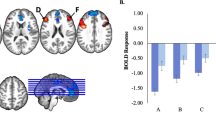
Abstract
Substantial evidence implicates the amygdala and related structures in the processing of negative emotions. Furthermore, neuroimaging evidence suggests that variations in amygdala volumes are related to trait-like individual differences in neuroticism/negative emotionality, although many questions remain about the nature of such associations. We conducted planned tests of the directional prediction that dispositional negative emotionality measured at 10–17 years using parent and youth ratings on the Child and Adolescent Dispositions Scale (CADS) would predict larger volumes of the amygdala in adulthood and conducted exploratory tests of associations with other regions implicated in emotion processing. Participants were 433 twins strategically selected for neuroimaging during wave 2 from wave 1 of the Tennessee Twins Study (TTS) by oversampling on internalizing and/or externalizing psychopathology risk. Controlling for age, sex, race-ethnicity, handedness, scanner, and total brain volume, youth-rated negative emotionality positively predicted bilateral amygdala volumes after correction for multiple testing. Each unit difference of one standard deviation (SD) in negative emotionality was associated with a .12 SD unit difference in larger volumes of both amygdalae. Parent-rated negative emotionality predicted greater thickness of the left caudal/dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (β = 0.28). Associations of brain structure with negative emotionality were not moderated by sex. These results are striking because dispositions assessed at 10–17 years of age were predictive of grey matter volumes measured 12–13 years later in adulthood. Future longitudinal studies should examine the timing of amygdala/cingulate associations with dispositional negative emotionality to determine when these associations emerge during development.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M., McConaughy, S. H., & Howell, C. T. (1987). Child and adolescent behavioral and emotional problems: Implications of cross-informant correlations for situational specificity. Psychological Bulletin, 101(2), 213–232. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.101.2.213
Allen, T. A., & DeYoung, C. G. (2017). Personality neuroscience and the Five Factor Model. In T. A. Widiger (Ed.), Oxford handbook of the Five Factor Model (pp. 319–349). Oxford University Press.
Asman, A. J., & Landman, B. A. (2011). Robust Statistical Label Fusion Through Consensus Level, Labeler Accuracy, and Truth Estimation (COLLATE). Ieee Transactions on Medical Imaging, 30(10), 1779–1794. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2011.2147795
Asman, A. J., & Landman, B. A. (2012). Formulating Spatially Varying Performance in the Statistical Fusion Framework. Ieee Transactions on Medical Imaging, 31(6), 1326–1336. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2012.2190992
Asman, A. J., & Landman, B. A. (2014). Hierarchical performance estimation in the statistical label fusion framework. Medical Image Analysis, 18(7), 1070–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2014.06.005
Avants, B. B., Tustison, N., & Song, G. (2009). Advanced normalization tools (ANTS). Insight Journal, 2(365), 1–35.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 57, 289–300.
Blankstein, U., Chen, J. Y. W., Mincic, A. M., McGrath, P. A., & Davis, K. D. (2009). The complex minds of teenagers: Neuroanatomy of personality differs between sexes. Neuropsychologia, 47(2), 599–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2008.10.014
Caspi, A., Henry, B., McGee, R. O., Moffitt, T. E., & Silva, P. A. (1995). Temperamental origins of child and adolescent behavior problems: From age 3 to age 15. Child Development, 66(1), 55–68. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.1995.tb00855.x
Caspi, A., Houts, R. M., Belsky, D. W., Goldman-Mellor, S. J., Harrington, H., Israel, S., & Moffitt, T. E. (2014). The p factor: One general psychopathology factor in the structure of psychiatric disorders? Clinical Psychological Science, 2, 119–137.
Cha, J., Greenberg, T., Carlson, J. M., DeDora, D. J., Hajcak, G., & Mujica-Parodi, L. R. (2014). Circuit-wide structural and functional measures predict ventromedial prefrontal cortex rear generalization: Implications for generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Neuroscience, 34(11), 4043–4053. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3372-13.2014
Class, Q. A., Rathouz, P. J., Van Hulle, C. A., Applegate, B., Waldman, I. D., Zald, D. H., & Lahey, B. B. (2019). Socioemotional dispositions of children and adolescents predict general and specific second-order factors of psychopathology in early adulthood across informants: A 12-year prospective study. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 128, 574–584.
Delaparte, L., Bartlett, E., Grazioplene, R., Perlman, G., Gardus, J., DeLorenzo, C., Kotov, R. (2019). Structural correlates of the orbitofrontal cortex and amygdala and personality in female adolescents. Psychophysiology, e13376. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.13376
Desikan, R. S., Ségonne, F., Fischl, B., Quinn, B. T., Dickerson, B. C., Blacker, D., & Hyman, B. T. (2006). An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage, 31(3), 968–980.
Destrieux, C., Fischl, B., Dale, A., & Halgren, E. (2010). Automatic parcellation of human cortical gyri and sulci using standard anatomical nomenclature. NeuroImage, 53, 1–15.
Dewey, J., Hana, G., Russell, T., Price, J., McCaffrey, D., Harezlak, J., & Navia, B. (2010). Reliability and validity of MRI-based automated volumetry software relative to auto-assisted manual measurement of subcortical structures in HIV-infected patients from a multisite study. NeuroImage, 51(4), 1334–1344.
DeYoung, C. G., Hirsh, J. B., Shane, M. S., Papademetris, X., Rajeevan, N., & Gray, J. R. (2010). Testing Predictions From Personality Neuroscience: Brain Structure and the Big Five. Psychological Science, 21(6), 820–828. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797610370159
DeYoung, C. G., & Krueger, R. F. (2018). A cybernetic theory of psychopathology. Psychological Inquiry, 29(3), 117–138.
Ducharme, S., Albaugh, M. D., Hudziak, J. J., Botteron, K. N., Nguyen, T. V., Truong, C., & Brain Dev Cooperative, G. (2014). Anxious/Depressed Symptoms are Linked to Right Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortical Thickness Maturation in Healthy Children and Young Adults. Cerebral Cortex, 24(11), 2941–2950. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bht151.
Etkin, A., Buchel, C., & Gross, J. J. (2015). The neural bases of emotion regulation. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 16(11), 693–700. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn4044
Etkin, A., Buchel, C., & Gross, J. J. (2016). Emotion regulation involves both model-based and model-free processes. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 17(8). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2016.79
Etkin, A., Egner, T., & Kalisch, R. (2011). Emotional processing in anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(2), 85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2010.11.004
Ferschmann, L., Fjell, A. M., Vollrath, M. E., Grydeland, H., Walhovd, K. B., & Tamnes, C. K. (2018). Personality Traits Are Associated With Cortical Development Across Adolescence: A Longitudinal Structural MRI Study. Child Development, 89(3), 811–822. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13016
Fischl, B. (2012). FreeSurfer. Neuroimage, 62(2), 774–781.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., & Klaveness, S. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3), 341–355.
Gennatas, E. D., Avants, B. B., Wolf, D. H., Satterthwaite, T. D., Ruparel, K., Ciric, R., & Gur, R. C. (2017). Age-Related Effects and Sex Differences in Gray Matter Density, Volume, Mass, and Cortical Thickness from Childhood to Young Adulthood. Journal of Neuroscience, 37(20), 5065–5073. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3550-16.2017
Ghashghaei, H., Hilgetag, C. C., & Barbas, H. (2007). Sequence of information processing for emotions based on the anatomic dialogue between prefrontal cortex and amygdala. NeuroImage, 34(3), 905–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.09.046
Giedd, J. N., Castellanos, F. X., Rajapakse, J. C., Vaituzis, A. C., & Rapoport, J. L. (1997). Sexual dimorphism of the developing human brain. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 21, 1185–1201.
Gray, J. C., Owens, M. M., Hyatt, C. S., Miller, J. D. (2018). No evidence for morphometric associations of the amygdala and hippocampus with the five-factor model personality traits in relatively healthy young adults. PLoS One, 9 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204011
Gross, J. J. (2015). Emotion regulation: Current status and future prospects. Psychological Inquiry, 26(1), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/1047840x.2014.940781
Gross, J. J., & Barrett, L. F. (2011). Emotion generation and emotion regulation: One or two depends on your point of view. Emotion Review, 3(1), 8–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/1754073910380974
Hammen, C. (1991). Generation of stress in the course of unipolar depression. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 100(4), 555–561. https://doi.org/10.1037//0021-843x.100.4.555
Hammen, C. (2006). Stress generation in depression: Reflections on origins, research, and future directions. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 62(9), 1065–1082. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.20293
Holmes, A. J., Lee, P. H., Hollinshead, M. O., Bakst, L., Roffman, J. L., Smoller, J. W., & Buckner, R. L. (2012). Individual differences in amygdala-medial prefrontal anatomy link negative affect, impaired social functioning, and polygenic depression risk. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(50), 18087–18100. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2531-12.2012
Jansen, A. G., Mous, S. E., White, T., Posthuma, D., & Polderman, T. J. C. (2015). What Twin Studies Tell Us About the Heritability of Brain Development, Morphology, and Function: A Review. Neuropsychology Review, 25(1), 27–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-015-9278-9
Krueger, R. F., & Markon, K. E. (2006). Understanding psychopathology: Melding behavior genetics, personality, and quantitative psychology to develop an empirically based model. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 15, 113–117.
Kuhn, S., Schubert, F., & Gallinat, J. (2011). Structural correlates of trait anxiety: Reduced thickness in medial orbitofrontal cortex accompanied by volume increase in nucleus accumbens. Journal of Affective Disorders, 134(1–3), 315–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2011.06.003
Lahey, B. B. (2009). Public health significance of neuroticism. American Psychologist, 64, 241–256.
Lahey, B. B., Applegate, B., Chronis, A. M., Jones, H. A., Williams, S. H., Loney, J., & Waldman, I. D. (2008a). Psychometric characteristics of a measure of emotional dispositions developed to test a developmental propensity model of conduct disorder. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 37, 794–807.
Lahey, B. B., Class, Q. A., Zald, D. H., Rathouz, P. J., Applegate, B., & Waldman, I. D. (2018). Prospective test of the developmental propensity model of antisocial behavior: from childhood and adolescence into early adulthood. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 59, 676–683.
Lahey, B. B., Krueger, R. F., Rathouz, P. J., Waldman, I. D., & Zald, D. H. (2017). A hierarchical causal taxonomy of psychopathology across the life span. Psychological Bulletin, 143, 142–186.
Lahey, B. B., Rathouz, P. J., Applegate, B., Tackett, J. L., & Waldman, I. D. (2010). Psychometrics of a self-report version of the child and adolescent dispositions scale. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 39, 351–361.
Lahey, B. B., Rathouz, P. J., Applegate, B., Van Hulle, C., Garriock, H. A., Urbano, R. C., & Waldman, I. D. (2008b). Testing structural models of DSM-IV symptoms of common forms of child and adolescent psychopathology. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 36, 187–206.
Lewis, G. J., Panizzon, M. S., Eyler, L., Fennema-Notestine, C., Chen, C. H., Neale, M. C., & Franz, C. E. (2014). Heritable influences on amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex contribute to genetic variation in core dimensions of personality. NeuroImage, 103, 309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.09.043
Makris, N., Gasic, G. P., Seidman, L. J., Goldstein, J. M., Gastfriend, D. R., Elman, I., & Breiter, H. C. (2004). Decreased absolute amygdala volume in cocaine addicts. Neuron, 44(4), 729–740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2004.10.027
Marwha, D., Halari, M., & Eliot, L. (2017). Meta-analysis reveals a lack of sexual dimorphism in human amygdala volume. NeuroImage, 147, 282–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.12.021
Menary, K., Collins, P. F., Porter, J. N., Muetzel, R., Olson, E. A., Kumar, V., & Luciana, M. (2013). Associations between cortical thickness and general intelligence in children, adolescents and young adults. Intelligence, 41(5), 597–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2013.07.010
Mincic, A. M. (2015). Neuroanatomical correlates of negative emotionality-related traits: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia, 77, 97–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.08.007
Modat, M., Ridgway, G. R., Taylor, Z. A., Lehmann, M., Barnes, J., Hawkes, D. J., & Ourselin, S. (2010). Fast free-form deformation using graphics processing units. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 98(3), 278–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2009.09.002
Morey, R. A., Petty, C. M., Xu, Y., Hayes, J. P., Wagner, H. R., II., Lewis, D. V., & McCarthy, G. (2009). A comparison of automated segmentation and manual tracing for quantifying hippocampal and amygdala volumes. NeuroImage, 45(3), 855–866.
Muris, P., & Ollendick, T. H. (2005). The role of temperament in the etiology of child psychopathology. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 8(4), 271–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-005-8809-y
Nigg, J. T. (2006). Temperament and developmental psychopathology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 47, 395–422.
Opel, N., Amare, A.T., Redlich, R., Repple, J., Kaehler, C.,, Grotegerd, D., Dohm, K., Zaremba, D., Leehr, E.J., Böhnlein, J., Förster, K., Bürger, C., Meinert, S., Enneking, V., Emden, D., Leenings, R., Winter, N., Hahn, T., Heindel, W., Bauer, J., Wilhelms, D., Schmitt, S., Jansen, A., Krug, A., Nenadic, I., Rietschel, M., Witt, S., Forstner, A.J., Nöthen, M.M., Kircher, T., Arolt, V., Baune, B.T., & Dannlowski, D. (2020). Cortical surface area alterations shaped by genetic load for neuroticism. Molecular Psychiatry, 25(12), 3422–3431. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0236-9
Panizzon, M. S., Fennema-Notestine, C., Eyler, L. T., Jernigan, T. L., Prom-Wormley, E., Neale, M., & Kremen, W. S. (2009). Distinct genetic influences on cortical surface area and cortical thickness. Cerebral Cortex, 19(11), 2728–2735. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhp026
Panksepp, J. (2004). Affective neuroscience: The foundations of human and animal emotions. Oxford University Press.
Perlaki, G., Horvath, R., Nagy, S. A., Bogner, P., Doczi, T., Janszky, J., & Orsi, G. (2017). Comparison of accuracy between FSL’s FIRST and Freesurfer for caudate nucleus and putamen segmentation. Scientific reports, 7(1), 2418.
Phelps, E. A., & LeDoux, J. E. (2005). Contributions of the amygdala to emotion processing: From animal models to human behavior. Neuron, 48(2), 175–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2005.09.025
Phillips, M., Ladouceur, C., & Drevets, W. (2008). A neural model of voluntary and automatic emotion regulation: implications for understanding the pathophysiology and neurodevelopment of bipolar disorder. Molecular Psychiatry, 13(9), 833–857. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2008.65
Plassard, A. J., & Landman, B. A. (2017). Multiprotocol, multiatlas statistical fusion: theory and application. Journal of Medical Imaging, 4(3). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.jmi.4.3.034002
Pujol, J., Lopez, A., Deus, J., Cardoner, N., Vallejo, J., Capdevila, A., & Paus, T. (2002). Anatomical variability of the anterior cingulate gyrus and basic dimensions of human personality. NeuroImage, 15(4), 847–855. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2001.1004
Ray, R. D., & Zald, D. H. (2012). Anatomical insights into the interaction of emotion and cognition in the prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 26, 479–501.
Reardon, P. K., Seidlitz, J., Vandekar, S., Liu, S. Y., Patel, R., Park, M. T. M., & Raznahan, A. (2018). Normative brain size variation and brain shape diversity in humans. Science, 360(6394), 1222–1226. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar2578
Rive, M. M., van Rooijen, G., Veltman, D. J., Phillips, M. L., Schene, A. H., & Ruhe, H. G. (2013). Neural correlates of dysfunctional emotion regulation in major depressive disorder. A systematic review of neuroimaging studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 37(10), 2529–2553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.07.018
Rothbart, M. K., S Ahadi, S. A., & Evans, D. E. (2000). Temperament and personality: Origins and outcomes. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 78, 122–35.
Salm, A. K., Pavelko, M., Krouse, E. M., Webster, W., Kraszpulski, M., & Birkle, D. L. (2004). Lateral amygdaloid nucleus expansion in adult rats is associated with exposure to prenatal stress. Developmental Brain Research, 148(2), 159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devbrainres.2003.11.005
Schoemaker, D., Buss, C., Head, K., Sandman, C. A., Davis, E. P., Chakravarty, M. M., & Pruessner, J. C. (2016). Hippocampus and amygdala volumes from magnetic resonance images in children: Assessing accuracy of FreeSurfer and FSL against manual segmentation. NeuroImage, 129, 1–14.
Seeley, W. W., Menon, V., Schatzberg, A. F., Keller, J., Glover, G. H., Kenna, H., & Greicius, M. D. (2007). Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. Journal of Neuroscience, 27(9), 2349–2356. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.5587-06.2007
Servaas, M. N., van der Velde, J., Costafreda, S. G., Horton, P., Ormel, J., Riese, H., & Aleman, A. (2013). Neuroticism and the brain: A quantitative meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies investigating emotion processing. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 37(8), 1518–1529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.05.005
Shackman, A. J., Tromp, D. P. M., Stockbridge, M. D., Kaplan, C. M., Tillman, R. M., & Fox, A. S. (2016). Dispositional negativity: An integrative psychological and neurobiological perspective. Psychological Bulletin, 142(12), 1275–1314. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000073
Shaw, D. S., Hyde, L. W., & Brennan, L. M. (2012). Early predictors of boys’ antisocial trajectories. Development and Psychopathology, 24(3), 871–888. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579412000429
Sitnick, S. L., Brennan, L. M., Forbes, E., & Shaw, D. S. (2014). Developmental pathways to sexual risk behavior in high-risk adolescent boys. Pediatrics, 133(6), 1038–1045. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2013-3976
Spampinato, M. V., Wood, J. N., De Simone, V., & Grafman, J. (2009). Neural Correlates of Anxiety in Healthy Volunteers: A Voxel-Based Morphometry Study. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 21(2), 199–205.
Swagerman, S. C., Brouwer, R. M., de Geus, E. J. C., Pol, H. E. H., & Boomsma, D. I. (2014). Development and heritability of subcortical brain volumes at ages 9 and 12. Genes Brain and Behavior, 13(8), 733–742. https://doi.org/10.1111/gbb.12182
Sweeney, M., Tsapanou, A., & Stern, Y. (2019). Regional cortical thickness and neuroticism across the lifespan. Psychiatry Research-Neuroimaging, 286, 39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2019.03.005
Tackett, J. L. (2011). Parent Informants for Child Personality: Agreement, Discrepancies, and Clinical Utility. Journal of Personality Assessment, 93(6), 539–544. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223891.2011.608763
Tackett, J. L., Waldman, I. D., Van Hulle, C. A., & Lahey, B. B. (2011). Shared genetic influences on negative emotionality and major depression/conduct disorder comorbidity. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 50, 818–827.
Taylor, J., Allan, N., Mikolajewski, A. J., & Hart, S. A. (2013). Common genetic and nonshared environmental factors contribute to the association between socioemotional dispositions and the externalizing factor in children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 54, 67–76.
Thomas, A., & Chess, S. (1957). An approach to the study of sources of individual differences in child behavior. Journal of clinical and experimental psychopathology, 18, 347–357.
Trentacosta, C. J., Hyde, L. W., Shaw, D. S., & Cheong, J. W. (2009). Adolescent dispositions for antisocial behavior in context: The roles of neighborhood dangerousness and parental knowledge. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 118, 564–575. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0016394
Tsang, O., Gholipour, A., Kehtarnavaz, N., Gopinath, K., Briggs, R., & Panahi, I. (2008). Comparison of tissue segmentation algorithms in neuroimage analysis software tools. Paper presented at the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2008. EMBS 2008. 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE.
van der Plas, E. A. A., Boes, A. D., Wemmie, J. A., Tranel, D., & Nopoulos, P. (2010). Amygdala volume correlates positively with fearfulness in normal healthy girls. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 5(4), 424–431. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsq009
Waldman, I. D., Tackett, J. L., Van Hulle, C. A., Applegate, B., Pardini, D., Frick, P. J., & Lahey, B. B. (2011). Child and adolescent conduct disorder substantially shares genetic influences with three socioemotional dispositions. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 120, 57–70. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0021351
Widiger, T. A., & Oltmanns, J. R. (2017). Neuroticism is a fundamental domain of personality with enormous public health implications. World Psychiatry, 16(2), 144–145. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20411
Wright, C. I., Williams, D., Feczko, E., Barrett, L. F., Dickerson, B. C., Schwartz, C. E., & Wedig, M. M. (2006). Neuroanatomical correlates of extraversion and neuroticism. Cerebral Cortex, 16, 1809–1819.
Winkler, A. M., Kochunov, P., Blangero, J., Almasy, L., Zilles, K., Fox, P. T., & Glahn, D. C. (2010). Cortical thickness or grey matter volume? The importance of selecting the phenotype for imaging genetics studies. NeuroImage, 53, 1135–1146.
Zald, D. H. (2003). The human amygdala and the emotional evaluation of sensory stimuli. Brain Research Reviews, 41(1), 88–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-0173(02)00248-5
Zald, D. H., & Kim, S. W. (1996). Anatomy and function of the orbital frontal cortex, II: Function and relevance to obsessive-compulsive disorder. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 8, 249–261.
Zhang, J. Y., Liu, T. H., He, Y., Pan, H. Q., Zhang, W. H., Yin, X. P., Pan, B. X. (2019). Chronic stress remodels synapses in an amygdala circuit-specific manner. Biological Psychiatry, 85(3), 189–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.06.019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed Consent
Participants gave in-person written informed consent using a form approved by the Vanderbilt University, University of Wisconsin Madison, and University of Chicago Institutional Review Boards.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lahey, B.B., Hinton, K.E., Burgess, L. et al. Dispositional Negative Emotionality in Childhood and Adolescence Predicts Structural Variation in the Amygdala and Caudal Anterior Cingulate During Early Adulthood: Theoretically and Empirically Based Tests. Res Child Adolesc Psychopathol 49, 1275–1288 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-021-00811-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-021-00811-2