Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to explore the expression of lncRNA MALAT1 in patients with T2DM and its clinical significance. A total of 25 normal controls and 69 patients with T2DM were selected.
Methods
Real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to determine the expression level of lncRNA MALAT1 in blood leukocytes of the two groups.
Results
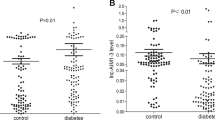
The expression level of lncRNA MALAT1 in patients with T2DM was significantly higher than that in the control group (p < 0.001). The binary regression analysis revealed that lncRNA MALAT1 (p < 0.001, OR = 11.667) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) (p = 0.018, OR = 0.958) were the risk factors for the onset of T2DM. Spearman correlation analysis showed that the expression level of lncRNA MALAT1 correlated positively with cortisol (8 AM), hemoglobin, and blood glucose levels (60, 120, and 180 min) and negatively with SOD and insulin levels after 60 min in the oral glucose tolerance test. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) results demonstrated that the area under the curve of ROC was 0.804, sensitivity was 78.3%, and specificity was 84% (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
LncRNA MALAT1 was highly expressed in patients with T2DM, and high expression of lncRNA MALAT1 is associated with decreased insulin secretion under hyperglycemic stress.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Diabetes A. Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2012. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(4):1033–46.
Halim M, Halim A. The effects of inflammation, aging and oxidative stress on the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus (type 2 diabetes). Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019;13(2):1165–72.
Gomes BF, Accardo CM. Immunoinflammatory mediators in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2019;17(1):eRB4596.
Dong G, Qu L, Gong X, Pang B, Yan W, Wei J. Effect of social factors and the natural environment on the etiology and pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Int J Endocrinol. 2019;2019:8749291.
Leung A, Natarajan R. Long noncoding RNAs in diabetes and diabetic complications. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018;29(11):1064–73.
Feng SD, Yang JH, Yao CH, Yang SS, Zhu ZM, Wu D, et al. Potential regulatory mechanisms of lncRNA in diabetes and its complications. Biochem Cell Biol. 2017;95(3):361–7.
Mei H, Liu Y, Zhou Q, Hu K, Liu Y. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 acts as a potential biomarker in cancer diagnosis and detection: a meta-analysis. Biomark Med. 2019;13(1):45–54.
Cardamone G, Paraboschi EM, Solda G, Cantoni C, Supino D, Piccio L, et al. Not only cancer: the long non-coding RNA MALAT1 affects the repertoire of alternatively spliced transcripts and circular RNAs in multiple sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet. 2019;28(9):1414–28.
Abdulle LE, Hao JL, Pant OP, Liu XF, Zhou DD, Gao Y, et al. MALAT1 as a diagnostic and therapeutic target in diabetes-related complications: a promising long-noncoding RNA. Int J Med Sci. 2019;16(4):548–55.
Zhang Y, Wu H, Wang F, Ye M, Zhu H, Bu S. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 expression in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2018;140(2):164–9.
Liu SX, Zheng F, Xie KL, Xie MR, Jiang LJ, Cai Y. Exercise reduces insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus via mediating the lncRNA MALAT1/MicroRNA-382-3p/resistin axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;18:34–44.
Yan B, Tao Z-F, Li X-M, Zhang H, Yao J, Jiang Q. Aberrant expression of long noncoding RNAs in early diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(2):941.
Zhang M, Gu H, Xu W, Zhou X. Down-regulation of lncRNA MALAT1 reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improves left ventricular function in diabetic rats. Int J Cardiol. 2016;203:214–6.
Hu M, Wang R, Li X, Fan M, Lin J, Zhen J, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 is dysregulated in diabetic nephropathy and involved in high glucose-induced podocyte injury via its interplay with beta-catenin. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(11):2732–47.
American Diabetes A. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(Suppl 1):S13–27.
Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;128:40–50.
Chatterjee S, Khunti K, Davies MJ. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2017;389(10085):2239–51.
Lin C, Yang L. Long noncoding RNA in cancer: wiring signaling circuitry. Trends Cell Biol. 2018;28(4):287–301.
Yao RW, Wang Y, Chen LL. Cellular functions of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(5):542–51.
Zhang N, Geng T, Wang Z, Zhang R, Cao T, Camporez JP, et al. Elevated hepatic expression of H19 long noncoding RNA contributes to diabetic hyperglycemia. JCI Insight. 2018;3(10):e120304.
Ghaedi H, Zare A, Omrani MD, Doustimotlagh AH, Meshkani R, Alipoor S, et al. Genetic variants in long noncoding RNA H19 and MEG3 confer risk of type 2 diabetes in an Iranian population. Gene. 2018;675:265–71.
Zhao X, Rong C, Pan F, Xiang L, Wang X, Hu Y. Expression characteristics of long noncoding RNA uc.322 and its effects on pancreatic islet function. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(11):9239–48.
Zhang Y, Qu L, Ni H, Wang Y, Li L, Yang X, et al. Expression and function of lncRNA MALAT1 in gestational diabetes mellitus. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020;29(8):903–10.
Shi S, Yang J, Fan W, Zhou Z, Chen G, Zhang J. Effects of LncRNA MALAT1 on microangiopathy and diabetic kidney disease in diabetic rats by regulating ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. Minerva Med. 2020;111(2):184–6.
Liu P, Jia SB, Shi JM, Li WJ, Tang LS, Zhu XH, et al. LncRNA-MALAT1 promotes neovascularization in diabetic retinopathy through regulating miR-125b/VE-cadherin axis. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(5):BSR20181469.
Feng T, Shao F, Wu Q, Zhang X, Xu D, Qian K, et al. miR-124 downregulation leads to breast cancer progression via LncRNA-MALAT1 regulation and CDK4/E2F1 signal activation. Oncotarget. 2016;7(13):16205–16.
Ding H, Wang F, Shi X, Ma H, Du Y, Hou L, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 induces the dysfunction of beta cells via reducing the histone acetylation of the PDX-1 promoter in type 1 diabetes. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020;114:104432.
Gong W, Zhu G, Li J, Yang X. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes the apoptosis and oxidative stress of human lens epithelial cells via p38MAPK pathway in diabetic cataract. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;144:314–21.
Chen J, Ke S, Zhong L, Wu J, Tseng A, Morpurgo B, et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates generation of reactive oxygen species and the insulin responses in male mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018;152:94–103.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81960875).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the ethics committee of the hospital, and all participants signed an informed consent form.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Dw., Zhou, L., Huang, Q. et al. High expression of lncRNA MALAT1 is associated with decreased insulin secretion under hyperglycemic stress in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 42, 70–76 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-021-00945-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-021-00945-5