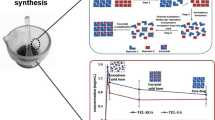
Abstract
In this study, the cationic monomer [2-(acryloyloxy)ethyl]trimethylammonium chloride solution (AETAC) and vinyl imidazole (VI) were used with the free radical polymerization technique, which is a simple and rapid synthesis method, to synthesize p(AETAC-co-VI) hydrogels. To increase the density of cationic charge on the hydrogel, it underwent the protonation process with HCl. The obtained p(AETAC-co-VI)/Q hydrogel was modified with Au nanoparticles to increase bactericidal effect to obtain the AuNPs/p(AETAC-co-VI)/Q nanocomposite hydrogel. The morphology and chemical structure of the hydrogels were characterized with SEM and FTIR. Additionally, the swelling capabilities were tested in different pH media. XRD and TEM confirmed the formation of the nanocomposite hydrogel. The antibacterial activity of the hydrogels was tested against E. coli and S. aureus, and controlled release implementations were completed with sodium diclofenac (NaDc) drug. The NaDc drug release profiles of the hydrogels were researched using the Korsmeyer–Peppas model at 37 °C in different simulated buffer (pH 6.0, 7.2, and 8.0) solutions. It was found that both the hydrogel and nanocomposite hydrogel followed non-Fickian diffusion mechanisms as free release mechanism. Here, the maximum drug release efficacy was found to be 97%, and drug release was more rapid in basic media when release media were compared. The AuNPs/p(AETAC-co-VI)/Q nanocomposite hydrogels produced in this study with advanced antibacterial features were suitable for recommendation as good carriers for in vitro release of NaDc drugs in areas like the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aswathy SH, Narendrakumar U, Manjubala I (2020) Commercial hydrogels for biomedical applications. Heliyon 6:e03719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03719
Chen J, Peng Q, Peng X, Han L, Wang X, Wang J, Zeng H (2020) Recent advances in mechano-responsive hydrogels for biomedical applications. ACS Appl Polym Mater 2:1092–1107. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.0c00019
Mantha S, Pillai S, Khayambashi P, Upadhyay A, Zhang Y, Tao O, Pham HM, Tran SD (2019) Smart hydrogels in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Materials (Basel) 12(20):3323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203323
Rezvani Ghomi E, Khalili S, Nouri Khorasani S, Esmaeely Neisiany R, Ramakrishna S (2019) Wound dressings: current advances and future directions. J Appl Polym Sci 136(27):47738. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47738
Cascone S, Lamberti G (2020) Hydrogel-based commercial products for biomedical applications: a review. Int J Pharm 573:118803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118803
Xiang J, Shen L, Hong Y (2020) Status and future scope of hydrogels in wound healing: synthesis, materials and evaluation. Eur Polym J 130:109609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.109609
Muñoz-Bonilla A, Fernández-García M (2015) The roadmap of antimicrobial polymeric materials in macromolecular nanotechnology. Eur Polym J 65:46–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2015.01.030
Gupta A, Kowalczuk M, Heaselgrave W, Britland ST, Martin C, Radecka I (2019) The production and application of hydrogels for wound management: a review. Eur Polym J 111:134–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.12.019
Zhang L, Yin H, Lei X, Lau JNY, Yuan M, Wang X, Zhang F, Zhou F, Qi S, Shu B, Wu J (2019) A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical effectiveness and safety of hydrogel dressings in the management of skin wounds. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7(342):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00342
Zhu T, Mao J, Cheng Y, Liu H, Lv L, Ge M, Li S, Huang J, Chen Z, Li H, Yang L, Lai Y (2019) Recent progress of polysaccharide-based hydrogel interfaces for wound healing and tissue engineering. Adv Mater Interfaces 6(17):1900761. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201900761
Li S, Dong S, Xu W, Tu S, Yan L, Zhao C, Ding J, Chen X (2018) Antibacterial hydrogels. Adv Sci (Weinh) 5(5):1700527. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201700527
Bhowmick S, Mohanty S, Koul V (2016) Fabrication of transparent quaternized PVA/silver nanocomposite hydrogel and its evaluation as an antimicrobial patch for wound care systems. J Mater Sci Mater Med 27:160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-016-5772-8
Xue Y, Xiao H, Zhang Y (2015) Antimicrobial polymeric materials with quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts. Int J Mol Sci 16(12):3626–3655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16023626
Druvari D, Koromilas N, Bekiari V, Bokias G, Kallitsis J (2018) Polymeric antimicrobial coatings based on quaternary ammonium compounds. Coatings 8(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8010008
Wang K, Wang J, Li L, Xu L, Feng N, Wang Y, Fei X, Tian J, Li Y (2019) Synthesis of a novel anti-freezing, non-drying antibacterial hydrogel dressing by one-pot method. Chem Eng J 372:216–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.107
Caillier L, de Givenchy ET, Levy R, Vandenberghe Y, Géribaldi S, Guittard F (2009) Synthesis and antimicrobial properties of polymerizable quaternary ammoniums. Eur J Med Chem 44(8):3201–3208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2009.03.031
Xu C, Akakuru OU, Ma X, Zheng J, Zheng J, Wu A (2020) Nanoparticle-based wound dressing: recent progress in the detection and therapy of bacterial infections. Bioconjug Chem 31(7):1708–1723. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.0c00297
Bhowmick S, Koul V (2016) Assessment of PVA/silver nanocomposite hydrogel patch as antimicrobial dressing scaffold: synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 59:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.10.003
Dykman LA, Khlebtsov NG (2011) Gold nanoparticles in biology and medicine: recent advances and prospects. Acta Nat 3(2):34–55. https://doi.org/10.32607/20758251-2011-3-2-34-55
Singh J, Kumar S, Dhaliwal AS (2020) Controlled release of amoxicillin and antioxidant potential of gold nanoparticles-xanthan gum/poly (acrylic acid) biodegradable nanocomposite. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec 55:101384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101384
Hashmi ASK, Hutchings GJ (2006) Gold catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:7896–7936. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200602454
Hendrich CM, Sekine K, Koshikawa T, Tanaka K, Hashmi ASK (2020) Homogeneous and heterogeneous gold catalysis for materials science. Chem Rev. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00824
Nasef SM, Khozemy EE, Mahmoud GA (2019) Characterization and in vitro drug release properties of chitosan/acrylamide/gold nanocomposite prepared by gamma irradiation. Int J Polym Mater Po 68:723–732. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2018.1493685
Grzelczak M, Pérez-Juste J, Mulvaney P, Liz-Marzán LM (2008) Shape control in gold nanoparticle synthesis. Chem Soc Rev 37(8):1783–1791. https://doi.org/10.1039/b711490g
Katas H, Lim CS, Nor Azlan AYH, Buang F, Mh Busra MF (2019) Antibacterial activity of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles using biomolecules from Lignosus rhinocerotis and chitosan. Saudi Pharm J 27(2):283–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2018.11.010
Folorunso A, Akintelu S, Oyebamiji AK, Ajayi S, Abiola B, Abdusalam I, Morakinyo A (2019) Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of gold nanoparticles from leaf extracts of Annona muricata. J Nanostruct Chem 9:111–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-019-0301-1
Lin S, Jiang S, Zhang Y, Dai Z, Dai Y, Xia F, Zhang X (2021) Gold nanorods crosslinking PNIPAM hydrogels via dynamic Au-thiolate interaction with stretchable, adhesive, self-healing, and photothermal properties. Gold Bull 54:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13404-021-00293-6
Mordorski B, Prow T (2016) Nanomaterials for wound healing. Curr Derm Rep 5:278–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13671-016-0159-0
Kavetskyy T, Stasyuk N, Smutok O, Demkiv O, Kukhazh Y, Hoivanovych N, Boev V, Ilcheva V, Petkova T, Gonchar M (2019) Improvement of amperometric laccase biosensor using enzyme-immobilized gold nanoparticles coupling with ureasil polymer as a host matrix. Gold Bull 52:79–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13404-019-00255-z
Ma K, Cheng Y, Wei X, Chen D, Zhao X, Jia P (2020) Gold embedded chitosan nanoparticles with cell membrane mimetic polymer coating for pH-sensitive controlled drug release and cellular fluorescence imaging. J Biomater Appl 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885328220952594
Zhu S, Wang X, Liu L, Li L (2020) Gold nanocluster grafted conjugated polymer nanoparticles for cancer cell imaging and photothermal killing. Colloid Surf A 597:124764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124764
Marsich E, Travan A, Donati I, Di Luca A, Benincasa M, Crosera M, Paoletti S (2011) Biological response of hydrogels embedding gold nanoparticles. Colloid Surface B 83(2):331–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.12.002
Im P, Kim J (2018) On-demand macroscale delivery system based on a macroporous cryogel with a high drug loading capacity for enhanced cancer therapy. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 4(10):3498–3505. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00911
Kurdtabar M, Baghestani G, Bardajee GR (2019) Development of a novel thermo-responsive hydrogel-coated gold nanorods as a drug delivery system. Gold Bull 52(1):9–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13404-018-0248-x
Sadat Akhavi S, Moradi Dehaghi S (2020) Drug delivery of amphotericin B through core-shell composite based on PLGA/Ag/Fe3O4: In Vitro Test. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 191:496–510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03181-0
Singh B, Dhiman A (2016) Design of acacia gum–carbopol–cross-linked-polyvinylimidazole hydrogel wound dressings for antibiotic/anesthetic drug Delivery. Ind Eng Chem Res 55(34):9176–9188. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b01963
Onder A, Ilgin P, Ozay H, Ozay O (2020) Removal of dye from aqueous medium with pH-sensitive poly[(2-(acryloyloxy)ethyl)trimethylammonium chloride-co-1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone] cationic hydrogel. J Environ Chem Eng 8(5):104436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104436
Kıvanç MR, Ozay O, Ozay H, Ilgin P (2020) Removal of anionic dyes from aqueous media by using a novel high positively charged hydrogel with high capacity. J Dispers Sci Technol:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2020.1847658
Ilgin P, Ozay H, Ozay O (2020) Synthesis and characterization of pH responsive alginate based-hydrogels as oral drug delivery carrier. J Polym Res 27:251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02231-0
Ozay H, Ilgin P, Ozay O (2019) Novel hydrogels based on crosslinked chitosan with formyl-phosphazene using Schiff-base reaction. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2019.1706514
Ilgin P, Ozay H, Ozay O (2019) A new dual stimuli responsive hydrogel: modeling approaches for the prediction of drug loading and release profile. Eur Polym J 113:244–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.02.003
Siepmann J, Peppas NA (2001) Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Adv Drug Deliv Rev 48(2-3):139–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(01)00112-0
Pekel N, Güven O (2002) Synthesis and characterization of poly(N -vinyl imidazole) hydrogels crosslinked by gamma irradiation. Polym Int 51(12):1404–1410. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.1065
Genç F, Uzun C, Güven O (2016) Quaternized poly(1-vinylimidazole) hydrogel for anion adsorption. Polym Bull 73:179–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1479-0
Heidari S, Esmaeilzadeh F, Mowla D, Ghasemi S (2018) Synthesis of an efficient copolymer of acrylamide and acrylic acid and determination of its swelling behavior. J Pet Explor Prod Technol 8:1331–1340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13202-017-0428-x
Horkay F, Tasaki I, Basser PJ (2000) Osmotic swelling of polyacrylate hydrogels in physiological salt solutions. Biomacromolecules 1(1):84–90. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm9905031
Primo GA, Garcia Manzano MF, Romero MR, Alvarez Igarzabal CI (2015) Synthesis and characterization of hydrogels from 1-vinylimidazole. Highly resistant co-polymers with synergistic effect. Mater Chem Phys 153:365–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.01.027
Veerakumar P, Sangili A, Chen S-M, Lin K-C (2020) Ultrafine gold nanoparticle embedded poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride)–graphene oxide hydrogels for voltammetric determination of an antimicrobial drug (metronidazole). J Mater Chem C 8:7575–7590. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TC06690J
Tepale N, Fernández-Escamilla VVA, Carreon-Alvarez C, González-Coronel VJ, Luna-Flores A, Carreon-Alvarez A, Aguilar J (2019) Nanoengineering of gold nanoparticles: green synthesis, characterization, and applications. Crystals 9(12):612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9120612
Bardajee GR, Mizani F, Hosseini SS (2017) pH sensitive release of doxorubicin anticancer drug from gold nanocomposite hydrogel based on poly(acrylic acid) grafted onto salep biopolymer. J Polym Res 24:4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1197-4
Ozay H, Tarımeri N, Gungor Z, Demirbakan B, Özcan B, Sezgintürk MK, Ozay O (2020) A new approach to synthesis of highly dispersed gold nanoparticles via glucose oxidase-immobilized hydrogel and usage in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. ChemistrySelect 5(29):9143–9152. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202002327
Mandal B, Rameshbabu AP, Dhara S, Pal S (2017) Nanocomposite hydrogel derived from poly (methacrylic acid)/carboxymethyl cellulose/AuNPs: a potential transdermal drugs carrier. Polymer 120:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2017.05.042
Prusty K, Swain SK (2019) Release of ciprofloxacin drugs by nano gold embedded cellulose grafted polyacrylamide hybrid nanocomposite hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol 126:765–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.258
Pereira AKDS, Reis DT, Barbosa KM, Scheidt GN, da Costa LS, Santos LSS (2020) Antibacterial effects and ibuprofen release potential using chitosan microspheres loaded with silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr Res 488:107891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2019.107891
Ozay H, Ilgin P, Ozyurt C, Ozay O (2020) The single-step synthesis of thiol-functionalized phosphazene-based polymeric microspheres as drug carrier. Polymer-Plastics Technol Mater 59(17):1944–1955. https://doi.org/10.1080/25740881.2020.1784212
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University Scientific Research Coordination Unit (project number: FBA-2020-3231).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durmuş, S., Yilmaz, B., Kıvanç, M.R. et al. Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro drug release properties of AuNPs/p(AETAC-co-VI)/Q nanocomposite hydrogels. Gold Bull 54, 75–87 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13404-021-00295-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13404-021-00295-4