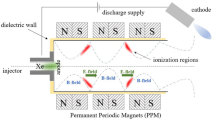
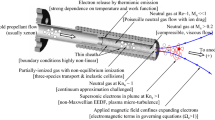
Abstract
The electrodynamic tether (EDT) is a type of propulsion system that uses the geomagnetic field and ionospheric plasma and has the potential to conduct a space-debris removal mission without consuming a large amount of propellant. To understand the dynamic properties of the bare EDT system, an orbital dynamic model based on a detailed environmental space model and the real discharge characteristics of a hollow cathode plasma contactor (HCPC) was built. By numerical simulation, the differences in the bare tether performance caused by various orbital conditions and HCPC voltage models (at constant or various voltages) were compared and discussed. The results suggest that dynamic distinctions generated by the two bias voltage models increased as the latitude increased from 0° to 60°.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Abbreviations
- A:
-
Cross-sectional area, mm-2
- \( \hat{A} \) :
-
Pre-exponential factor of Maxwellian distribution
- a :
-
Semi-major axis, km
- \( \hat{a} \) :
-
Factor in the fitting equation, the same as \( \hat{b} \), \( \hat{c} \), \( \hat{d} \),\( \hat{e} \), and \( \hat{f} \)
- B :
-
Magnetic field strength, nT
- C D :
-
Atmospheric drag coefficient
- E :
-
Electric field strength, V/m
- e :
-
Orbital eccentricity
- F :
-
Force, mN
- f :
-
Specific force, m/s2
- G:
-
Gravitational constant, 6.67 × 10-11 N∙m2/kg2
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration, m/s2
- \( {g}_n^m \) :
-
Gaussian coefficient, which is also shown as \( {h}_n^m \)
- H:
-
Scale height of the atmosphere, km
- h :
-
Altitude, km
- h ∗ :
-
Reference height, km
- I :
-
Current, A
- i :
-
Orbital inclination, degrees
- i :
-
Unit vector
- L :
-
Bare tether length, km
- l :
-
Length coordinate along the tether, km
- M P :
-
Magnetic potential, V∙m/s
- M :
-
Mass, kg
- n :
-
Numerical density, m-3
- \( {P}_n^m \) :
-
Regularised Legendre function
- p :
-
Latus rectum, km
- q:
-
Elementary charge, 1.602×10-19C
- r :
-
Radius, km
- T :
-
Temperature, eV
- v :
-
Velocity, m/s
- V :
-
Potential, V
- A:
-
Spacecraft end of the bare tether
- a :
-
Ambient
- B:
-
Current transition point of the tether
- C:
-
HCPC end of the bare tether
- CGe :
-
From the bare EDT center of gravity to the earth core
- e :
-
Electron
- emission :
-
Emissions of electrons
- ex :
-
External force
- g :
-
Gravitation
- k :
-
Keeper
- ion :
-
Ion
- lorentz :
-
Lorentz force
- n :
-
Normal direction
- neutral :
-
Neutral particle
- o :
-
Original
- p :
-
Plasma in ambient
- pe :
-
From any point to the center of Earth
- relative :
-
Bare EDT velocity relative to the geomagnetic field
- tether :
-
On the bare tether
- θ :
-
True anomaly
- μ :
-
Gmearth, m3/s
- Π :
-
Perimeter
- ρ :
-
Density, kg/m3
- ρ ∗ :
-
Density at the reference point, kg/m3
- \( \hat{\rho} \) :
-
Radius of curvature, km
- σ :
-
Collision cross-sectional area, m2
- Ω :
-
Longitude ascending node, degrees
- ω :
-
Argument of periapsis, degrees
- ω r :
-
Angular velocity, rad/s
References
Ahedo, E., Sanmartin, J.: Analysis of electrodynamic tethers as deorbiting systems. In: 36th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit. Joint Propulsion Conferences. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, (2000)
Ahedo, E., Sanmartin, J.R.: Analysis of bare-tether Systems for Deorbiting low-Earth-Orbit Satellites. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 39(2), 198–205 (2002). https://doi.org/10.2514/2.3820
Beletsky, V.V., Levin, E.M.: Traveling Tether. In: Dynamics of Space Tether Systems, 1st ed. San Diego (1993)
Bilitza, D., Reinisch, B.W.: International reference ionosphere 2007: improvements and new parameters. Adv. Space Res. 42(4), 599–609 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2007.07.048
Bombardelli, C.: Power density of a bare Electrodynamic tether Generator. J. Propuls. Power. 28(3), 664–668 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.B34189
Cash, J.R., Moore, D.R.: A high order method for the numerical solution of two-point boundary value problems. BIT Numer. Math. 20(1), 44–52 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01933584
Colombo, G., Martinez-Sanchez, M., Arnold, D.: The study of the use of tethers for payload orbital transfer. Continuation of investigation of electrodynamic stabilization and control of long orbiting tethers. In. (1982)
Englert, C.R., Bays, J.T., Marr, K.D., Brown, C.M., Nicholas, A.C., Finne, T.T.: Optical orbital debris spotter. Acta Astronaut. 104(1), 99–105 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2014.07.031
Gilchrist, B., Bilen, S., Hoyt, R., Stone, N., Vaughn, J., Fuhrhop, K., Krause, L., Khazanov, G., Johnson, L.: The PROPEL Electrodynamic Tether Mission and Connecting to the Ionosphere. In: 12th Spacecraft Charging Technology Conference (2012)
Goebel, D.M., Watkins, R.M., Jameson, K.K.: LaB6 hollow cathodes for ion and hall thrusters. J. Propuls. Power. 23(3), 552–558 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.25475
Goldberg, H.R., Gilchrist, B.E.: The Icarus student satellite project. Acta Astronaut. 56(1–2), 107–114 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2004.09.016
Hedin, A.E.: The atmospheric model in the region 90 to 2000 km. Adv. Space Res. 8(5), 9–25 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-1177(88)90038-5
Johnson, L., Gilchrist, B., Estes, R.D., Lorenzini, E.: Overview of future NASA tether applications. In: James, H.G., Raitt, W.J., Sultzer, M.P. (eds.) active experiments in space plasmas, vol. 24. Adv. Space Res. 8, 1055–1063 (1999)
Katz, I., Lilley, J.R., Greb, A., McCoy, J.E., Galofaro, J., Ferguson, D.C.: Plasma turbulence enhanced current collection - results from the plasma motor generator electrodynamic tether flight. J Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 100(A2), 1687–1690 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1029/94ja03142
Khazanov, G.V., Krivorutsky, E., Sheldon, R.B.: Solid and grid sphere current collection in view of the tethered satellite system TSS 1 and TSS 1R mission results. J Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 110(A12) (2005). doi:https://doi.org/10.1029/2005ja011100
Kruijff, M.: Tethers in space: a propellantless propulsion in-orbit demonstration. Doctoral Thesis (2011)
Li, W., Li, H., Ding, Y., Wei, L., Lu, H., Gao, Q., Ning, Z., Yu, D.: An experimental setup for hollow cathode independent life test simulating hall thruster discharge current oscillations. Adv. Space Res. 62(9), 2551–2555 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2018.07.020
Maus, S., Macmillan, S., McLean, S., Hamilton, B., Thomson, A., Nair, M., Rollins, C.: The US/UK World Magnetic Model for 2010–2015. In. NOAA Technical Report NESDIS/NGDC, (2010)
Ning, Z.-X., Zhang, H.-G., Zhu, X.-M., Ouyang, L., Liu, X.-Y., Jiang, B.-H., Yu, D.-R.: 10000-ignition-cycle investigation of a LaB6 hollow cathode for 3-5-kilowatt hall thruster. J. Propuls. Power. 35(1), 87–93 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.B37192
Ohkawa, Y., Kawamoto, S., Okumura, T., Iki, K., Horikawa, Y., Kawashima, K., Miura, Y., Takai, M., Washiya, M., Kawasaki, O., Tsujita, D., Kasai, T., Uematsu, H., Inoue, K.: Preparation for an On-Orbit Demonstration of an Electrodynamic Tether on the H-II Transfer Vehicle. Transactions of the Japan Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, Aerospace Technology Japan. 14(ists30), Pb_1–Pb_6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2322/tastj.14.Pb_1
Oks, E.M., Anders, A., Brown, I.G.: Some effects of magnetic field on a hollow cathode ion source. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75(4), 1030–1033 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1651633
Okumura, T., Ohkawa, Y., Koga, K., Kawakita, S., Kawamoto, S., Kobayashi, Y., Kasai, T.: Charging of the H-II transfer vehicle at rendezvous and docking phase. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 55(4), 971–983 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.A34068
Pardini, C., Hanada, T., Krisko, P.H.: Benefits and risks of using electrodynamic tethers to de-orbit spacecraft. Acta Astronaut. 64(5–6), 571–588 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2008.10.007
Pardini, C., Hanada, T., Krisko, P.H., Anselmo, L., Hirayama, H.: Are de-orbiting missions possible using electrodynamic tethers? Task review from the space debris perspective. Acta Astronaut. 60(10–11), 916–929 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2006.11.001
Pedrini, D., Ducci, C., Misuri, T., Paganucci, F., Andrenucci, M.: Sitael hollow cathodes for low-power hall effect thrusters. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 46(2), 296–303 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2017.2778317
Pelaez, J., Andres, Y.N.: Dynamic stability of electrodynamic tethers in inclined elliptical orbits. J Guidance Control Dyn. 28(4), 611–622 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.6685
Pelaez, J., Sanjurjo, M.: Generator regime of self-balanced electrodynamic bare tethers. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 43(6), 1359–1369 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.20471
Qin, Y., Xie, K., Guo, N., Zhang, Z., Zhang, C., Gu, Z., Zhang, Y., Jiang, Z., Ouyang, J.: The analysis of high amplitude of potential oscillations near the hollow cathode of ion thruster. Acta Astronaut. 134, 265–277 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2017.02.012
Qin, Y., Xie, K., Zhang, Y., Ouyang, J.: Self-pulsing in a low-current hollow cathode discharge: From Townsend to glow discharge. Phys. Plasmas 23(2) (2016). doi:https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4941281
Sanchez-Arriaga, G., Bombardelli, C., Chen, X.: Impact of nonideal effects on bare Electrodynamic tether performance. J. Propuls. Power. 31(3), 951–955 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.B35393
Sanjurjo-Rivo, M., Pelaez, J.: Energy analysis of bare Electrodynamic tethers. J. Propuls. Power. 27(1), 246–256 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.48168
Sanmartin, J., Charro, M., Lorenzini, E., Cosmo, M., Estes, R.: Analysis of ProSEDS Test of Bare-tether Collection. Paper presented at the 39th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit (2003)
Sanmartin, J.R., Martinezsanchez, M., Ahedo, E.: Bare wire anodes for electrodynamic tethers. J. Propuls. Power. 9(3), 353–360 (1993). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.23629
van der Heide, E.J., Carroll, J.A., Kruijff, M.: Options for coordinated multi-point sensing in the lower thermosphere. Phys. Chem. Earth Part C Solar Terrestial Planet. Sci. 26(4), 285–291 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/s1464-1917(00)00122-7
Vaughn, J., Curtis, L., Gilchrist, B., Bilen, S., Lorenzini, E.: Review of the ProSEDS Electrodynamic Tether Mission Development. In: 40th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit 2004
Watanabe, T., Fujii, H.A., Kusagaya, T., Sahara, H., Kojima, H., Takehara, S., Yamagiwa, Y., Sasaki, S., Abe, T., Tanaka, K., Oyama, K., Ebinuma, T., Johnson, L., Khazanov, G.V., Sanmartin, J.R., Charro, M., Kruijff, M., Heide, E.J.V.D., Rubin, B., Quiros, F.J.G.D., Trivailo, P.M., Williams, P.: T-Rex: Bare Electro-Dynamic Tape-Tether Technology Experiment on Sounding Rocket S520. The Journal of Space Technology and Science. 26(1), 1_14–11_20 (2012). https://doi.org/10.11230/jsts.26.1_14
Williams, S.D., Gilchrist, B.E., Aguero, V.M., Indiresan, R.S., Thompson, D.C., Raitt, W.J.: TSS-1R vertical electric fields: long baseline measurements using an electrodynamic tether as a double probe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25(4), 445–448 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1029/97gl03259
Xie, K., Farnell, C.C., Williams, J.D.: The plasma properties and electron emission characteristics of near-zero differential resistance of hollow cathode-based plasma contactors with a discharge chamber. Phys. Plasmas 21(8) (2014a). doi:https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4892953
Xie, K., Martinez, R.A., Williams, J.D.: Current-voltage characteristics of a cathodic plasma contactor with discharge chamber for application in electrodynamic tether propulsion. J Phys. D Appl. Phys. 47(15) (2014b). doi:https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/47/15/155501
Xie, K., Xia, Q., Williams, J.D., Martinez, R.A., Farnell, C.C.: Extracted current, Bias voltage, and ion production of Cathodic hollow-cathode-driven plasma contactors. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 52(4), 1181–1192 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.A33049
Yu, B., Dai, P., Jin, D.: Modeling and dynamics of a bare tape-shaped tethered satellite system. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 79, 288–296 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2018.05.046
Zhong, R., Zhu, Z.: Dynamics of Nanosatellite deorbit by bare Electrodynamic tether in low earth orbit. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 50(3), 691–700 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.A32336
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, K., Yuan, H., Liang, F. et al. Lorentz Force Characteristics of a Bare Electrodynamic Tether System with a Hollow Cathode. J Astronaut Sci 68, 327–348 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40295-021-00256-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40295-021-00256-1