Abstract
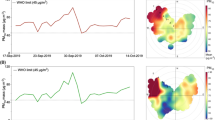
Approximately 1 billion tons of phosphogypsum (PG), a by-product of the fertilizer industry, are currently stacked in Florida. PG emits radon gas, which is a risk factor for lung cancer and can also increase particulate matter (PM) associated non-cancer mortality in exposed individuals. We measured concentrations of atmospheric radon and particulate matter near PG stacks and their short-term variations at different distances to estimate exposures in nearby communities. Specifically, we measured atmospheric levels of radon, and mass concentrations of PM1, PM2.5, and PM10, and number concentrations of PM0.3, PM0.5, PM1, PM2.5, PM5, and PM10 near three large PG stacks in Florida. Atmospheric radon was collected at distances of 2.5, 5.0, and 7.5 miles downwind from three large PG stacks using charcoal-based kits and measured by liquid scintillation counting. A professional radon monitor was used to take 24-h-average radon reading at 5.0 miles from each stack for comparison purposes. The median (IQR) radon levels were 0.325 (0.150, 0.675), 0.150 (0.150, 0.650), and 0.500 (0.150, 0.700) pCi/L at 2.5, 5, and 7.5 miles, respectively. The median (IQR) PM2.5 levels were 5 (4, 6), 5 (3, 7), and 5 (2, 9) µg/m3 at 2.5, 5, and 7.5 miles, respectively. Non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test could not detect any association between radon or PM levels and distances (2.5–7 miles) from PG stacks. With scintillation counting, median radon levels detected were above the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommended standard in some of the sites; however, much higher levels were detected through the more advanced digital monitor. PM2.5 levels were below the US-EPA 24-h average national ambient air quality standard in the study area. We conclude that ambient radon levels near PG stacks could exceed US EPA recommended outdoor standards and do not vary within a short distance from the sources, implying similar exposures in nearby communities.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abbady, A., Uosif, M., & El-Taher, A. (2005). Natural radioactivity and dose assessment for phosphate rocks from Wadi El-Mashash and El-Mahamid Mines. Egypt. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 84(1), 65–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2005.04.003
Alvarez, J. (1990). Radon analysis methods. Air Chek Inc. https://www.radon.com/radon_analysis/ Accessed 16 August 2020.
Bair, W. J. (1995). The ICRP human respiratory tract model for radiological protection. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 60(4), 307–310. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a082732
Barros, N., Field, D. W., Steck, D. J., & Field, R. W. (2015). Comparative survey of outdoor, residential and workplace radon concentrations. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 163(3), 325–332. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncu185
Bersimbaev, R. I., & Bulgakova, O. (2015). The health effects of radon and uranium on the population of Kazakhstan. Genes and Environment, 37(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41021-015-0019-3
Birky, B. K., Tolaymat, T., & Warren, B. C. (1998). Evaluation of exposure to technologically enhanced naturally occurring radioactive materials (Tenorm) in the Phosphate Industry. Florida Institute of Phosphate Research. http://fipr.state.fl.us/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/05-046-155Final.pdf Accessed 24 July 2020.
Blomberg, A., Coull, B., Jhun, I., Vieira, C., Zanobetti, A., Garshick, E., et al. (2019). Effect modification of ambient particle mortality by radon: A time series analysis in 108 US cities. Journal of The Air & Waste Management Association, 69(3), 266–276. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2018.1523071
Calin, M., Botezatu, E., Druker, A., & Radulescu, I. (2013). Radiometric ratings for phosphogypsum in industrial areas in Romania. International Journal of Environmental Technology and Management, 16(3), 223. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijetm.2013.053619
Citizen Times. Missouri radon levels higher than previously thought. November, 2015. https://www.citizen-times.com/story/news/2015/11/23/5-on-your-side-investigates-radon-gas/76260574/ Accessed on August 29, 2020.
Dueñas, C., Fernández, M., Cañete, S., & Pérez, M. (2010). Radiological impacts of natural radioactivity from phosphogypsum piles in Huelva (Spain). Radiation Measurements, 45(2), 242–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2010.01.007
E Silva, C., Smoak, J., & da Silva-Filho, E. (2020). Residential radon exposure and seasonal variation in the countryside of southeastern Brazil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(8). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08513-w
Elloumi, N., Zouari, M., Chaari, L., Abdallah, F. B., Woodward, S., & Kallel, M. (2015). Effect of phosphogypsum on growth, physiology, and the antioxidative defense system in sunflower seedlings. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 22(19), 14829–14840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4716-z
Florida Industrial and Phosphate Research Institute (FIPRI). (2020). Phosphogypsum stacks. Accessed 24 July 2020, from http://www.fipr.state.fl.us/about-us/phosphate-primer/phosphogypsum-stacks/
Heim, M., Mullins, B. J., Umhauer, H., & Kasper, G. (2008). Performance evaluation of three particle counters with an efficient “multimodal” calibration method. Journal of Aerosol Science, 39, 1019–1031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2008.07.006
Hertel, S., Viehmann, A., Moebus, S., Mann, K., Bröcker-Preuss, M., & Möhlenkamp, S. et al. (2010). Influence of short-term exposure to ultrafine and fine particles on systemic inflammation. European Journal of Epidemiology, 25(8), 581–592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-010-9477-x
Hopper, R. D., Levy, R. A., Rankin, R. C., & Boyd, M. A. (1991). National ambient radon study. In: Proceedings of the 1991 International Symposium on Radon and Radon Reduction Technology, 2–5 April 1991, Philadelphia, PA. Research Triangle Park, NC: US Environmental Protection Agency.
Hornung, R. W., Pinney, S. M., Lodwick, J., Killough, G. G., Brewer, D. E., & Nasuta, J. (2008). Estimation of radon exposures to workers at the Fernald Feed Materials Production Center 1952–1988. Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology, 18(5), 512–523. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jes.7500645
Hsu, Y. M., Wu, C. Y., Lundgren, D. A., Nall, J. W., & Birky, B. K. (2007). Chemical characteristics of aerosol mists in phosphate fertilizer manufacturing facilities. Journal of Occupational and environmental Hygiene, 4(1), 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/15459620601067225
Karottki, D. G., Spilak, M., Frederiksen, M., Jovanovic Andersen, Z., Madsen, A. M., Ketzel, M., Massling, A., Gunnarsen, L., Møller, P., & Loft, S. (2015). Indoor and outdoor exposure to ultrafine, fine and microbiologically derived particulate matter related to cardiovascular and respiratory effects in a panel of elderly urban citizens. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(2), 1667–1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120201667
Kim, K. P., Wu, C.-Y., Birky, B., Nall, W., & Bolch, W. (2006). Characterization of radioactive aerosols in Florida phosphate processing. Aerosol Science & Technology, 40, 410–421. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786820600643313
Kümmel, M., Dushe, C., Müller, S., & Gehrcke, K. (2014). Outdoor 222Rn-concentrations in Germany – part 1 – natural background. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 132, 123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2014.01.012
Lurdes Dinis, M., & Fiúza, A. (2005). Simulation of liberation and dispersion of radon from a waste disposal. Advances in Air Pollution Modeling for Environmental Security, 133-142. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3351-6_12
Mulenga, D., & Siziya, S. (2019). Indoor air pollution related respiratory ill health, a sequel of biomass use. SciMedicine Journal, 1(1), 30–37. https://doi.org/10.28991/SciMedJ-2019-0101-5
National Research Council (US). (1999). Committee on Health Risks of Exposure to Radon (BEIR VI). Health Effects of Exposure to Radon: BEIR VI. Washington (DC): National Academy Press (US). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK233262/ Accessed 24 July, 2020.
Nisti, M., de Campos, M., & Mazzilli, B. (2013). Natural radionuclides content and radon exhalation rate from Brazilian phosphogypsum piles. Journal of Radioanalytical And Nuclear Chemistry, 299(1), 261–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-013-2752-z
Rutherford, P. M., Dudas, M. J., & Arocena, J. M. (1995). Radon emanation coefficients for phosphogypsum. Health Perspectives, 107, 123–127. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004032-199510000-00010
Smetanová, I., Holý, K., Luhová, Ľ., Csicsay, K., Haviarová, D., & Kunáková, L. (2020). Seasonal variation of radon and CO2 in the Važecká Cave, Slovakia. Nukleonika, 65(2), 153–157. https://doi.org/10.2478/nuka-2020-0025
Tchorz-Trzeciakiewicz, D., & Solecki, A. (2012). Atmospheric radon concentration around a phosphogypsum stack at Wislinka (Northern Poland). Journal of Elementology, 17(2), 317–328. https://doi.org/10.5601/jelem.2012.17.2.13
Tokonami, S. (2000). Experimental verification of the attachment theory of radon progeny onto ambient aerosols. Health Physics, 78(1), 74–79. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004032-200001000-00012
TSI. (2020). DustTrak II Aerosol Monitor 8532. Accessed 27 July 2020, from https://tsi.com/products/aerosol-and-dust-monitors/dust-monitors/dusttrak-ii-aerosol-monitor-8532/
United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Health Risk of Radon. https://www.epa.gov/radon/health-risk-radon Accessed on August 23, 2020.
US EPA. (1997). Office of Solid Waste. A comparison of phosphogypsum and uranium mill tailing waste unit designs. https://archive.epa.gov/epawaste/hazard/web/pdf/gypvu.pdf Accessed 16 August 2020.
UNSCEAR 93. (1993). Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. Report to the General Assembly, United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. New York: United Nations.
Wasiolek, P. T., & James, A. C. (1995). Outdoor radon dose conversion coefficient in south-western and southeastern United States. Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 59(4), 269–278. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a082660
Wu, F., Lu, Y., Wang, M., Zhang, X., & Yang, C. (2019). Catalytic removal of ozone by Pd/ACFs and optimal design of ozone converter for air purification in aircraft cabin. Civil Engineering Journal, 5(8), 1656–1671. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-2019-03091361
Yazzie, S. A., Davis, S., Seixas, N., & Yost, M. G. (2020). Assessing the impact of housing features and environmental factors on home indoor radon concentration levels on the Navajo nation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(8), 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17082813
Yin, J. H., Daniels, R. D., Kubale, T. L., Dunn, K. L., & Stayner, L. T. (2015). A study update of mortality in workers at a phosphate fertilizer production facility. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 59(1), 12–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajim.22542
Yu, K. N., Wong, B. T. Y., Law, J. Y. P., Lau, B. M. F., & Nikezic, D. (2001). Indoor dose conversion coefficients for radon progeny for different ambient environments. Environmental Science & Technology, 35(11), 2136–2140. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001920k
Zielinski, R., Al-Hwaiti, M., Budahn, J., & Ranville, J. (2010). Radionuclides, trace elements, and radium residence in phosphogypsum of Jordan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 33(2), 149–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-010-9328-4
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the contribution of Mr. Andre Mele for identifying the PG stacks; without his initiative and constant encouragement, this study would not have been possible. The authors also appreciate the assistance from the local community of southwest Florida while conducting environmental sampling.
Funding
This study was supported by an FY20 Seed grant awarded to Dr. Atin Adhikari from the Faculty Research Committee, Georgia Southern University, Statesboro, Georgia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adeoye, C., Gupta, J., Demers, N. et al. Variations of radon and airborne particulate matter near three large phosphogypsum stacks in Florida. Environ Monit Assess 193, 284 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09054-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09054-6