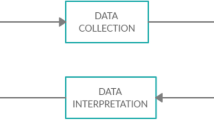
Abstract
Over the last decade, the amount of Arabic content created on websites and social media has grown significantly. Opinions are shared openly and freely on social media and thus provide a rich source for trend analyses, which are accomplished by conventional methods of language interpretation, such as sentiment analysis. Due to its accuracy in studying unstructured data, deep learning has been increasingly used to test opinions. Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are a promising approach in textual analysis and exhibit large morphological variations. In total, 193 studies used RNNs in English-language sentiment analysis, and 24 studies used RNNs in Arabic-language sentiment analysis. Those studies varied in the areas they address, the functionality and weaknesses of the models, and the number and scale of the available datasets for different dialects. Such variations are worthy of attention and monitoring; thus, this paper presents a systematic examination of the literature to label, evaluate, and identify state-of-the-art studies using RNNs for Arabic sentiment analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Abbes M, Kechaou Z, Alimi AM (2017) Enhanced deep learning models for sentiment analysis in Arab social media. In: Liu D, Xie S, Li Y et al (eds) Neural information processing. Springer, Cham, pp 667–676
Abdou M, Kulmizev A, Ginés i Ametllé J (2018) AffecThor at SemEval-2018 Task 1: A cross-linguistic approach to sentiment intensity quantification in tweets. In: Proceedings of The 12th international workshop on semantic evaluation. Association for Computational Linguistics, New Orleans, Louisiana, pp 210–217
Abdulla NA, Ahmed NA, Shehab MA, Al-Ayyoub M (2013) Arabic sentiment analysis: Lexicon-based and corpus-based. In: 2013 IEEE Jordan conference on applied electrical engineering and computing technologies (AEECT). IEEE, Amman, Jordan, pp 1–6
Abdullah M, Shaikh S (2018) TeamUNCC at SemEval-2018 Task 1: emotion detection in English and Arabic tweets using deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 12th international workshop on semantic evaluation. Association for Computational Linguistics, New Orleans, Louisiana, pp 350–357
Abdullah M, Hadzikadicy M, Shaikhz S (2018) SEDAT: sentiment and emotion detection in Arabic text using CNN-LSTM deep learning. In: 2018 17th IEEE international conference on machine learning and applications (ICMLA). pp 835–840
Abdul-Mageed M, Alhuzali H, Abu Elhija D, Diab M (2016) Dina: A multidialect dataset for arabic emotion analysis. In: The 2nd workshop on Arabic Corpora and processing tools 2016 theme: Social Media, p 29
Adhikari NCD, Kurva VK, S S, et al (2018) Sentiment classifier and analysis for epidemic prediction. In: Computer science & information technology (CS & IT). AIRCC Publishing Corporation, pp 31–48
Ain QT, Ali M, Riaz A, et al (2017) Sentiment analysis using deep learning techniques: a review. thesai, pp 424–433
Alayba AM, Palade V, England M, Iqbal R (2017) Arabic language sentiment analysis on health services. In: 2017 1st international workshop on Arabic script analysis and recognition (ASAR), pp 114–118. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1109/ASAR.2017.8067771
Alayba AM, Palade V, England M, Iqbal R (2018a) Improving sentiment analysis in Arabic using word representation. In: 2018 IEEE 2nd international workshop on Arabic and derived script analysis and recognition (ASAR). IEEE, London, pp 13–18
Alayba AM, Palade V, England M, Iqbal R (2018b) A combined CNN and LSTM model for arabic sentiment analysis. In: Holzinger A, Kieseberg P, Tjoa AM, Weippl E (eds) Machine learning and knowledge extraction. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 179–191
Al-Azani S, El-Alfy E-SM (2017) Hybrid deep learning for sentiment polarity determination of Arabic microblogs. In: Liu D, Xie S, Li Y et al (eds) Neural information processing. Springer, Cham, pp 491–500
Al-Azani S, El-Alfy E-S (2018) Emojis-based sentiment classification of Arabic microblogs using deep recurrent neural networks. In: 2018 international conference on computing sciences and engineering (ICCSE). IEEE, Kuwait City, pp 1–6
Albadi N, Kurdi M, Mishra S (2018) Are they our brothers? Analysis and detection of religious hate speech in the Arabic Twittersphere. In: 2018 IEEE/ACM international conference on advances in social networks analysis and mining (ASONAM). IEEE, Barcelona, pp 69–76
Alhumoud S, Albuhairi T, Altuwaijri M (2015) Arabic sentiment analysis using WEKA a hybrid learning approach. In: 2015 7th international joint conference on knowledge discovery, knowledge engineering and knowledge management (IC3K), pp 402–408
Alhuzali H, Abdul-Mageed M, Ungar L (2018) Enabling deep learning of emotion with first-person seed expressions. In: Proceedings of the second workshop on computational modeling of people’s opinions, personality, and emotions in social media. Association for Computational Linguistics, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, pp 25–35
Al-Rfou R, Perozzi B, Skiena S (2013) Polyglot: distributed word representations for multilingual NLP. In: Proceedings of the seventeenth conference on computational natural language learning. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 183–192
Alsayat A, Elmitwally N (2020) A comprehensive study for Arabic sentiment analysis (challenges and applications). Egypt Inf J 21:7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eij.2019.06.001
Al-Smadi M, Qawasmeh O, Al-Ayyoub M et al (2018) Deep Recurrent neural network vs. support vector machine for aspect-based sentiment analysis of Arabic hotels’ reviews. J Comput Sci 27:386–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2017.11.006
Al-Smadi M, Talafha B, Al-Ayyoub M, Jararweh Y (2019) Using long short-term memory deep neural networks for aspect-based sentiment analysis of Arabic reviews. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10:2163–2175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-0799-4
AL-Smadi M, Qwasmeh O, Talafha B et al (2016) An enhanced framework for aspect-based sentiment analysis of Hotels’ reviews: Arabic reviews case study. In: 2016 11th international conference for internet technology and secured transactions (ICITST). IEEE, Barcelona, Spain, pp 98–103
Altowayan AA, Tao L (2016) Word embeddings for Arabic sentiment analysis. In: 2016 IEEE international conference on big data (big data). IEEE, Washington DC, USA, pp 3820–3825
Al-Twairesh N, Al-Khalifa H, Al-Salman A, Al-Ohali Y (2017) AraSenTi-Tweet: a Corpus for Arabic Sentiment Analysis of Saudi Tweets. Proc Comput Sci 117:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.10.094
Alwehaibi A, Roy K (2018) Comparison of pre-trained word vectors for Arabic text classification using deep learning approach. In: 2018 17th IEEE international conference on machine learning and applications (ICMLA), pp 1471–1474
Aly M, Atiya A (2013) LABR: a large scale arabic book reviews dataset. Unpublished. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.13140/2.1.3960.5761
Ayyadevara VK (2018) Recurrent neural network. In: Ayyadevara VK (ed) Pro Machine learning algorithms : a hands-on approach to implementing algorithms in Python and R. Apress, Berkeley, pp 217–257
Baccouche A, Garcia-Zapirain B, Elmaghraby A (2018) Annotation technique for health-related tweets sentiment analysis. In: 2018 IEEE international symposium on signal processing and information technology (ISSPIT). IEEE, Louisville, KY, USA, pp 382–387
Badaro G, Baly R, Hajj H, et al (2014) A large scale Arabic sentiment lexicon for Arabic opinion mining. In: Proceedings of the EMNLP 2014 workshop on arabic natural language processing (ANLP). Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha, Qatar, pp 165–173
Badaro G, El Jundi O, Khaddaj A et al (2018) EMA at SemEval-2018 Task 1: emotion mining for Arabic. In: Proceedings of the 12th international workshop on semantic evaluation. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 236–244
Baly R, El-Khoury G, Moukalled R et al (2017) Comparative evaluation of sentiment analysis methods across Arabic dialects. Proc Comput Sci 117:266–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.10.118
Baly R, Badaro G, El-Khoury G, et al (2017a) A characterization study of Arabic Twitter data with a benchmarking for state-of-the-art opinion mining models. In: Proceedings of the third Arabic natural language processing workshop. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 110–118
Banea C, Mihalcea R, Wiebe J (2010) Multilingual subjectivity: are more languages better? In: Coling 2010—23rd international conference on computational linguistics, proceedings of the conference. pp 28–36
Baniata LH, Park S-B (2016) Sentence representation network for arabic sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 43rd annual meeting and winter conference (제43회 정기총회 및 동계학술발표회). Gangwon-do , South Korea, pp 470–472
Bengio Y, Simard P, Frasconi P (1994) Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 5:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.279181
Boudad N, Faizi R, Oulad Haj Thami R, Chiheb R (2018) Sentiment analysis in Arabic: a review of the literature. Ain Shams Eng J 9:2479–2490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2017.04.007
Brun C, Perez J, Roux C (2016) XRCE at SemEval-2016 Task 5: feedbacked ensemble modeling on syntactico-semantic knowledge for aspect based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 10th international workshop on semantic evaluation (SemEval-2016). Association for Computational Linguistics, San Diego, California, pp 277–281
Cho K, van Merrienboer B, Gulcehre C et al (2014) Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder–decoder for statistical machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP). Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha, Qatar, pp 1724–1734
Chung J, Gulcehre C, Cho K, Bengio Y (2014) Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv:14123555 [cs]
Cliche M (2017) BB_twtr at SemEval-2017 Task 4: Twitter sentiment analysis with CNNs and LSTMs. In: Proceedings of the 11th international workshop on semantic evaluation (SemEval-2017). Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver, Canada, pp 573–580
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20:273–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00994018
Dahou A, Xiong S, Zhou J et al (2016) Word Embeddings and convolutional neural network for Arabic sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of COLING 2016, the 26th international conference on computational linguistics: technical papers. The COLING 2016 Organizing Committee, Osaka, Japan, pp 2418–2427
Dashtipour K, Poria S, Hussain A et al (2016) Multilingual sentiment analysis: state of the art and independent comparison of techniques. Cogn Comput 8:757–771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-016-9415-7
El-khair IA (2016) 1.5 billion words Arabic Corpus. arXiv:161104033 [cs]
El-Kilany A, Azzam A, El-Beltagy SR (2018) Using deep neural networks for extracting sentiment targets in Arabic Tweets. In: Shaalan K, Hassanien AE, Tolba F (eds) Intelligent natural language processing: trends and applications. Springer, Cham, pp 3–15
Elmadany AA, Mubarak H, Magdy W (2018) An Arabic speech-act and sentiment Corpus of Tweets. In: Proceedings of the eleventh international conference on language resources and evaluation (LREC 2018). European Language Resources Association (ELRA)
Elman J (1990) Finding structure in time. Cogn Sci 14:179–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/0364-0213(90)90002-E
Elnagar A, Lulu L, Einea O (2018) An Annotated huge dataset for standard and colloquial Arabic reviews for subjective sentiment analysis. Proc Comput Sci 142:182–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.474
González J-Á, Pla F, Hurtado L-F (2017) ELiRF-UPV at SemEval-2017 Task 4: sentiment analysis using deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 11th international workshop on semantic evaluation (SemEval-2017). Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 723–727
Graves A, Mohamed A, Hinton G (2013) Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing. IEEE, Vancouver, BC, Canada, pp 6645–6649
Habash NY (2010) Introduction to Arabic natural language processing. Synth Lect Hum Lang Technol 3:1–187. https://doi.org/10.2200/S00277ED1V01Y201008HLT010
Heckman S, Williams L (2011) A systematic literature review of actionable alert identification techniques for automated static code analysis. Inf Softw Technol 53:363–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2010.12.007
Heikal M, Torki M, El-Makky N (2018) Sentiment analysis of Arabic tweets using deep learning. Proc Comput Sci 142:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.466
Hemmatian F, Sohrabi MK (2017) A survey on classification techniques for opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Artif Intell Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9599-6
Hermans M, Schrauwen B (2013) Training and analyzing deep recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 26th international conference on neural information processing systems—volume 1. Curran Associates Inc., USA, pp 190–198
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long short-term memory. Neural Comput 9:1735–1780. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Irsoy O, Cardie C (2014) Opinion mining with deep recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP). Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha, Qatar, pp 720–728
Karpathy A (2015) The unreasonable effectiveness of recurrent neural networks. In: Andrej Karpathy blog. http://karpathy.github.io/2015/05/21/rnn-effectiveness/
Kemp S (2018) Digital in 2018: essential insights into internet, social media, mobile, and ecommerce use around the world
Kim Y (2014) Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification. In: Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP). Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha, Qatar, pp 1746–1751
Kiritchenko S, Mohammad S, Salameh M (2016) SemEval-2016 Task 7: determining sentiment intensity of English and Arabic Phrases. In: Proceedings of the 10th international workshop on semantic evaluation (SemEval-2016). Association for Computational Linguistics, San Diego, California, pp 42–51
Kitchenham B (2004) Procedures for performing systematic reviews. Keele Univ, Keele, p 33
Kobayashi T, Hirose K, Nakamura S (eds) (2010) Recurrent neural network based language model. ISCA, Makuhari, Chiba, pp 1045–1048
Kumar A, Kohail S, Kumar A, et al (2016) IIT-TUDA at SemEval-2016 Task 5: beyond sentiment Lexicon: combining domain dependency and distributional semantics features for aspect based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 10th international workshop on semantic evaluation (SemEval-2016). Association for Computational Linguistics, San Diego, California, pp 1129–1135
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521:436–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Liu B, Zhang L (2012) A survey of opinion mining and sentiment analysis. In: Aggarwal CC, Zhai C (eds) Mining text data. Springer, Boston, pp 415–463
MacAvaney S, Yao H-R, Yang E et al (2019) Hate speech detection: challenges and solutions. PLoS ONE 14:e0221152. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0221152
Madhoushi Z, Hamdan AR, Zainudin S (2015) Sentiment analysis techniques in recent works. In: 2015 science and information conference (SAI), pp 288–291
Medhat W, Hassan A, Korashy H (2014) Sentiment analysis algorithms and applications: a survey. Ain Shams Eng J 5:1093–1113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2014.04.011
Mikolov T, Chen K, Corrado G, Dean J (2013) Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. In: ICLR workshop papers
Mohammad SM, Salameh M, Kiritchenko S (2016) How translation alters sentiment. J Artif Intell Res 55:95–130. https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.4787
Mohammad S, Bravo-Marquez F, Salameh M, Kiritchenko S (2018) SemEval-2018 Task 1: affect in tweets. In: Proceedings of the 12th international workshop on semantic evaluation. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 1–17
Mourad A, Darwish K (2013) Subjectivity and sentiment analysis of modern standard Arabic and Arabic microblogs. In: Proceedings of the 4th workshop on computational approaches to subjectivity, sentiment and social media analysis. Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 55–64
Nabil M, Aly M, Atiya A (2015) ASTD: Arabic sentiment tweets dataset. In: Proceedings of the 2015 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing. Association for Computational Linguistics, Lisbon, Portugal, pp 2515–2519
Najafabadi MM, Villanustre F, Khoshgoftaar TM et al (2015) Deep learning applications and challenges in big data analytics. J Big Data. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-014-0007-7
Oueslati O, Cambria E, HajHmida MB, Ounelli H (2020) A review of sentiment analysis research in Arabic language. Futur Gener Comput Syst 112:408–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2020.05.034
Pang B, Lee L (2008) Opinion Mining and Sentiment Analysis. Found Trends® Inf Retr 2:1–135. https://doi.org/10.1561/1500000011
Pang B, Lee L, Vaithyanathan S (2002) Thumbs up? Sentiment classification using machine learning techniques. In: Proceedings of the ACL-02 conference on Empirical methods in natural language processing - EMNLP ’02. Association for Computational Linguistics, Not Known, pp 79–86
Pascanu R, Mikolov T, Bengio Y (2013) On the difficulty of training recurrent neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 30th international conference on international conference on machine learning—volume 28. JMLR.org, p III-1310-III–1318
Pennington J, Socher R, Manning C (2014) Glove: global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP). Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha, Qatar, pp 1532–1543
Ponti EM, Vulić I, Korhonen A (2017) Decoding sentiment from distributed representations of sentences. In: Proceedings of the 6th joint conference on lexical and computational semantics (*SEM 2017). Association for Computational Linguistics, Vancouver, Canada, pp 22–32
Pontiki M, Galanis D, Papageorgiou H et al (2016a) SemEval-2016 Task 5 data and tools. http://alt.qcri.org/semeval2016/task5/index.php?id=data-and-tools
Pontiki M, Galanis D, Papageorgiou H, et al (2016b) SemEval-2016 task 5: aspect based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 10th international workshop on semantic evaluation (SemEval-2016). Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 19–30
Rani S, Kumar P (2019) A journey of Indian languages over sentiment analysis: a systematic review. Artif Intell Rev 52:1415–1462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-018-9670-y
Refaee E, Rieser V (2014) An Arabic Twitter corpus for subjectivity and sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the ninth international conference on language resources and evaluation (LREC’14). European Language Resources Association (ELRA), Reykjavik, Iceland, pp 2268–2273
Reinsel D, Gantz J, Rydning J (2018) The digitization of the world from edge to core
Rohith VDM (2018) Sentiment analysis on twitter: a survey. Int J Pure Appl Math 118:365–375
Rosenthal S, Farra N, Nakov P (2017) SemEval-2017 task 4: sentiment analysis in Twitter. In: Proceedings of the 11th international workshop on semantic evaluation (SemEval-2017). pp 502–518
Ruder S, Ghaffari P, Breslin JG (2016a) A hierarchical model of reviews for aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2016 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing. Association for Computational Linguistics, Austin, Texas, pp 999–1005
Ruder S, Ghaffari P, Breslin JG (2016b) INSIGHT-1 at SemEval-2016 Task 5: deep learning for multilingual aspect-based sentiment analysis. In: Proceedings of the 10th international workshop on semantic evaluation (SemEval-2016). Association for Computational Linguistics, San Diego, California, pp 330–336
Saleh IM (2009) Automatic extraction of lemma-based bilingual dictionaries for morphologically rich languages. In: Proceedings of MT summit, Ottawa, Canada
Samy AE, El-Beltagy SR, Hassanien E (2018) A context integrated model for multi-label emotion detection. Proc Comput Sci 142:61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.461
Schmidhuber J (2015) Deep learning in neural networks: an overview. Neural Netw 61:85–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2014.09.003
Schuster M, Paliwal KK (1997) Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans Signal Process 45:2673–2681. https://doi.org/10.1109/78.650093
Shoukry A, Rafea A (2012) Sentence-level Arabic sentiment analysis. In: 2012 International conference on collaboration technologies and systems (CTS). IEEE, Denver, CO, USA, pp 546–550
Socher R, Perelygin A, Wu J et al (2013) Recursive deep models for semantic compositionality over a sentiment Treebank. In: Proceedings of the 2013 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing. Association for Computational Linguistics, Seattle, Washington, USA, pp 1631–1642
Soliman AB, Eissa K, El-Beltagy SR (2017) AraVec: a set of Arabic word embedding models for use in Arabic NLP. Proc Comput Sci 117:256–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2017.10.117
Souri A, El Maazouzi Z, Al Achhab M, El Mohajir BE (2018) Arabic text generation using recurrent neural networks. In: Tabii Y, Lazaar M, Al Achhab M, Enneya N (eds) Big data, cloud and applications. Springer, Cham, pp 523–533
Sundermeyer M, Ney H, Schluter R (2015) From feedforward to recurrent LSTM neural networks for language modeling. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 23:517–529. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASLP.2015.2400218
Tai KS, Socher R, Manning CD (2015) Improved semantic representations from tree-structured long short-term memory networks. In: Proceedings of the 53rd annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th international joint conference on natural language processing (volume 1: long papers). Association for Computational Linguistics, Beijing, China, pp 1556–1566
Tamchyna A, Veselovská K (2016) UFAL at SemEval-2016 Task 5: recurrent neural networks for sentence classification. In: Proceedings of the 10th international workshop on semantic evaluation (SemEval-2016). Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 367–371
Tang D, Qin B, Liu T (2015) Document modeling with gated recurrent neural network for sentiment classification. In: Proceedings of the 2015 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing. Association for Computational Linguistics, Lisbon, Portugal, pp 1422–1432
Turki Khemakhem I, Jamoussi S, Ben Hamadou A (2010) Arabic morpho-syntactic feature disambiguation in a translation context. In: Proceedings of the 4th workshop on syntax and structure in statistical translation. Coling 2010 Organizing Committee, Beijing, China, pp 61–65
Vohra MSM, Teraiya J (2013) A comparative study of sentiment analysis techniques 1. J Inf Knowl Res Comput Eng 12:313–317
Wang B, Lu W (2018) Learning latent opinions for aspect-level sentiment classification. AAAI, pp 5537–5544
Yadav A, Vishwakarma DK (2019) Sentiment analysis using deep learning architectures: a review. Artif Intell Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09794-5
Yin W, Kann K, Yu M, Schütze H (2017) Comparative study of CNN and RNN for natural language processing. arXiv:170201923 [cs]
Young T, Hazarika D, Poria S, Cambria E (2018) Recent trends in deep learning based natural language processing [Review Article]. IEEE Comput Intell Mag 13:55–75. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCI.2018.2840738
Zhang Y, Jin R, Zhou Z-H (2010) Understanding bag-of-words model: a statistical framework. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 1:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-010-0001-0
Zhang L, Wang S, Liu B (2018) Deep learning for sentiment analysis: A survey. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Data Min Knowl Discov 8:e1253. https://doi.org/10.1002/widm.1253
Acknowledgement
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University for funding and supporting this work through Graduate Students Research Support Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alhumoud, S.O., Al Wazrah, A.A. Arabic sentiment analysis using recurrent neural networks: a review. Artif Intell Rev 55, 707–748 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-09989-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-09989-9