Abstract
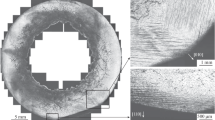
A scanning electron microscopic study has shown that exposure of spheroplastics based on an organosilicon elastomer to a microsecond shock-wave pulse causes the formation of whisker structures up to 10 \(\mu\)m long. Whisker structures are formed on the surface of fractured microspheres. Their formation is facilitated by the metallization of the surface of glass spheres. The paper presents the results of an experimental study of changes in the dielectric and mechanical characteristics of a metallized spheroplastic under shock-wave loading. Possible reasons for the formation of whiskers during shock-wave loading of spheroplastics are discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. A. Berlin and F. A. Shutov, Reinforced Gas-Filled Plastics (Khimiya, Moscow, 1980) [in Russian].
I. G. Gurtovnik, V. I. Sokolov, N. N. Trofimov, and S. I. Shalgunov, Radiotransparent Products Made of Fiberglass (Mir, Moscow 2002) [in Russian].
Yu. M. Milekhin, D. N. Sadovnichii, K. Yu. Sheremet’ev, Yu. G. Kalinin, D. Kazakov, and M. B. Markov, “Formation of Nanowhiskers in Tungsten-Containing Syntactic Foam under Nanosecond Relativistic Electron Beam," Dokl. Akad. Nauk 487(2), 159–163 (2019) [Dokl. Chem. 487 (2), 184–187 (2019); https://doi.org/10.1134/S0012500819070085].
Yu. D. Tret’yakov and E. A. Gudilin, “Main Directions of Basic and Applied Research in the Field of Nanomaterials," Usp. Khim.78 (9), 867–887 (2009).
A. A. Rempel’, “Nanotechnologies. Properties and Applications of Nanostructured Materials," Usp. Khim. 76 (5), 474–500 (2007) [Russ. Chem. Rev. 76 (5) 435–461 (2007)].
G. V. Sakovich, A. S. Zharkov, and E. A. Petrov, “Results of Research into the Physicochemical Processes of Detonation Synthesis and Nanodiamond Applications," Ros. Nanotekh. 8(9–10), 11–20 (2013) [Nanotechnol. Russia 8, 581–591 (2013); https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078013050121].
V. M. Aul’chenko, V. V. Zhulanov, G. N. Kulipanov, K. A. Ten, B. P. Tolochko, and L. I. Shekhtman, “Investigations of Fast Processes by X-ray Diffraction Methods at the Siberian Synchrotron and Terahertz Radiation Center," Usp. Fiz. Nauk 188 (6), 577–594 (2018) [Phys.-Usp. 188 (6), 515–532 (2018)].
A. A. Shterzer, V. Yu. Uliyanitsky, I. S. Batraev, S. A. Gromilov, A. V. Okotrub, and A. I. Saprykin, “Diagnostics of the Structure and Somposition Ultrafine Carbon Obtained by Detonation," Zh. Strukt. Khim. 55 (5), 1031–1034 (2014) [J. Struct. Chem.55, 986–989 (2014); https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476614050291].
K. Wang, S. Y. Chung, and D. Kim, “Morphology of Si Nanowires Fabricated by Laser Ablation Gold Catalysts," Appl. Phys. A79, 895–897 (2004).
E. B. Gordon, A. V. Karabulin, S. A. Krasnokutskii, V. I. Matyushenko, and I. I. Khodes, “Formation of Nanostructures upon Coagulation of Semiconductors in Superfluid Helium," Khim. Vysok. Energii 51 (4), 261–265 (2017).
B. P. Tolochko, A. P. Chernyshev, K. A. Ten, E. R. Pruuel, I. L. Zhogin, P. I. Zubkov, N. Z. Lyakhov, L. A. Lukyanchikov, and M. A. Sheromov, “Physicochemical Model of Detonation Synthesis of Nanoparticles from Metal Carboxylates," Fiz. Metal. Metalloved.105 (2), 145–151 (2008).
S. I. Bodrenko, Yu. A. Krysanov, and S. A. Novikov, “Propagation of Shock Waves in Foamed Polystyrene," Prikl. Mekh. Tekh. Fiz.20 (6), 140–144 (1979) [J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys.20 (6), 771–775 (1979); https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00908673].
L. A. Merzhievskii and A. D. Resnyanskii, “Modeling of the Dynamic Deformation of Spheroplastics," Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva28 (3), 119–121 (1992).
L. A. Merzhievskii, “Simulation of the Dynamic Compression of Porous Al2O3," Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva 35 (6), 105–111 (1999) [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves 35 (6), 698–703 (1999); https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02674545].
A. N. Zubareva, A. V. Utkin, and V. P. Efremov, “Shock-Wave Properties of Spheroplastics," Konstr. Kompoz. Mater., No. 3, 45–50 (2016).
N. Gupta, S. J. Priya, R. A. Islam, and W. Ricci, “Characterization of Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Epoxy–Glass Microballoon Syntactic Composites," Ferroelectrics 345, 1–12 (2006).
N. Gupta and E. Woldesenbet, “Microballoon Wall Thickness Effect on Properties of Syntactic Foams," J. Cell. Plastics40, 461–480 (2004).
P. Viot, K. Shankar, and D. Bernard, “Effect of Strain Rate and Density on Dynamic Behaviour of Syntactic Foam," Composite Struct. 86 (4), 314–327 (2008).
Yu. I. Dimitrienko, S. V. Sborshchikov, A. P. Sokolov, B. R. Gafarov, and D. N. Sadovnichii, “Numerical and Experimental Modeling of the Strength Characteristics of Spheroplastics," Kompoz. Nanostr., No. 3, 35–51 (2013).
A. A. Cheprunov, A. V. Ostrik, and D. N. Nikolaev, “Explosive Technologies for Strength Testing of Thin-Walled Composite Structures on the Action of Lateral Non-Stationary Loads of Various Physical Nature," Konstr. Kompoz. Mat., No. 3, 55–63 (2019).
V. N. Bakulin, V. M. Gribanov, A. V. Ostrik, E. A. Romadinova, and A. A. Cheprunov, Methods of Optimal Design and Calculation of Composite Structures (Fizmatlit, Moscow, 2008), Vol. 2.
N. N. Trofimov, M. Z. Kanovich, E. M. Kartashov, V. I. Natrusov, A. T. Ponomarenko, V. G. Shevchenko, V. I. Sokolov, and I. D. Simonov-Emel’yanov, Physics of Composite Materials (Mir, Moscow, 2005), Vol. 2 [in Russian].
P. Saini, V. Choudhary, N. Vijayan, and R. K. Kotnala, “Improved Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Response of Poly(aniline)-Coated Fabrics Containing Dielectric and Magnetic Nanoparticles," J. Phys. Chem. C 116 (13), 13403–13412 (2012).
S. P. Pawar, M. Gandi, C. Saraf, and S. Bose, “Exception Microwave Absorption in Soft Polymeric Nanocomposites Facilitated by Engineered Nanostructures," J. Mater. Chem. C 4 (22), 4954–4966 (2016).
I. M. De Rosa, A. Dinescu, F. Sarasini, M. S. Sarto, and A. Tamburrano, “Effect of Short Carbon Fibers and MWCNTs on Microwave Absorbing Properties of Polyester Composites Containing Nickel-Coated Carbon Fiber," Compos. Sci. Technol. 70 (1), 102–109 (2010).
V. G. Dubrovskii, G. E. Cirlin, and V. M. Ustinov, “Semiconductor Nanowhiskers: Synthesis, Properties, and Application," Fiz. Tekh. Poluprovod. 43 (12), 1586–1628 (2009) [Semiconductors43, 1539 (2009); https://doi.org/10.1134/S106378260912001X].
V. V. Budov and R. V. Lukavova, “Comparative Assessment of the Strength of Glass Microspheres," in Refractory Fibers and Fine Fillers, Ed. by V. E. Khazanov (NPO Stekloplastik, Moscow, 1990), pp. 27–30.
E. I. Romenskii, “Relaxation Model for Describing the Strain of Porous Materials," Prikl. Mekh. Tekh. Fiz. 29 (5), 145–149 [J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 29 (5), 735–738 (1988); https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00857925].
S. M. Karakhanov, A. V. Plastinin, D. S. Bordzilovskii, and S. A. Bordzilovskii, “Time of Hot-Spot Formation in Shock Compression of Microballoons in a Condensed Medium," Fiz. Goreniya Vzryva52 (3), 105–113 (2016); [Combust., Expl., Shock Waves52 (3), 350–357 (2016); https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508216030151].
A. V. Ganeev, R. K. Islamgaliev, and R. Z. Valiev, “Features Grinding the Microstructure of Tungsten in the Process of Intensive Plastic Deformation," Fiz. Metal. Metalloved. 115(2), 149–155 (2014) [Phys. Metals Metallogr. 115 (2), 139–145 (2014); https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X14020070].
V. Yu. Khomich and V. A. Shmakov, “Formation of Periodic Nanodimensional Structures on the Surface of Solids during Phase and Structural Transformations," Dokl. Akad. Nauk 446(3), 276–278 (2012) [Dokl. Phys. 57, 349–351 (2012); https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028335812090091].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizika Goreniya i Vzryva, 2021, Vol. 57, No. 2, pp. 123–131.https://doi.org/10.15372/FGV20210213.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadovnichii, D.N., Milekhin, Y.M., Malinin, S.A. et al. Experimental Study of Whisker Formation and Properties of Spheroplastic under Shock-Wave Loading. Combust Explos Shock Waves 57, 238–245 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508221020131
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508221020131