Abstract
Purpose
Differences in the composition and properties of soil organic matter (SOM) components with different decomposition stages determine their ability and mechanism to sequester heavy metals in contaminated soils. However, very little research has emphasized the adsorption properties of heavy metals on humic acid (HA) versus particulate organic matter (POM).
Materials and methods
X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectral analysis, in combination with Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), was applied to investigate the structures and compositions of tropical secondary soil-derived POM and HA and their adsorption characteristics for lead (Pb).
Results and discussion
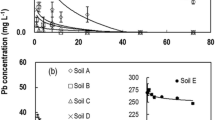
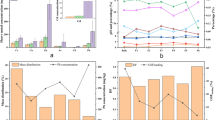
Results revealed that HA was characterized by high aromaticity and cation exchange capacity (CEC) and a smoother structure, while POM mainly consisted of aliphatic components with comparable polarities with high H/C and (N+O)/C ratios was embedded with soil minerals (e.g., gibbsite, silicate, and phosphate) and possessed a larger specific surface area and high content of Si-O-Si and free -OH groups. The equilibrium adsorption data for HA followed fit the Langmuir model with a maximum capacity of 72.57 mg g−1 while those for POM the Freundlich model with a maximum capacity of 22.27 mg g−1. Freundlich-n and KF values suggested that sorption of Pb on POM displayed a nonlinear isotherm and lower initial affinity relative to that on HA. XAFS results showed that two major Pb species similar to Pb(C2H3O2)2 and PbO were formed in Pb-loaded HA, while four major Pb species similar to Pb-loaded Al2O3, Pb(C2H3O2)2, Pb3(PO4)2, and PbSiO3 were formed in Pb-loaded POM. Based on desorption and spectroscopic studies, Pb sorption sites on HA were primarily ascribed to metal exchange and surface inner-sphere complexation with phenolic hydroxyl and carboxyl functional groups, while Pb sorption on POM involved coprecipitation, electrostatic cation exchange, and inner-sphere complexation with complexed organic functional groups and mineral oxides, and these processes accounted for 65% and 48% of the total sorbed Pb on HA and POM, respectively, and led to a series of Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, and Na+ releases during the sorption process. In addition, the contribution of hydrogen bonding to Pb sorption on HA and POM was significant, accounting for 34% and 46%, respectively. Thus, differences in sorption mechanisms between HA and POM help us choose effective strategies for enhancing Pb(II) removal and environmental risk assessment in aqueous (e.g., wastewater) and soil environments.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelrahman H, Cocozza C, Olk D, Ventrella D, Miano T (2017) Carbohydrates and amino compounds as short-term indicators of soil management. Clean (Soil Air Water) 45. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201600076
Andreas R, Zhang J (2014) Characteristics of adsorption interactions of cadmium (II) onto humin from peat soil in freshwater and seawater media. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92:352–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1205-x
Balabane M, van Oort F (2002) Metal enrichment of particulate organic matter in arable soils with low metal contamination. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1513–1516. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0038-0717(02)00066-4
Basolo F, Johnson RC (eds) (1986) Coordination Chemistry. W.A. Benjamin, New York
Buffle J (1984) Natural organic matter and metal-organic interactions in aquatic systems. Met Ions Biol Syst 18:165–221
Buffle J, DeVitre RR (1993) Chemical and biological regulation of aquatic systems. CRC press, Boca Raton
Cao X, Ma L, Gao B, Harris W (2009) Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine. Environ Sci Technol 43:3285–3291. https://doi.org/10.1021/es803092k
Cerli C, Celi L, Kalbitz K, Guggenberger G, Kaiser K (2012) Separation of light and heavy organic matter fractions in soil—testing for proper density cut-off and dispersion level. Geoderma 170:403–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.10.009
Chen Y, Furmann A, Mastalerz M, Schimmelmann A (2014) Quantitative analysis of shales by KBr-FTIR and micro-FTIR. Fuel 116:538–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.08.052
DiDonato N, Chen H, Waggoner D, Hatcher PG (2016) Potential origin and formation for molecular components of humic acids in soils. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 178:210–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2016.01.013
Ellingham ST, Thompson TJ, Islam M (2018) Scanning electron microscopy–energy-dispersive X-ray (SEM/EDX): a rapid diagnostic tool to aid the identification of burnt bone and contested cremains. J Forensic Sci 63:504–510. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.13541
Fulda B, Voegelin A, Kretzschmar R (2013) Redox-controlled changes in cadmium solubility and solid-phase speciation in a paddy soil as affected by reducible sulfate and copper. Environ Sci Technol 47:12775–12783. https://doi.org/10.1021/es401997d
Gezici O, Kara H, Yanık S, Ayyildiz HF, Kucukkolbasi S (2007) Investigating sorption characteristics of copper ions onto insolubilized humic acid by using a continuously monitored solid phase extraction technique. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 298:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.12.007
Ghabbour EA, Scheinost AC, Davies G (2007) XAFS studies of cobalt (II) binding by solid peat and soil-derived humic acids and plant-derived humic acid-like substances. Chemosphere 67:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.09.094
Gregorich E, Beare M, McKim U, Skjemstad J (2006) Chemical and biological characteristics of physically uncomplexed organic matter. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:975–985. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2005.0116
Guo X, Zhang S, Shan X q, Luo L, Pei Z, Zhu YG, Liu T, Xie Y n, Gault A (2006) Characterization of Pb, Cu, and Cd adsorption on particulate organic matter in soil. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2366–2373. https://doi.org/10.1897/05-636R.1
Guo X, Luo L, Ma Y, Zhang S (2010) Sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on particulate organic matters. J Hazard Mater 173:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.065
Houben D, Sonnet P, Cornelis J-T (2014) Biochar from Miscanthus: a potential silicon fertilizer. Plant Soil 374:871–882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1885-8
Huang Z, Lu Q, Wang J, Chen X, Mao X, He Z (2017) Inhibition of the bioavailability of heavy metals in sewage sludge biochar by adding two stabilizers. PLoS One 12:e0183617. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183617
Ippolito J, Strawn D, Scheckel K, Novak J, Ahmedna M, Niandou M (2012) Macroscopic and molecular investigations of copper sorption by a steam-activated biochar. J Environ Qual 41:1150–1156. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2011.0113
Jiang R, Wang M, Chen W (2018) Characterization of adsorption and desorption of lawn herbicide siduron in heavy metal contaminated soils. Chemosphere 204:483–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.045
Johnson MD, Huang W, Weber WJ (2001) A distributed reactivity model for sorption by soils and sediments. 13. Simulated diagenesis of natural sediment organic matter and its impact on sorption/desorption equilibria. Environ Sci Technol 35:1680–1687. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001390s
Kaiser K, Eusterhues K, Rumpel C, Guggenberger G, Kögel-Knabner I (2002) Stabilization of organic matter by soil minerals—investigations of density and particle-size fractions from two acid forest soils. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 165:451–459. https://doi.org/10.1002/1522-2624(200208)165:43.0.CO;2-B
Kim MT (1997) Deposition behavior of hexamethydisiloxane films based on the FTIR analysis of Si–O–Si and Si–CH3 bonds. Thin Solid Films 311:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(97)00683-4
Kuo S, Lai M, Lin C (2006) Influence of solution acidity and CaCl2 concentration on the removal of heavy metals from metal-contaminated rice soils. Environ Pollut 144:918–925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.02.001
Lan T (2016) The research continuous extraction of soil organic matter and adsorption of Pb2+, Cu2+ by the organic matter. (Master Thesis) Hainan University, Haikou, Hainan, China
Lehmann J, Kleber M (2015) The contentious nature of soil organic matter. Nature 528:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16069
Li J, Zheng L, Wang S-L, Wu Z, Wu W, Niazi NK, Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J, Bolan N, Ok YS (2019) Sorption mechanisms of lead on silicon-rich biochar in aqueous solution: Spectroscopic investigation. Sci Total Environ 672:572–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.003
Lu H, Zhang W, Yang Y, Huang X, Wang S, Qiu R (2012) Relative distribution of Pb2+ sorption mechanisms by sludge-derived biochar. Water Res 46:854–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.058
Marinari S, Liburdi K, Masciandaro G, Ceccanti B, Grego S (2007) Humification-mineralization pyrolytic indices and carbon fractions of soil under organic and conventional management in central Italy. Soil Tillage Res 92:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2005.12.009
Marsac R, Banik NL, Marquardt CM, Kratz JV (2014) Stabilization of polynuclear plutonium (IV) species by humic acid. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 131:290–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2014.01.039
Martínez-Mejía MJ, Sato I, Rath S (2017) Sorption mechanism of enrofloxacin on humic acids extracted from Brazilian soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:15995–16006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9210-3
Mohamed I, Ahamadou B, Li M, Gong C, Cai P, Liang W, Huang Q (2010) Fractionation of copper and cadmium and their binding with soil organic matter in a contaminated soil amended with organic materials. J Soils Sediments 10:973–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0199-1
Mokhtar A, Medjhouda ZAK, Djelad A, Boudia A, Bengueddach A, Sassi M (2018) Structure and intercalation behavior of copper II on the layered sodium silicate magadiite material. Chem Pap 72:39–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-017-0255-z
Muhanna FJ, Dari KA, Mubarak MS (2012) Chelation properties of chitosan functionalized with 1-hydroxy-2-pyridinethione-4-carboxylic acid toward some heavy metal ions in aqueous solutions. J Macromol Sci A 49:15–29. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2012.630930
Olk DC (2006) A chemical fractionation for structure–function relations of soil organic matter in nutrient cycling. Soil Sci Soc Am J 70:1013–1022. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2005.0108
Qin F, Wu X, Zhai S, Qin S, Yang K, Chen D, Li Y (2014) Pressure-induced phase transition of lead phosphate Pb3 (PO4) 2: X-ray diffraction and XANES. Phase Transit 87:1255–1264. https://doi.org/10.1080/01411594.2014.953504
Qiu M, Sun K, Jin J, Gao B, Yan Y, Han L, Wu F, Xing B (2014) Properties of the plant-and manure-derived biochars and their sorption of dibutyl phthalate and phenanthrene. Sci Rep 4:5295. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05295
Ramadan MA, Al-Ashkar EA (2007) The effect of different fertilizers on the heavy metals in soil and tomato plant. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 1:300–306
Ravel B, Newville M (2005) ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J Synchrotron Radiat 12:537–541. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0909049505012719
Rayment G, Higginson FR (1992) Australian laboratory handbook of soil and water chemical methods. Inkata Press Pty Ltd, Melbourne
Schmidt MW, Torn MS, Abiven S, Dittmar T, Guggenberger G, Janssens IA, Kleber M, Kögel-Knabner I, Lehmann J, Manning DA (2011) Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property. Nature 478:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10386
Sébastia J, VanOort F, Lamy I (2008) Buffer capacity and Cu affinity of soil particulate organic matter (POM) size fractions. Eur J Soil Sci 59:304–314. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2007.01001.x
Shaker MA (2014) Dynamics and thermodynamics of toxic metals adsorption onto soil-extracted humic acid. Chemosphere 111:587–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.088
Shi J, Wu Q, Zheng C, Yang J (2018) The interaction between particulate organic matter and copper, zinc in paddy soil. Environ Pollut 243:1394–1402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.085
Szalay A (1964) Cation exchange properties of humic acids and their importance in the geochemical enrichment of UO2++ and other cations. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 28:1605–1614. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(64)90009-2
Terbouche A, Djebbar S, Benali-Baitich O, Hauchard D (2011) Complexation study of humic acids extracted from forest and Sahara soils with zinc (II) and cadmium (II) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry (DPASV) and conductimetric methods. Water Air Soil Pollut 216:679–691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0562-2
Tonelli D, Seeber R, Ciavatta C, Gessa C (1997) Extraction of humic acids from a natural matrix by alkaline pyrophosphate. Evaluation of the molecular weight of fractions obtained by ultrafiltration. Fresenius J Anal Chem 359:555–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160050631
Ucun H, Bayhana YK, Kaya Y, Cakici A, Algur OF (2003) Biosorption of lead (II) from aqueous solution by cone biomass of Pinus sylvestris. Desalination 154:233–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(03)80038-3
Wang Y (2019) Effect of decomposition processes of organic fertilizers on adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in liquid phase. (Master Thesis) Hainan University, Haikou, Hainan, China
Weber WJ Jr, McGinley PM, Katz LE (1992) A distributed reactivity model for sorption by soils and sediments. 1. Conceptual basis and equilibrium assessments. Environ Sci Technol 26:1955–1962. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00034a012
Wu W, Yang M, Feng Q, McGrouther K, Wang H, Lu H, Chen Y (2012) Chemical characterization of rice straw-derived biochar for soil amendment. Biomass Bioenergy 47:268–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.09.034
Wu Z, McGrouther K, Huang J, Wu P, Wu W, Wang H (2014) Decomposition and the contribution of glomalin-related soil protein (GRSP) in heavy metal sequestration: field experiment. Soil Biol Biochem 68:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.10.010
Wu W, Li J, Niazi NK, Müller K, Chu Y, Zhang L, Yuan G, Lu K, Song Z, Wang H (2016) Influence of pyrolysis temperature on lead immobilization by chemically modified coconut fiber-derived biochars in aqueous environments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:22890–22896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7428-0
Wu W, Li J, Lan T, Müller K, Niazi NK, Chen X, Xu S, Zheng L, Chu Y, Li J (2017) Unraveling sorption of lead in aqueous solutions by chemically modified biochar derived from coconut fiber: a microscopic and spectroscopic investigation. Sci Total Environ 576:766–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.163
Xing B (2001) Sorption of anthropogenic organic compounds by soil organic matter: a mechanistic consideration. Can J Soil Sci 81:317–323. https://doi.org/10.4141/S00-067
Xiong J, Koopal LK, Tan W, Fang L, Wang M, Zhao W, Liu F, Zhang J, Weng L (2013) Lead binding to soil fulvic and humic acids: NICA-Donnan modeling and XAFS spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 47:11634–11642. https://doi.org/10.1021/es402123v
Yu Z, Huang W, Song J, Qian Y, Peng P a (2006) Sorption of organic pollutants by marine sediments: implication for the role of particulate organic matter. Chemosphere 65:2493–2501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.04.036
Yu S, Wang X, Yang S, Sheng G, Alsaedi A, Hayat T, Wang X (2017) Interaction of radionuclides with natural and manmade materials using XAFS technique. SCIENCE CHINA Chem 60:170–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-016-0317-3
Zaccone C, Soler-Rovira P, Plaza C, Cocozza C, Miano T (2009) Variability in As, Ca, Cr, K, Mn, Sr, and Ti concentrations among humic acids isolated from peat using NaOH, Na4P2O7 and NaOH + Na4P2O7 solutions. J Hazard Mater 167:987–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.078
Zalups RK, Koropatnick DJ (2000) Molecular biology and toxicology of metals. CRC Press, London
Zeng F, Ali S, Zhang H, Ouyang Y, Qiu B, Wu F, Zhang G (2011) The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environ Pollut 159:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.09.019
Zeng Y, Zeng Z, Ju T, Zhang F (2015) Adsorption performance and mechanism of perchloroethylene on a novel nano composite β-FeOOH-AC. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 210:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.02.021
Zhou T, Wu L, Luo Y, Christie P (2018) Effects of organic matter fraction and compositional changes on distribution of cadmium and zinc in long-term polluted paddy soils. Environ Pollut 232:514–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.081
Zhu F, Cheng Q, Xue S, Li C, Hartley W, Wu C, Tian T (2018) Influence of natural regeneration on fractal features of residue microaggregates in bauxite residue disposal areas. Land Degrad Dev 29:138–149. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.2848
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to all staff at the 1W1B station for providing us beamtime of the Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility at the Institute of High Energy Physics, and beamline 15U1 of Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Education Department of Hainan Province, project number (Hnky2021ZD-8), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41807326), and the Scientific Research Foundation of Quanzhou Normal University (H20009), Fujian Province Young and Middle-Aged Teacher Education Research Foundation (JAT190523).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors had no conflict of interests in authorship and publication of this contribution. This research did not involve human participants and animals.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Ravi Naidu
The paper is not under consideration elsewhere. None of the paper’s contents has been previously published.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Yong Qiu contributed to the work equally and should be considered co-first authors.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 406 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Q., Qiu, Y., Lan, T. et al. Comparison of lead adsorption characteristics onto soil-derived particulate organic matter versus humic acid. J Soils Sediments 21, 2589–2603 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02911-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02911-4