No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Trans-vocalic coronal consonant coarticulation in Central Arrernte: An electro-palatographic study
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 April 2021
Abstract
This study examines trans-vocalic CVC coarticulation of the coronal (dental, alveolar, retroflex and (alveo-)palatal) stop, nasal and lateral consonants 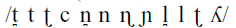 of Arrernte, an Aboriginal language of Central Australia, using electro-palatographic (EPG) recordings of continuous speech. Coronal consonants are known to be more coarticulatorily resistant than peripheral consonants such as bilabials and velars, and this study teases out the coarticulatory differences between these four coronal places of articulation. Results confirm findings from previous studies that laminal consonants (dental and alveo-palatal) are broadly more coarticulatorily aggressive than apical consonants (alveolars and retroflexes), with the alveolars the least resistant to coarticulation. Dental consonants exert fronting effects on both preceding and following consonants, a result consistent with previous acoustic results for these sounds. Similarly, alveo-palatal consonants show both anticipatory and carryover effects, though their exact coarticulatory effect depends on the affected consonant place and manner. The retroflex consonants exert strong fronting effects on the following consonant, and it is suggested that this is due to the anterior release of retroflexes following ballistic forward movement during closure. There is also some evidence of a retraction effect of retroflexes on preceding consonants. Despite this evidence of coarticulatory aggression, retroflexes are particularly affected by preceding and following palatals: in these cases, the retroflex articulation becomes more forward, and dorsal contact for the retroflex is increased. In sum, by examining speech in an understudied language, we learn that there are still greater complexities in the co-ordination of consonants produced using the tongue tip and blade.
of Arrernte, an Aboriginal language of Central Australia, using electro-palatographic (EPG) recordings of continuous speech. Coronal consonants are known to be more coarticulatorily resistant than peripheral consonants such as bilabials and velars, and this study teases out the coarticulatory differences between these four coronal places of articulation. Results confirm findings from previous studies that laminal consonants (dental and alveo-palatal) are broadly more coarticulatorily aggressive than apical consonants (alveolars and retroflexes), with the alveolars the least resistant to coarticulation. Dental consonants exert fronting effects on both preceding and following consonants, a result consistent with previous acoustic results for these sounds. Similarly, alveo-palatal consonants show both anticipatory and carryover effects, though their exact coarticulatory effect depends on the affected consonant place and manner. The retroflex consonants exert strong fronting effects on the following consonant, and it is suggested that this is due to the anterior release of retroflexes following ballistic forward movement during closure. There is also some evidence of a retraction effect of retroflexes on preceding consonants. Despite this evidence of coarticulatory aggression, retroflexes are particularly affected by preceding and following palatals: in these cases, the retroflex articulation becomes more forward, and dorsal contact for the retroflex is increased. In sum, by examining speech in an understudied language, we learn that there are still greater complexities in the co-ordination of consonants produced using the tongue tip and blade.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Journal of the International Phonetic Association , Volume 52 , Issue 3 , December 2022 , pp. 389 - 420
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of the International Phonetic Association





