheological properties of a polystyrene melt. Polym. Eng. Sci. 19(9), 617–624 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.760190905
Helfand, E., Tagami, Y.: Theory of the interface between immiscible polymers. J. Chem. Phys. 57(4), 1812–1813 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1678491
Gersappe, D., Robbins, M.O.: Where do polymer adhesives fail? Europhys. Lett. 48(2), 150–155 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1209/epl/i1999-00459-5
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof Miriam Rafailovich and Prof Sherif Abdelaziz for useful discussions. This research was sponsored by the US Army Engineer Research and Development Center (ERDC) and was accomplished under Cooperative Agreement Number W912HZ2020054. The views and conclusions contained in this document are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing the official policies, either expressed or implied, of the Army Research Office, ERDC or the U.S. Government. The U.S. Government is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for Government purposes notwithstanding any copyright notation herein.
Funding
This research was sponsored by the US Army Engineer Research and Development Center (ERDC) and was accomplished under Cooperative Agreement Number W912HZ2020054.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, S., Xu, D. & Gersappe, D. Effect of Compatibilizers on the Structure and Dynamics at Polymer Blend Interfaces. Tribol Lett 69, 61 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-021-01435-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-021-01435-9