Abstract
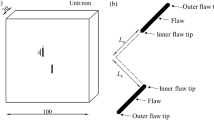
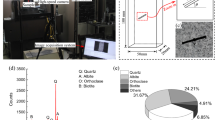
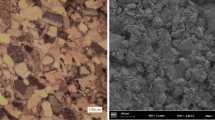
As a representative non-interferometric optical technique, the digital image correlation (DIC) can provide full-field displacement and strain measurement for the deformed rocks. However, the standard DIC technique has a limitation in measuring the displacements at the discontinuity and cannot be directly used for identifying the crack mechanism. Thus, a new DIC-based method is proposed for automatically tracing the discontinuities and quantitatively identifying the crack mechanism, i.e. mode I, mode II, and mixed-mode I/II. The new method involves three steps, including displacement measurement from the standard DIC technique, displacement field reconstruction at the discontinuity with the modified subset splitting technique, and post-processing for crack identification and displacement jump measurement. The effectiveness and robustness of the modified subset splitting technique and post-processing method have been verified with the synthetic images and theoretical displacement fields of mode I crack and dislocation. Then, the proposed method is utilized to locate cracks and quantitatively identify the crack mechanism of the initiated cracks in red sandstone containing a single flaw under uniaxial compression. The crack development in the flawed red sandstone specimens is analyzed and the crack types are summarized, in which wing cracks are in mode I, while horsetail cracks and anti-wing cracks are identified as mixed-mode I/II crack. It is shown that the new method avoids some ambiguous identification of crack mechanism and present more objective results.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourdin F et al (2018) Measurements of plastic localization by heaviside-digital image correlation. Acta Mater 157:307–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2018.07.013
Bruck H, McNeill S, Sutton MA, Peters W (1989) Digital image correlation using Newton–Raphson method of partial differential correction. Exp Mech 29:261–267
Chen D, Chiang F-P, Tan Y, Don H (1993) Digital speckle-displacement measurement using a complex spectrum method. Appl Opt 32:1839–1849
Chen J, Zhan N, Zhang X, Wang J (2015) Improved extended digital image correlation for crack tip deformation measurement. Opt Lasers Eng 65:103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2014.06.010
Cheng Y, Wong LNY, Zou C (2015) Experimental study on the formation of faults from en-echelon fractures in Carrara Marble. Eng Geol 195:312–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.06.004
Deb D, Bhattacharjee S (2015) Extended digital image correlation method for analysis of discrete discontinuity. Opt Lasers Eng 74:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2015.05.006
Dettmers T (2015) Understanding convolution in deep learning. Retrieved March 25:2018
Fagerholt E, Børvik T, Hopperstad OS (2013) Measuring discontinuous displacement fields in cracked specimens using digital image correlation with mesh adaptation and crack-path optimization. Opt Lasers Eng 51:299–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2012.09.010
Han J, Pan B (2018) A novel method for measuring discontinuous deformation in digital image correlation based on partition and dividing strategy. Eng Fract Mech 204:185–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.09.036
Hassan HH, Goussev S (2019) Deep learning approach to automatic detection of faults and fractures from magnetic data using the convolutional neural network (CNN)
Hassan GM, MacNish C, Dyskin A (2015) Extending digital image correlation to reconstruct displacement and strain fields around discontinuities in geomechanical structures under deformation. Paper presented at the 2015 IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision
Hassan GM, Dyskin AV, MacNish CK, Pasternak E, Shufrin I (2018) Discontinuous digital image correlation to reconstruct displacement and strain fields with discontinuities: dislocation approach. Eng Fract Mech 189:273–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2017.11.022
Hedan S, Valle V, Cosenza P (2020) Subpixel precision of crack lip movements by Heaviside-based digital image correlation for a mixed-mode fracture. Strain. https://doi.org/10.1111/str.12346
Liebowitz H, Sih G (1968) Mathematical theories of brittle fracture
Miao S, Pan P-Z, Wu Z, Li S, Zhao S (2018) Fracture analysis of sandstone with a single filled flaw under uniaxial compression. Eng Fract Mech 204:319–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.10.009
Nguyen TL, Hall SA, Vacher P, Viggiani G (2011) Fracture mechanisms in soft rock: identification and quantification of evolving displacement discontinuities by extended digital image correlation. Tectonophysics 503:117–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2010.09.024
Pan B, Qian K, Xie H, Asundi A (2009) Two-dimensional digital image correlation for in-plane displacement and strain measurement: a review. Meas Sci Technol 20:062001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-0233/20/6/062001
Pan B, Li K, Tong W (2013) Fast, robust and accurate digital image correlation calculation without redundant computations. Exp Mech 53:1277–1289
Pan B, Wang B, Lubineau G (2016) Comparison of subset-based local and FE-based global digital image correlation: theoretical error analysis and validation. Opt Lasers Eng 82:148–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2016.02.019
Pan P-Z, Miao S, Jiang Q, Wu Z, Shao C (2019) The influence of infilling conditions on flaw surface relative displacement induced cracking behavior in hard rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-02033-x
Pan P-Z, Miao S, Wu Z, Feng X-T, Shao C (2020) Laboratory observation of spalling process induced by tangential stress concentration in hard rock tunnel. Int J Geomech. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0001620
Park CH, Bobet A (2010) Crack initiation, propagation and coalescence from frictional flaws in uniaxial compression. Eng Fract Mech 77:2727–2748
Pilch A, Mahajan A, Chu T (2004) Measurement of whole-field surface displacements and strain using a genetic algorithm based intelligent image correlation method. J Dyn Syst Meas Control 126:479–488
Poissant J, Barthelat F (2009) A novel, “subset splitting” procedure for digital image correlation on discontinuous displacement fields. Exp Mech 50:353–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-009-9220-2
Réthoré J, Roux S, Hild F (2009) An extended and integrated digital image correlation technique applied to the analysis of fractured samples: the equilibrium gap method as a mechanical filter. Eur J Comput Mech 18:285–306
Sagong M, Bobet A (2002) Coalescence of multiple flaws in a rock-model material in uniaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 39:229–241
Shen B, Stephansson O, Einstein HH, Ghahreman B (1995) Coalescence of fractures under shear stresses in experiments. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 100:5975–5990. https://doi.org/10.1029/95jb00040
Sutton M, Turner J, Bruck H, Chae T (1991) Full-field representation of discretely sampled surface deformation for displacement and strain analysis. Exp Mech 31:168–177
Valle V, Hedan S, Cosenza P, Fauchille AL, Berdjane M (2014) Digital image correlation development for the study of materials including multiple crossing cracks. Exp Mech 55:379–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-014-9948-1
Wang Y, Zhou X, Shou Y (2017) The modeling of crack propagation and coalescence in rocks under uniaxial compression using the novel conjugated bond-based peridynamics. Int J Mech Sci 128–129:614–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.05.019
Whittaker BN, Singh RN, Sun G (1992) Rock fracture mechanics: principles, design and applications. Elsevier
Wong LNY, Einstein HH (2008) Crack coalescence in molded gypsum and carrara marble: Part 1. Macroscopic observations and interpretation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 42:475–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-008-0002-4
Wong LNY, Einstein HH (2009) Systematic evaluation of cracking behavior in specimens containing single flaws under uniaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46:239–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.03.006
Yang S-Q (2015) Experimental investigation on strength and failure behavior of pre-cracked marble under conventional triaxial compression. Strength failure and crack evolution behavior of rock materials containing pre-existing fissures. Springer environmental science and engineering. Springer, pp 185–216
Yang S-Q, Jing H-W (2010) Strength failure and crack coalescence behavior of brittle sandstone samples containing a single fissure under uniaxial compression. Int J Fract 168:227–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-010-9576-4
Yin P, Wong RHC, Chau KT (2014) Coalescence of two parallel pre-existing surface cracks in granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 68:66–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.02.011
Zhou X-P, Wang Y-T, Zhang J-Z, Liu F-N (2018a) Fracturing behavior study of three-flawed specimens by uniaxial compression and 3D digital image correlation: sensitivity to brittleness. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:691–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1600-4
Zhou XP, Lian YJ, Wong LNY, Berto F (2018b) Understanding the fracture behavior of brittle and ductile multi-flawed rocks by uniaxial loading by digital image correlation. Eng Fract Mech 199:438–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.06.007
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the State Key Research Development Program of China (Grant no. 2017YFC0804203), International Partnership Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. 115242KYSB20160017), and Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant no. QYZDB-SSW-DQC029), and the Open Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Geomechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant no. Z018001). The first author would like to thank the Chinese Scholarship Council for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, S., Pan, PZ., Zhao, S. et al. A New DIC-Based Method to Identify the Crack Mechanism and Applications in Fracture Analysis of Red Sandstone Containing a Single Flaw. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54, 3847–3871 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02472-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02472-5