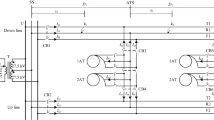
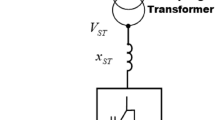
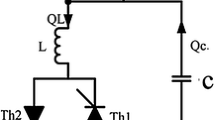
Abstract
FACTS devices are presently used to improve the power transfer capability of a transmission line and voltage stability of a power system network. Shunt injected current (Ish) by the Static Var Compensators (SVC) causes underreach or overreach of distance relay when not considered during relay calibration of protection system. This paper presents an adaptive relay setting procedure in the presence of a SVC connected at the midpoint of a transmission line. The remote terminal unit RTU is connected to the SVC terminal via a current transformer (CT) measures the injected shunt current when the SVC is the switch in or out of the network and transferred the measured value to the local station via fiber optic. The PSCAD/ EMTDC software is used to model an adaptive relay that implements the conventional and adaptive relay system settings. The proposed scheme presents a hybrid distance protection system whose setting is based on the prevailing SVC switching conditions; the relay system was implemented using mho characteristics relay. The results obtained show that the proposed scheme has a high accurate setting.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.K.Padiyar “FACTS controllers in power transmission and distribution”, New Age International Publishers; 2007
Maturu S, Shenoy UJ (2005) Performance issues o of distance relays for shunt FACTS compensated transmission lines. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 20(3):1837–1845
A. Ahmed, A. R. Singh, S. Dambhare, (2012) New Modified first zone Algorithm for Transmission lines with series compensators”, IEEE Fifth Power India Conference, Murthal, India . Pp.1–5
Sidhu TS, Varma RK, Gangadharan PK, Albasri FA, Ortiz GR (2005) Performance of distance relays on shunt—FACTS compensated transmission lines. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 20(3):1837–1845
Albasri FA, Sidhu TS, Varma RK (2007) Performance comparison of distance protection schemes for shunt-facts compensated transmission lines. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 22(4):2116–2125
Hingorani NG, Gyugyi L (1999) Understanding FACTS: concepts and technology of flexible AC transmission systems. Wiley, New York
El-Arroudi K, Joos G, and D T McGillis. (2002) Operation of impedance protection relays with the STATCOM”. IEEE Transactions Power Delivery; 17 (2):381–387
Sidhu TS, Varma RK, Gangadharan PK, Albasri FA, Ortiz GR (2005) Performance of distance relays on shunt—FACTS compensated transmission lines. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 20(3):1837–45
M. Khederzadeh, and A. Ghorbani. “STATCOM modeling impacts on performance evaluation of distance protection of transmission lines” Euro Transactions Electric Power 2011(8):2063–79.
P. K. Dash, A. K. Pradhan, G. Panda, and A.C. Liew (2000) Adaptive relay setting for flexible AC transmission systems (FACTS)”. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery; 15(1):38–43
Dash PK, Pradhan AK, Panda G (2000) Distance protection in the presence of unified power flow controller. Electric Power Syst Res 54:189–98
Khederzadeh M, Ghorbani A (2012) Impact of VSC-based multiline FACTS controllers on distance protection of transmission lines. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 27(1):32–9
Ghorbani A, Khederzadeh M, Mozafari B (2012) Impact of SVC on the protection of transmission lines. Electrical Power Energy Syst 42:702–709
B. Sandeep and M. Biswal, " Adaptive Distance Relay Algorithm for Shunt Compensated Transmission line" IEEE International Conference on Electric Power and Energy Systems, ICEPES, Bhopal, India, Dec. 2016, pp 426-431
Suonan J, Liu K, Song G (2011) A novel UHV/EHV transmission- line pilot protection based on fault component integrated impedance. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 26(1):127–134
Gupta OH, Tripathy M (2015) An Innovative Pilot Relaying Scheme for Shunt Compensated Line. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 30(3):1439–1448
Ghazizadeh M, Sadeh J (2012) Accurate fault location algorithm for transmission lines in the presence of shunt-connected flexible AC transmission system devices. IET Gener Trans Distrib 6(3):247–255
M.C. Janssen and A. P. Apostolov, “IEC 61850 impact on substation design.” IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition, pp. 1–7, Chicago, IL, USA, 2008
A.G. Phadke and J.S. Thorp “Computer Relaying Power Systems”. England: John Wiley and Sons Ltd; 2009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uma, U.U., Ekwue, A., Nmadu, D. et al. Adaptive Distance Protection Scheme Setting in Presence of SVC Using Remote Terminal Unit. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 16, 1867–1877 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-021-00731-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-021-00731-7