Abstract
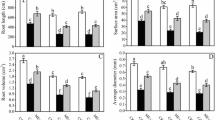
Globally, crop production has been widely threatened by contamination of arable lands with heavy metals including Nickel (Ni). Stress-relief molecule melatonin (ME) has been widely used to mitigate the phytotoxicity induced by heavy metals. The current study aimed to explore the response to Ni stress and the alleviating role of ME in boosting Ni-stress tolerance in tomato seedlings. The roots of tomato seedlings pretreated with ME (100 μM) for 3 days, followed by applied Ni (50 μM) for 7 days. The treatments were composed of (1) control (CK); (2) melatonin (ME, 100 μM); (3) nickel (Ni, 50 μM); and (4) melatonin and nickel treatment (ME+Ni, 100 μM + 50 μM). Nickel toxicity noticeably inhibited plant growth and biomass production by impairing the root architecture, photosynthesis process, nutrient uptake, and antioxidant enzymes. Conversely, ME-supplementation inhibited Ni-induced growth damage, improved root architecture, nutrient uptake, pigment contents, and leaf gas exchange parameters, and decreased Ni-accumulation. Furthermore, the electrolyte leakage (EL), malondialdehyde (MDA) content, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation were significantly reduced in ME-treated seedlings via improving antioxidant enzyme activity as well as upregulation of their encoding gene expression. In conclusion, our findings provide a shred of substantial evidence that ME improved Ni-induced phytotoxicity in tomato seedlings, mainly by improving the root architecture, biomass production, mineral homeostasis (reducing nickel accumulation in plants), and photosynthetic efficiency.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera Y, Herrera T, Benítez V, Arribas SM, Lopez De Pablo AL, Esteban RM (2015) Estimation of scavenging capacity of melatonin and other antioxidants: contribution and evaluationing germinated seeds. Food Chem 170:203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.08.071
Ahammed GJ, Wu M, Wang Y, Yan Y, Mao Q, Ren J, Ma R, Liu A, Chen S (2020) Melatonin alleviates iron stress by improving iron homeostasis, antioxidant defense and secondary metabolism in cucumber. Sci Hortic 265:109205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109205
Ahammed GJ, Xu W, Liu A, Chen S (2018) COMT1 silencing aggravates heat stress- induced reduction in photosynthesis by decreasing chlorophyll content, photosystem II activity, and electron transport efficiency in tomato. Front Plant Sci 9:998. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00998
Ahammed GJ, Xu W, Liu A, Chen S (2019) Endogenous melatonin deficiency aggravates high temperature-induced oxidative stress in Solanum lycopersicum L. Environ Exp Bot 161:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.06.006
Alloway BJ (1995) Heavy metal in soils, 2nd edn. Blackie Acad and Prof London, pp 25–34
Altaf MM, Diao XP, Ur Rehman A, Imtiaz M, Shakoor A, Altaf MA, Younas H, Fu P, Ghani MU (2020) Effect of vanadium on growth, photosynthesis, reactive oxygen species, antioxidant enzymes, and cell death of rice. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:2643–2656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00330-x
Altaf MA, Shahid R, Ren MX, Altaf MM, Khan LU, Shahid S, Jahan MS (2021) Melatonin alleviates salt damage in tomato seedling: a root architecture system, photosynthetic capacity, ion homeostasis, and antioxidant enzymes analysis. Sci Hortic 110145:110145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110145
Altaf MA, Shahid R, Ren MX, Mora-Poblete F, Arnao MB, Naz S, Anwar M, Altaf MM, Shahid S, Shakoor A, Sohail H, Ahmar A, Kamran M, Chen JT (2020) Phytomelatonin: an overview of the importance and mediating functions of melatonin against environmental stresses. Physiol Plant:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13262
Altaf MA, Shahid R, Ren MX, Naz S, Altaf MM, Qadir A, Anwar M, Shakoor A, Hayat F (2020) Exogenous melatonin enhances salt stress tolerance in tomato seedlings. Biol Plant 64:604–615. https://doi.org/10.32615/bp.2020.090
Arnao MB, Hernández-Ruiz J (2014) Melatonin: plant growth regulator and/or biostimulator during stress? Trends Plant Sci 19:789–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.07.006
Arnao MB, Hernández-Ruiz J (2015) Functions of melatonin in plants: a review. J Pineal Res 59:133–150. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12253
Cao YY, Qi CD, Li S, Wang Z, Wang X, Wang J, Ren S, Li X, Zhang N, Guo YD (2018) Melatonin alleviates copper toxicity via improving copper sequestration and ROS scavenging in cucumber. Plant Cell Physiol 60:562–574. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy226
Dubbels R, Reiter RJ, Klenke E, Goebel A, Schnakenberg E, Ehlers C, Schiwara HW, Schloot W (1995) Melatonin in edible plants identified by radioimmunoassay and by high performance liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. J Pineal Res 18:28–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1995.tb00136.x
FAO (2019) Food and Agriculture Organization. www.fao.org. Accessed 5 March 2017
Fashola MO, Ngole-Jeme VM, Babalola OO (2016) Heavy metal pollution from gold mines: environmental effects and bacterial strategies for resistance. Int J Environ Res Publ Health 13:1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13111047
Griffith OW (1980) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal Biochem 106:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(80)90139-6
Hardeland R, Cardinali DP, Srinivasan V (2011) Melatonin - a pleiotropic, orchestrating regulator molecule. Prog Neurobiol 93:350–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.12.004
Hasan M, Ahammed GJ, Yin L, Shi K, Xia X, Zhou Y, Yu J, Zhou J (2015) Melatonin mitigates cadmium phytotoxicity through modulation of phytochelatins biosynthesis, vacuolar sequestration, and antioxidant potential in Solanum lycopersicum L. Front Plant Sci 6:601. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00601
Hattori A, Migitaka H, Iigo M, Itoh M, Yamamoto K, Ohtani-Kaneko R, Hara M, Suzuki T, Reiter RJ (1995) Identification of melatonin in plants and its effects on plasma melatonin levels and binding to melatonin receptors in vertebrates. Biochem Mol Biol Int 5:627–634
Hosseini MS, Samsampour D, Zahedi SM, Zamanian K, Rahman MM, Mostofa MG, Tran LSP (2021) Melatonin alleviates drought impact on growth and essential oil yield of lemon verbena by enhancing antioxidant responses, mineral balance and abscisic acid content. Physiol Plant. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13335
Hussain MB, Ali S, Azam A, Hina S, Farooq MA, Ali B, Bharwana SA, Gill MB (2013) Morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of plants to nickel stress: a review. Afr J Agric Res 8:1596–1602. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajar12.407
Imtiaz M, Rizwan MS, Mushtaq MA, Yousaf B, Ashraf M, Ali M, Yousuf A, Rizwan M, Din M, Dai Z, Xiong S, Mehmood S, Tu S (2017) Interactive effects of vanadium and phosphorus on their uptake: growth and heat shock proteins in chickpea genotypes under hydroponic conditions. Environ Exp Bot 134:72–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.11.003
Jahan MS, Guo S, Baloch AR, Sun J, Shu S, Wang Y, Ahammed GJ, Kabir K, Roy R (2020) Melatonin alleviates nickel phytotoxicity by improving photosynthesis, secondary metabolism and oxidative stress tolerance in tomato seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 197:110593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110593
Jahan MS, Shu S, Wang Y, Chen Z, He M, Tao M, Guo S (2019) Melatonin alleviates heat-induced damage of tomato seedlings by balancing redox homeostasis and modulating polyamine and nitric oxide biosynthesis. BMC Plant Biol 19:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1992-7
Jahan MS, Shu S, Wang Y, Hasan MM, El-Yazied AA, Alabdallah NM, Hajjar D, Altaf MA, Sun J, Guo S (2021) Melatonin pretreatment confers heat tolerance and repression of heat-induced senescence in tomato through the modulation of ABA- and GA-mediated pathways. Front Plant Sci 12:650955. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.650955
Kanwar MK, Yu J, Zhou J (2018) Phytomelatonin: recent advances and future prospects. J Pineal Res 65:e12526. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12526
Kaya C, Okant M, Ugurlar F, Alyemeni MN, Ashraf M, Ahmad P (2019) Melatonin-mediated nitric oxide improves tolerance to cadmium toxicity by reducing oxidative stress in wheat plants. Chemosphere 225:627–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.026
Krupa Z, Siedlecka A, Maksymiec W, Baszynski T (1993) In vitro responses of photosynthetic apparatus of Phaseolus vulgaris L. to nickel toxicity. Plant Physiol 142:664–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0176-1617(11)80899-0
Li H, Chang J, Chen H, Wang Z, Gu X, Wei C, Zhang Y, Ma J, Yang J, Zhang X (2017) Exogenous melatonin confers salt stress tolerance to watermelon by improving photosynthesis and redox homeostasis. Front Plant Sci 8:295. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00295
Li C, Liang B, Chang C, Wei Z, Zhou S, Ma F (2016) Exogenous melatonin improved potassium content in Malus under different stress conditions. J Pineal Res 61:218–229. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12342
Li Z, Pei X, Yin S, Lang X, Zhao X, Qu GZ (2019) Plant hormone treatments to alleviate the effects of salt stress on germination of Betula platyphylla seeds. J Forest Res 30:779–787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0661-2
Li J, Zhao C, Zhang M, Yuan F, Chen M (2019) Exogenous melatonin improves seed germination in Limonium bicolor under salt stress. Plant Signal Behav 14:1659705. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2019.1659705
Liang C, Li A, Yu H, Li W, Liang C, Guo S, Zhang R, Chu C (2017) Melatonin regulates root architecture by modulating auxin response in rice. Front Plant Sci 8:134. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00134
Lichtenhaler K, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0110591
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Logan BA, Demmig-Adam B, Adams WW III (1998) Antioxidants and xanthophyll cycle-dependent energy dissipation in Cucurbita pepo L. and Vinca major L. upon a sudden increase in growth PPFD in the field. J Exp Bot 49:1881–1888. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/49.328.1881
Mittler R (2017) ROS are good. Trends Plant Sci 22:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2016.08.002
Nawaz MA, Huang Y, Bie Z, Ahmed W, Reiter RJ, Niu M, Hameed S (2016) Melatonin: current status and future perspectives in plant science. Front Plant Sci 6:1230. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01230
Nawaz MA, Jiao Y, Chen C, Shireen F, Zheng Z, Imtiaz M, Bie Z, Huang Y (2018) Melatonin pretreatment improves vanadium stress tolerance of watermelon seedlings by reducing vanadium concentration in the leaves and regulating melatonin biosynthesis and antioxidant-related gene expression. J Plant Physiol 220:115–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2017.11.003
Pál M, Horváth E, Janda T, Páldi E, Szalai G (2006) Physiological changes and defense mechanisms induced by cadmium stress in maize. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 169:239–246. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.200520573
Postma JA, Lynch JP (2012) Complementarity in root architecture for nutrient uptake in ancient maize/bean and maize/bean/squash poly cultures. Ann Bot 110:521–534. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcs082
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Terron MP (2007) Melatonin and its metabolites: new findings regarding their production and their radical scavenging actions. Acta biochim 54:1-9. https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2007_3264
Rizwan M, Imtiaz M, Dai Z, Mehmood S, Adeel M, Liu J, Tu S (2017) Nickel stressed responses of rice in Ni subcellular distribution, antioxidant production, and osmolyte accumulation. Environ Sci Pollut Control Ser 24:20587–20598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9665-2
Seregin IV, Ivanov VB (2001) Physiological aspects of cadmium and lead toxic effects on higher plants. Fiziol Rast Moscow Russ J Plant Physiol Engl Transl 48:523–544
Shafeeq-ur-Rahman, Xuebin Q, Yatao X (2020) Silicon and its application methods improve physiological traits and antioxidants in Triticum aestivum (L.) under cadmium stress. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00197-y
Shahzad B, Tanveer M, Rehman A, Cheema SA, Fahad S, Rehman S, Sharma A (2018) Nickel; whether toxic or essential for plants and environment-a review. Plant Physiol Biochem 132:641–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.10.014
Shi H, Chan Z (2014) The cysteine2/histidine2-type transcription factor zinc finger of Arabidopsis thaliana 6-activated C-REPEAT-BINDING FACTOR pathway is essential for melatonin-mediated freezing stress resistance in Arabidopsis. J Pineal Res 57:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12155
Siddiqui MH (2017) Sodium nitroprusside and indole acetic acid improve the tolerance of tomato plants to heat stress by protecting against DNA damage. J Plant Interact 12:177–186. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2017.1310941
Siddiqui MH, Alamri S, Al-Khaishany MY, Khan MN, Al-Amri A, Ali HM, Alsahli AA (2019) Exogenous melatonin counteracts NaCl-induced damage by regulating the antioxidant system, proline and carbohydrates metabolism in tomato seedlings. Int J Mol Sci 20:353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020353
Siddiqui MH, Alamri S, Alsubaie QD, Ali HM, Ibrahim AA, Alsadon A (2019) Potential roles of melatonin and sulfur in alleviation of lanthanum toxicity in tomato seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:656–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.05.043
Siddiqui MH, Alamri S, Khan MN, Corpas FJ, Al-Amri AA, Alsubaie QD, Ali HM, Kalaji HM, Ahmad P (2020) Melatonin and calcium function synergistically to promote the resilience through ROS metabolism under arsenic-induced stress. J Hazard Mat 398:122882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122882
Tan DX (1993) Melatonin: a potent, endogenous hydroxyl radical scavenger. Endocr J 1:57–60
Tan DX, Reiter RJ, Manchester LC, Yan MT, El-Sawi M, Sainz RM, Hardeland R (2002) Chemical and physical properties and potential mechanisms: melatonin as a broad spectrum antioxidant and free radical scavenger. Top Med Chem 2:181–197. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026023394443
Turan V, Ramzani PMA, Ali Q, Abbas F, Iqbal M, Irum A, Khan WD (2018) Alleviation of nickel toxicity and an improvement in zinc bioavailability in sunflower seed with chitosan and biochar application in pH adjusted nickel contaminated soil. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64:1053–1067. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2017.1410542
Ulhassan Z, Huang Q, Gill RA, Ali S, Mwamba TM, Ali B, Hina F, Zhou W (2019) Protective mechanisms of melatonin against selenium toxicity in Brassica napus: insights into physiological traits, thiol biosynthesis and antioxidant machinery. BMC Plant Biol 19:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-2110-6
Valivand M, Amooaghaie R, Ahadi A (2019) Interplay between hydrogen sulfide and calcium/calmodulin enhances systemic acquired acclimation and antioxidative defense against nickel toxicity in Zucchini. Environ Exp Bot 158:40–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.11.006
Viciedo DO, de Mello PR, Toledo RL, dos Santos LCN, Hurtado AC, Nedd LLT, Gonzalez LC (2019) Silicon supplementation alleviates ammonium toxicity in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:413–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00043-w
Wang PT, Chen X, Xu X, Lu CN, Zhang W, Zhao FJ (2018) Arsenate induced chlorosis 1/translocon at the outer envolope membrane of chloroplasts 132 protects chloroplasts from arsenic toxicity. Plant Physiol 178:1568–1583. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.01042
Wissuwa M, Kretzschmar T, Rose TJ (2016) From promise to application: root traits for enhanced nutrient capture in rice breeding. J Exp Bot 67:3605–3615. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw061
Wo-Niak K, Basiak J (2003) Free radicals-mediated induction of oxidized DNA-bases and DNA protein cross-links by nickel chloride. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 514:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1383-5718(01)00344-8
Zaid A, Mohammad F (2018) Methyl jasmonate and nitrogen interact to alleviate cadmium stress in Mentha arvensis by regulating physio-biochemical damages and ROS detoxification. J. Plant Growth Regul 37:1331–1348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9854-3
Zhang N, Sun Q, Zhang H, Cao Y, Weeda S, Ren S (2015) Roles of melatonin in abiotic stress resistance in plants. J Exp Bot 66:647–656. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru336
Zhang J, Zeng B, Mao Y, Kong X, Wang X, Yang Y, Zhang J, Xu J, Rengel Z, Chen Q (2017) Melatonin alleviates aluminum toxicity through modulating antioxidative enzymes and enhancing organic acid anion exudation in soybean. Funct Plant Biol 44:961–968. https://doi.org/10.1071/fp17003
Zhang N, Zhao B, Zhang HJ, Weeda S, Yang C, Yang ZC, Shuxin R, Guo YD (2012) Melatonin promotes water stress tolerance, lateral root formation, and seed germination in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J Pineal Res 54:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.01015.x
Zheng X, Tan DX, Allan AC, Zuo B, Zhao Y, Reiter RJ, Wang L, Wang Z, Guo Y, Zhou J, Shan D, Li Q, Han Z, Kong J (2017) Chloroplastic biosynthesis of melatonin and its involvement in protection of plants from salt stress. Sci Rep 7:41236. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41236
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Wang Zhiwei from the College of Horticulture and Landscape Architecture, Hainan University, Haikou for his kind guidance and laboratory equipment.
Funding
This program was financially supported by the Innovative Team Program of Hainan Natural Science Foundation (2018CXTD334), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41871041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altaf, M.A., Shahid, R., Ren, MX. et al. Melatonin Mitigates Nickel Toxicity by Improving Nutrient Uptake Fluxes, Root Architecture System, Photosynthesis, and Antioxidant Potential in Tomato Seedling. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21, 1842–1855 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00484-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00484-2